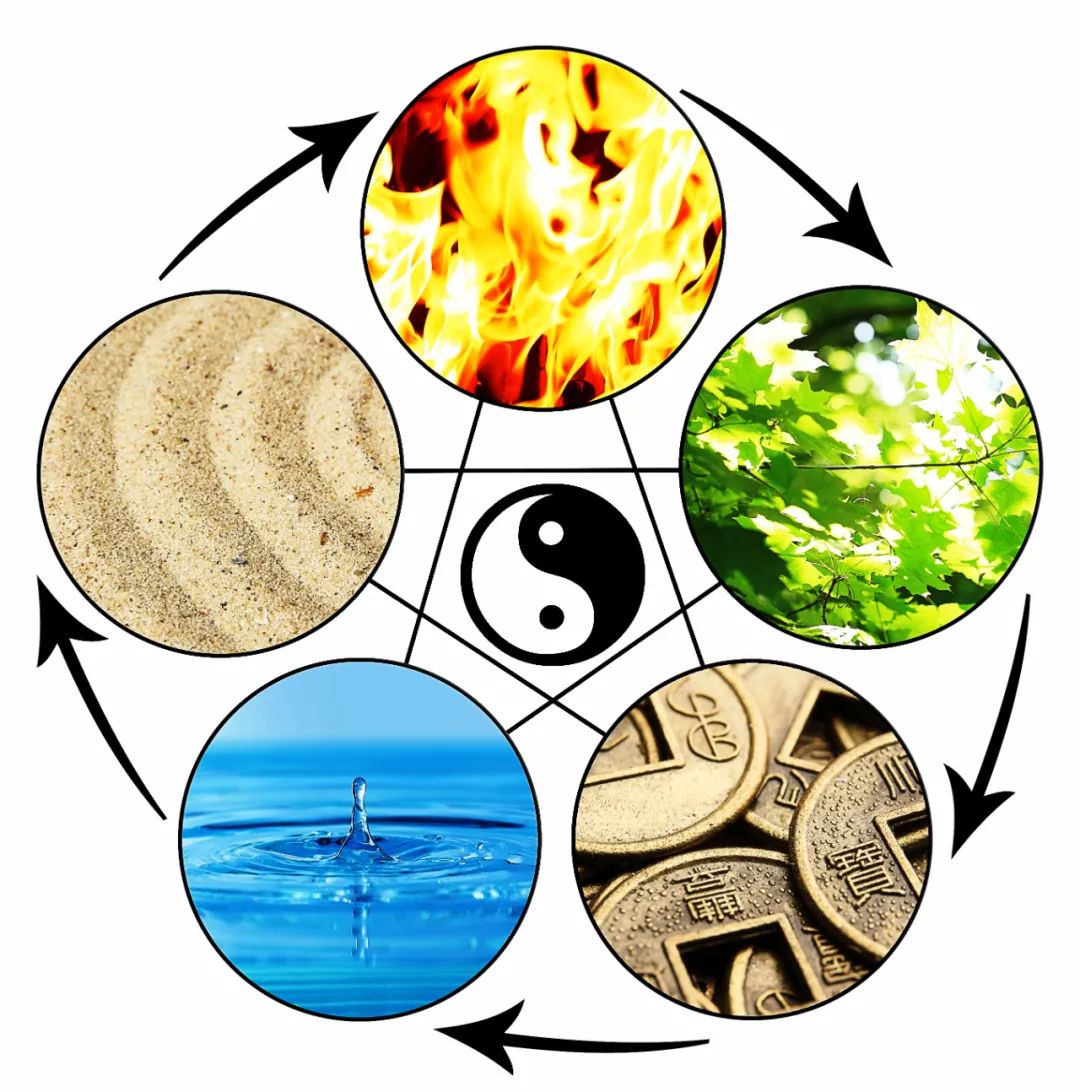
The “Five Elements” refers to the five categories of substances in nature: “Wood, Fire, Earth, Metal, and Water” and their movements.
The “Five Elements Theory” describes the movements and changes of these five categories of substances, as well as their interrelationships, using the concepts of mutual generation and mutual overcoming as tools to explain the interconnections and laws of movement and change among things.

In ancient medicine, the first step was to classify and explain the interrelationships between various parts of the human body and the external environment. Secondly, based on the classification of the Five Elements, the relationships among the five organs were explained with a focus on the mutual generation and overcoming relationships of the Five Elements during physiological processes. In pathological conditions, this relationship is also used to analyze and judge the condition.

