In the Yijing (I Ching), the concepts of Yin-Yang and the Five Elements are discussed. The world is essentially a model, with the Heavenly Stems and Earthly Branches forming the framework of this model, while Yin-Yang and the Five Elements represent the operational laws of this model. Yin-Yang divides things into two categories: all that is positive, good, and strong belongs to Yang, while negative, lesser, and poor aspects belong to Yin. The Five Elements—Wood, Fire, Earth, Metal, and Water—further subdivide things. The interactions of the Five Elements, including generating and overcoming, represent the laws governing the operation of all things in the world. The Heavenly Stems and Earthly Branches are methods of recording years in the lunar calendar, which is an ancient Chinese calendar. The commonly mentioned 60-year cycle refers to one complete cycle of the Stems and Branches lasting 60 years.

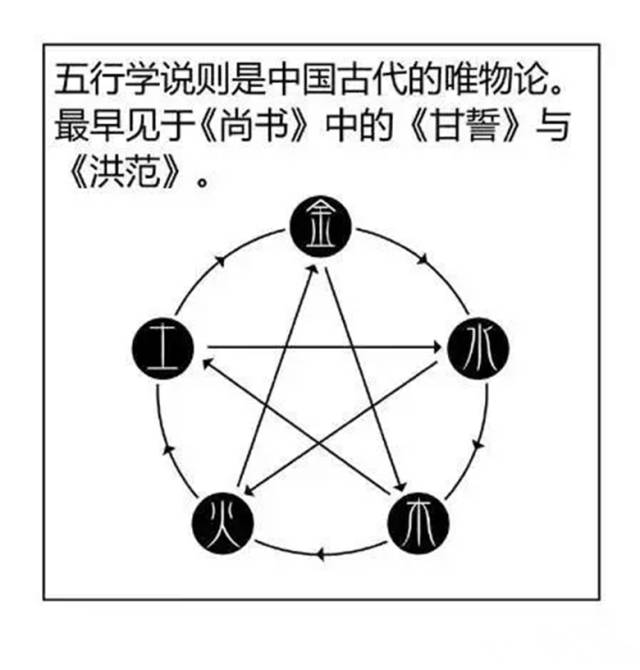




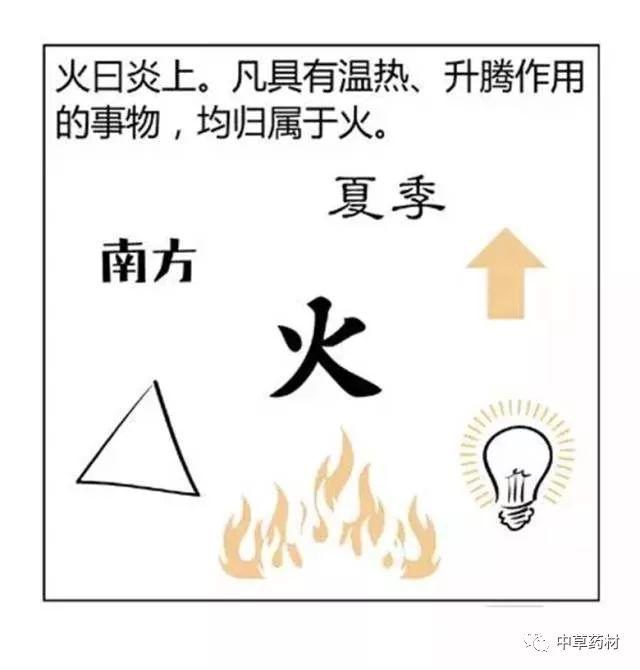
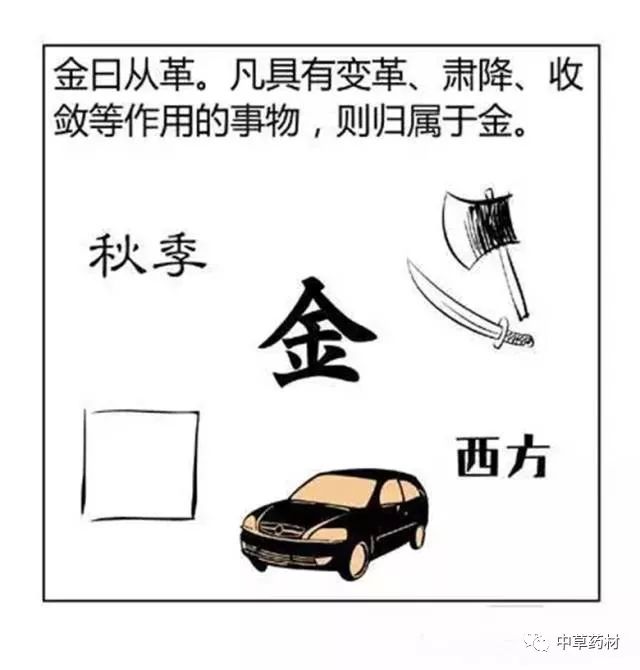
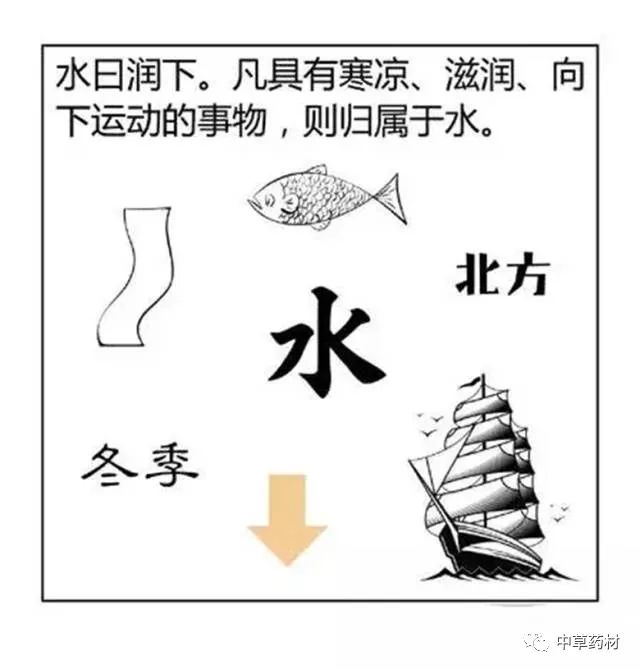




