Cupping therapy has a long history in China and is a common traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) treatment method. Due to its simplicity and effectiveness, it is favored by many. Nowadays, cupping has become a relatively common therapy, achieving effects such as warming the meridians, dispelling wind and cold, reducing swelling and pain, and detoxifying.
The Principle of Cupping
TCM believes that cupping can open the pores and support the body’s defenses while expelling pathogens. Disease is caused by pathogenic factors leading to an imbalance of yin and yang in the body, resulting in abnormal qi movement and dysfunction of the organs and blood.When the body is invaded by wind, cold, heat, dampness, dryness, fire, toxins, or injuries, it can lead to organ dysfunction and the production of pathological substances such as blood stasis, qi stagnation, phlegm, retained food, turbid water, and evil fire. These pathological products act as pathogenic factors, moving through the meridians and acupoints, disrupting qi movement and stagnating the organs, ultimately leading to various symptoms.The vacuum created by cupping generates a strong suction force that acts on the meridian acupoints, opening the pores and causing the skin to become congested, allowing pathological substances to be drawn out through the skin, thus unblocking the meridians and adjusting organ function to prevent and treat diseases.

TCM believes that cupping can unblock the meridians and adjust qi and blood.The meridians have physiological functions such as “transporting qi and blood, nourishing yin and yang, supporting muscles and bones, and benefiting joints.” If the meridians are blocked, qi cannot flow smoothly, and blood stagnation can occur, leading to malnourishment of the skin, flesh, tendons, vessels, and joints, or insufficient nourishment of the blood vessels and dysfunction of the six organs.Through the suction effect of cupping on the skin, pores, meridians, and acupoints, it can guide the qi of the defensive and nutritive levels to circulate, stimulate the flow of qi and blood in the meridians, nourish the organs and tissues, warm the skin, and invigorate the weakened organ functions, thus unblocking the meridians and adjusting the body’s yin and yang balance, allowing qi and blood to be regulated, achieving the purpose of health maintenance and disease treatment.
Common Types of Cupping
1Horn Cupping
Made from cow or sheep horn.The tip of the horn is cut off, leaving 1-2 cm of solid part as the bottom of the cup.The mouth is smoothed and polished. The length is about 10 cm, with diameters of 6 cm, 5 cm, and 4 cm. Its advantage is durability.
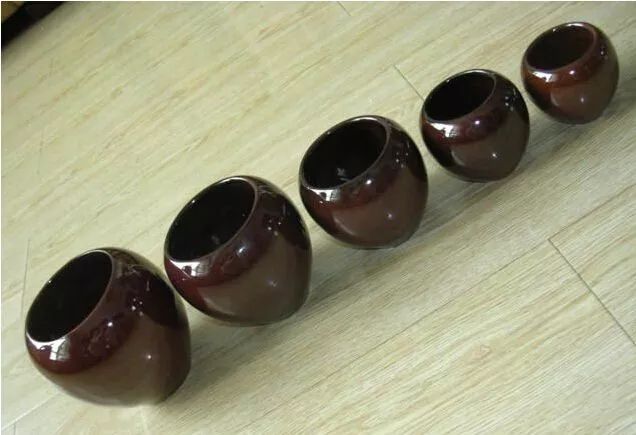

2Glass Cupping
Glass cupping is currently the most commonly used type at home, available in most medical supply stores.It is made of glass and generally comes in large, medium, and small sizes.It is shaped like a ball, with a small opening at the bottom and a wide belly.The advantage is that the cup is smooth and transparent, allowing observation of the skin’s congestion during use. However, it is prone to breakage.

3Air Pump Cupping
Common types include combination and assembly styles.The combination type consists of a glass funnel with a rubber bulb attached; the assembly type connects a rubber bulb with a switch and a rubber tube to a glass or transparent plastic cup.The advantage is that it does not require fire, preventing burns, and is safe and easy to use, with a smooth cup mouth for easy observation.
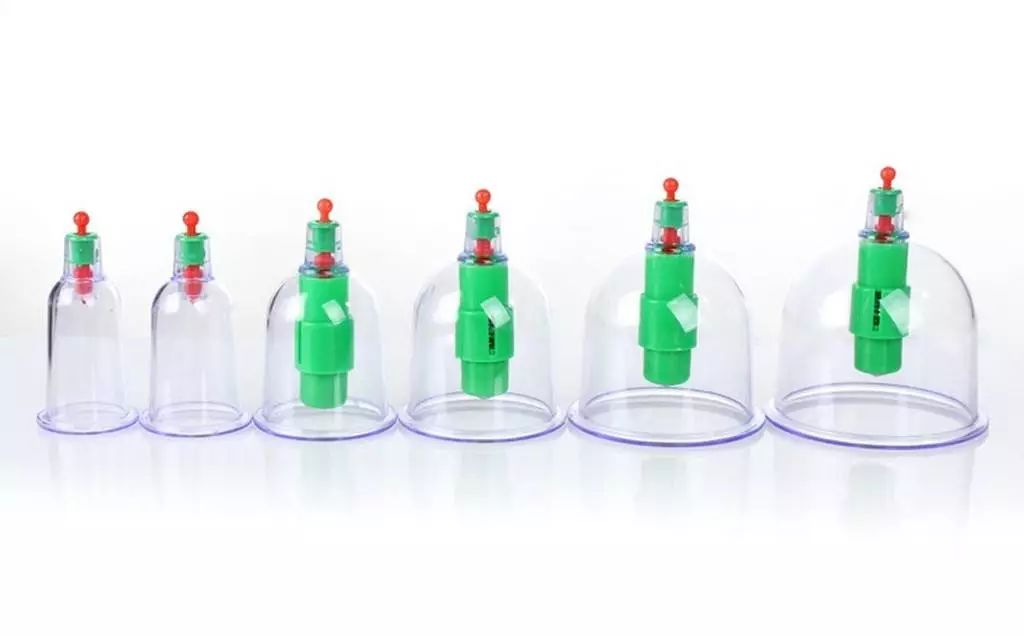