Attributes of the Five Elements
Wood – represents vitality and growth – “Wood signifies bending and straightening.” Fire – represents heat and upward movement – “Fire signifies rising flames.” Earth – represents nourishment – “Earth signifies agriculture and harvest.” Metal – represents destruction and harm – “Metal signifies transformation.” Water – represents coldness and downward movement – “Water signifies moistening and descending.” 
Fundamental Principles of the Five Elements Theory
1. Mutual Generation Principle: Generation implies nurturing, assisting, and promoting. The Five Elements have a mutually nurturing and assisting relationship, referred to as “Mutual Generation of the Five Elements.” The order of mutual generation is: Wood generates Fire, Fire generates Earth, Earth generates Metal, Metal generates Water, Water generates Wood. In the relationship of mutual generation, each element has both a nurturing and a being nurtured aspect, akin to a mother-child relationship. For example, Water generates Metal, thus Metal is the mother of Water; Water generates Wood, thus Wood is the child of Water. This applies to the other four elements as well. Since the Liver belongs to Wood, the Heart to Fire, the Spleen to Earth, the Lung to Metal, and the Kidney to Water, in relation to the five organs, it can be said that the Liver generates the Heart, the Heart generates the Spleen, the Spleen generates the Lung, the Lung generates the Kidney, and the Kidney generates the Liver, creating a nurturing and promoting effect. 2. Mutual Overcoming Principle: Overcoming implies restriction, suppression, and conquering. The Five Elements have a mutually restraining and overcoming relationship, referred to as “Mutual Overcoming of the Five Elements.” The order of mutual overcoming is: Wood overcomes Earth, Earth overcomes Water, Water overcomes Fire, Fire overcomes Metal, Metal overcomes Wood. In the relationship of mutual overcoming, each element has both an overcoming and a being overcome aspect, akin to the relationship of “victor” and “vanquished.” For example, Wood overcomes Metal, thus Metal is the “vanquished” by Wood, while Wood is overcome by Earth, thus Earth is the “victor” over Wood. This applies to the other four elements as well. In relation to the five organs, it can be said that the Liver overcomes the Spleen, the Spleen overcomes the Kidney, the Kidney overcomes the Heart, the Heart overcomes the Lung, and the Lung overcomes the Liver, playing a restraining and suppressing role. 3. Transformation of the Five Elements: Within the mutual generation of the Five Elements, there is also the concept of mutual overcoming, and within mutual overcoming, there is also the concept of mutual generation. This is a general law of movement and change in nature. If there is only mutual generation without mutual overcoming, normal balanced development cannot be maintained; if there is mutual overcoming without mutual generation, nothing will be born or transformed. Therefore, mutual generation and mutual overcoming are two indispensable conditions for maintaining relative balance in all things. Only on the basis of mutual interaction and coordination can the continuous generation of things be promoted. For example, Wood can overcome Earth, but Earth can also generate Metal to restrain Wood. Thus, in this case, although Earth is overcome, it does not necessarily decline. The same applies to Fire, Earth, Metal, and Water. The ancients referred to the internal connection between mutual generation and mutual overcoming of the Five Elements as “Transformation of the Five Elements.” The specific situations of the transformation laws are as follows: Wood overcomes Earth, Earth generates Metal, Metal overcomes Wood. Fire overcomes Metal, Metal generates Water, Water overcomes Fire. Earth overcomes Water, Water generates Wood, Wood overcomes Earth. Metal overcomes Wood, Wood generates Fire, Fire overcomes Metal. Water overcomes Fire, Fire generates Earth, Earth overcomes Water. 