Generating refers to the mutual assistance and promotion between two different attributes of things.
Understanding the generating cycle of the Five Elements in nature:
Metal generates Water, as the primordial water on Earth is transformed from within the Earth;
Water generates Wood, as water irrigates trees, allowing them to thrive;
Wood generates Fire, as fire uses wood as fuel; when the wood is consumed, the fire will extinguish;
Fire generates Earth, as burning objects turn to ash, and ash becomes soil;
Earth generates Metal, as metal is contained within soil and rocks, extracted through smelting.
Overcoming is the opposite of generating, referring to the relationship of mutual restraint between two different types of Five Element properties.
Understanding the overcoming cycle of the Five Elements in nature:
Metal overcomes Wood, as metal tools can cut down trees (land with minerals does not grow grass);
Wood overcomes Earth, as tree roots absorb nutrients from the soil, strengthening themselves while weakening the soil;
Earth overcomes Water, as earth can block water (soldiers block with earth when water comes);
Water overcomes Fire, as fire is extinguished by water;
Fire overcomes Metal, as intense fire can melt metal.
The multiplication and insult between the Five Elements refer to abnormal overcoming phenomena that occur when the normal generating and overcoming relationships are disrupted.
Multiplying:
refers to excessive overcoming between the Five Elements. Overcoming and multiplying are not the same; overcoming is the norm, while multiplying is pathological.
The causes of multiplying can be attributed to two aspects:
First, one of the Five Elements is overly strong, causing the element that overcomes it to excessively restrain it, leading to the weakened state of the overcome element. For example, if Wood is too strong, it will excessively overcome Earth, resulting in insufficient Earth, termed “Wood multiplies Earth.”
Second, if one of the Five Elements is inherently weak, the overcoming force against it will appear relatively stronger, further weakening it. For instance, if Earth is not overly strong, its overcoming force is within normal limits. However, due to the inherent weakness of Earth, the power of Wood overcoming Earth becomes relatively stronger, leading to further insufficiency of Earth, termed “Earth deficiency leads to Wood multiplying.”
Insulting:
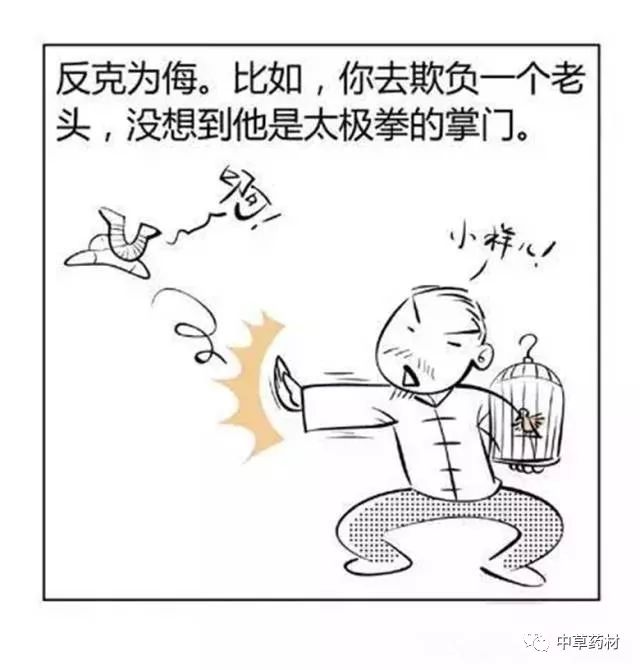
refers to the reverse overcoming between the Five Elements, where the originally restrained element reverses its position to restrain the other. For example, Metal originally overcomes Wood, but under abnormal circumstances, Metal cannot overcome Wood and is instead overcome by Wood; this reverse overcoming is termed “Wood insults Metal.”
Multiplying and insulting are both abnormal overcoming phenomena, with distinctions and connections between the two.
The main difference between multiplying and insulting is that the former occurs due to excessive restraint in the normal overcoming sequence of the Five Elements, leading to a pathological state; while the latter occurs in the opposite direction of the normal overcoming sequence, resulting in a pathological state.
The connection between the two is that when multiplying occurs, insulting can also happen; and when insulting occurs, multiplying can also happen.