4Vacuum Cupping
Vacuum cups are often made from blue or streptomycin bottles, with the bottom ground smooth to create a flat cup mouth, and the rubber stopper at the mouth should remain intact for vacuuming; ready-made vacuum cupping devices are also available in medical supply stores, made from organic glass or transparent plastic, shaped like a bell with a piston for easy vacuuming.The advantage is that it does not require fire, preventing burns, is safe, allows for adjustable internal negative pressure, and is easy to observe. It is the most suitable vacuum cupping for home use.
Methods of Cupping
When cupping, different methods can be selected based on the situation.The commonly used cupping methods include:
1. Retention Cupping:Retention cupping generally lasts for 10-15 minutes. This is a commonly used method applicable for most diseases.
2. Sliding Cupping:Before cupping, apply a layer of petroleum jelly or other lubricant to the skin or cup mouth, then apply the cup. Hold the cup with the right hand and slide it back and forth over the area to be treated until the skin appears red, congested, or bruised, then remove the cup. This method is suitable for larger areas with more muscle.
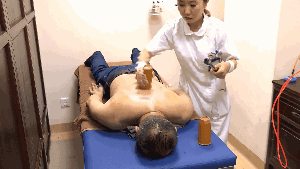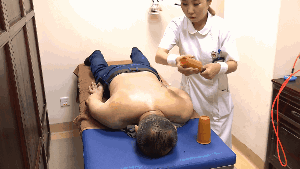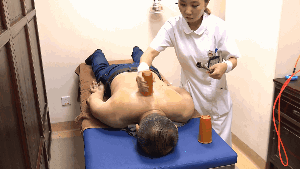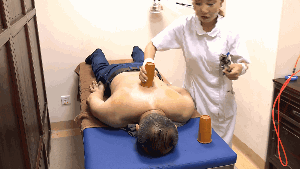
3. Flash Cupping:Flash cupping involves quickly placing and removing the cup repeatedly until the skin becomes red, congested, or bruised. This method is not suitable for children or young women on the face.
4. Bloodletting Cupping:This involves disinfecting the skin at the cupping site, using a three-edged needle to prick and draw blood, or tapping with a skin needle, then applying the cup to the pricked area to draw blood. This method is often used for treating erysipelas, sprains, and breast abscesses.

5. Needle Retention Cupping:This involves placing the cup over the area centered on the needle during acupuncture retention for about 5-10 minutes. When the skin becomes red, congested, or bruised, remove the cup and then take out the needle. This method combines the effects of acupuncture and cupping.
Cupping Effects and Indications
Cupping therapy has effects such as unblocking meridians, promoting qi and blood circulation, reducing swelling and pain, and dispelling wind and cold, with a wide range of indications.It is commonly used for conditions such as wind-cold bi syndrome, pain in the lower back, shoulders, arms, and legs, joint pain, soft tissue sprains, colds, headaches, coughs, asthma, stomach pain, vomiting, abdominal pain, diarrhea, dysmenorrhea, and post-stroke conditions.
Precautions for Cupping
1. Diabetic patients with sensitive skin should avoid cupping.
2. Cupping should aim for skin redness; do not excessively pursue purple bruising.
3. Cupping should not be prolonged; 5-10 minutes is sufficient, shorter for those with delicate skin.
4. Cupping is not suitable for those with edema or skin ulcers.
5. Cupping should be approached with caution for those with weak constitutions, children, and the elderly.
6. Cupping is not recommended for those with bleeding tendencies or during menstruation.
7. Avoid cupping after excessive alcohol, meat consumption, sweating, thirst, or overexertion, and in severe illness.
8. After cupping, the pores are open; avoid exposure to cold.
Cupping Mark Color Reactions
1. Dark purple-black marks:Generally indicate insufficient blood supply and blood stasis.
2. Purple marks with patches:Generally indicate cold-induced blood stasis.
3. Marks with scattered purple spots of uniform depth:Indicate qi stagnation and blood stasis.
4. Bright red marks:Generally indicate yin deficiency, qi and blood deficiency, or excess yin fire.
5. Dark red marks:Indicate high blood lipids and heat evil.
6. Gray-white marks that feel cool to the touch:Often indicate deficiency-cold or damp evil.
7. Marks with skin texture or slight itching:Indicate wind evil or dampness.
8. Moisture on the inner wall of the cup:Indicates dampness in that area.
9. Blisters on the marks:Indicate heavy dampness; if the blisters contain blood, it is a reaction to damp-heat toxins.
Recommended Quality Articles for Further Reading:
1. Interpretation of “Fundamentals of TCM” – The Heart
2. Interpretation of “Fundamentals of TCM” – The Liver
3. Interpretation of “Fundamentals of TCM” – The Spleen
4. Interpretation of “Fundamentals of TCM” – The Lung
5. Interpretation of “Fundamentals of TCM” – The Kidney

The Health Preservation Techniques of Qi Huang
Long press the left QR code to follow us
Contact Teacher He: 18538093861