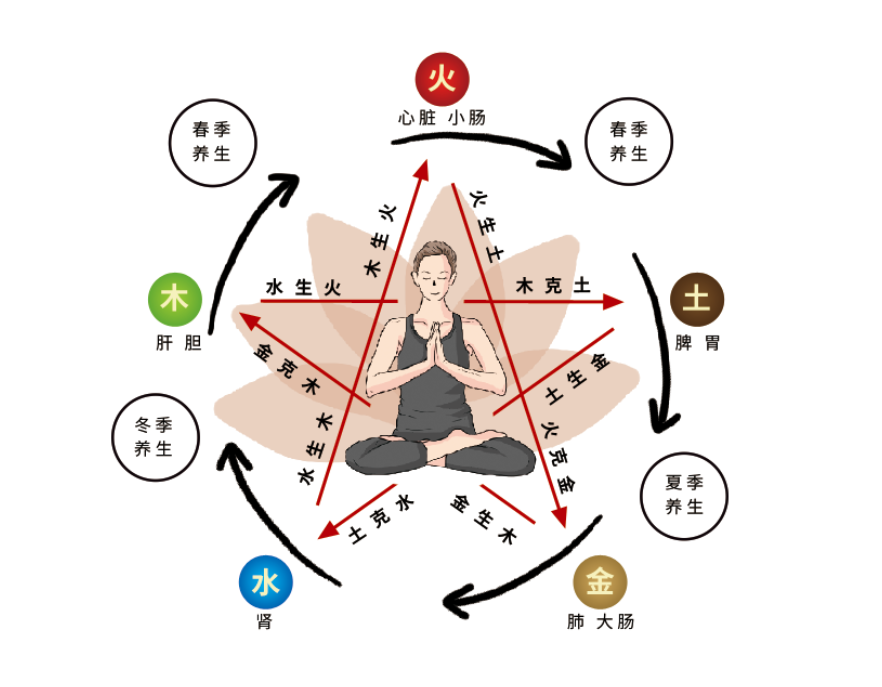 4. Mutual Accumulation Principle: Accumulation implies an increase or intensification. From the perspective of the generation and overcoming laws of the Five Elements, it is a pathological anomaly. Mutual accumulation is similar in meaning to mutual overcoming, but it exceeds the normal range and reaches a pathological level. The order of mutual accumulation is consistent with that of mutual overcoming, namely: Wood accumulates on Earth, Earth accumulates on Water, Water accumulates on Fire, Fire accumulates on Metal, Metal accumulates on Wood. For instance, when Wood overcomes Earth, if the Wood energy is excessive, Metal cannot normally restrain Wood, thus excessive Wood accumulates on Earth, leading to an overly strong Wood overcoming Earth, making Earth weaker and unable to generate Metal, resulting in Metal being weak and unable to restrain Wood. 5. Mutual Insult Principle: Insult implies bullying or oppression. From the perspective of the generation and overcoming laws of the Five Elements, mutual insult, like mutual accumulation, is also a pathological anomaly. However, mutual insult is similar in meaning to reverse overcoming, hence it is sometimes referred to as reverse insult. The order of mutual insult is also the opposite of mutual overcoming, namely: Wood insults Metal, Metal insults Fire, Fire insults Water, Water insults Earth, Earth insults Wood. The above two principles of mutual accumulation and mutual insult only occur in pathological conditions. For example, if Water energy is excessive, it can harm Fire energy (the vanquished), while simultaneously insulting Earth (the not vanquished). If Water energy is insufficient, then Earth will accumulate on it (the not vanquished), and Fire will insult it (the vanquished). These are all abnormal phenomena arising from excess and deficiency. (Excerpt from: Medical Network)
4. Mutual Accumulation Principle: Accumulation implies an increase or intensification. From the perspective of the generation and overcoming laws of the Five Elements, it is a pathological anomaly. Mutual accumulation is similar in meaning to mutual overcoming, but it exceeds the normal range and reaches a pathological level. The order of mutual accumulation is consistent with that of mutual overcoming, namely: Wood accumulates on Earth, Earth accumulates on Water, Water accumulates on Fire, Fire accumulates on Metal, Metal accumulates on Wood. For instance, when Wood overcomes Earth, if the Wood energy is excessive, Metal cannot normally restrain Wood, thus excessive Wood accumulates on Earth, leading to an overly strong Wood overcoming Earth, making Earth weaker and unable to generate Metal, resulting in Metal being weak and unable to restrain Wood. 5. Mutual Insult Principle: Insult implies bullying or oppression. From the perspective of the generation and overcoming laws of the Five Elements, mutual insult, like mutual accumulation, is also a pathological anomaly. However, mutual insult is similar in meaning to reverse overcoming, hence it is sometimes referred to as reverse insult. The order of mutual insult is also the opposite of mutual overcoming, namely: Wood insults Metal, Metal insults Fire, Fire insults Water, Water insults Earth, Earth insults Wood. The above two principles of mutual accumulation and mutual insult only occur in pathological conditions. For example, if Water energy is excessive, it can harm Fire energy (the vanquished), while simultaneously insulting Earth (the not vanquished). If Water energy is insufficient, then Earth will accumulate on it (the not vanquished), and Fire will insult it (the vanquished). These are all abnormal phenomena arising from excess and deficiency. (Excerpt from: Medical Network)

