

The concept of Warm Disease was first recorded in the Su Wen, specifically in the section Sheng Qi Tong Tian Lun: “In winter, injury from cold will lead to Warm Disease in spring.” This indicates that Warm Disease has been prevalent in China for a long time. However, it was during the Song and Jin dynasties that the Hejian School established the foundation of the theory of Warm Heat. In the Ming dynasty, Wu Youxing (also known as Youke) further extended the theory into the study of Warm Epidemics. In the Qing dynasty, Ye Gui (also known as Tianshi) made significant advancements in clinical practice, culminating in Wu Jutong‘s Wen Bing Tiao Bian, which is considered a comprehensive work on Warm Disease theory, indicating that the theory of Warm Disease had reached a mature stage.Warm Disease, also known as Warm Heat Disease, refers to a group of acute febrile diseases caused by the invasion of external warm and heat pathogens, characterized primarily by fever. From this, we can see that Warm Disease is an external pathogenic disease, not an internal injury or miscellaneous disease. Secondly, Warm Disease is caused by external warm and heat pathogens, thus excluding the cold pathogens of external cold diseases like Shang Han (Cold Damage). The emphasis on “four seasons” is due to the close relationship between Warm Disease and seasonal changes. Thirdly, the main clinical feature of Warm Disease is fever; any condition classified as Warm Disease must involve an acute fever process. Fourthly, Warm Disease is not a single disease but a collective term for various acute febrile diseases.
▲ Wu Jutong, author of Wen Bing Tiao Bian In Wen Bing Tiao Bian, Warm Disease is classified into two main categories based on the nature of the disease: Warm Heat Disease and Damp-Heat Disease. Those without dampness are referred to as Warm Heat Disease, or simply Warm Disease; those with both heat and dampness are classified as Damp-Heat Disease. This classification aims to simplify clinical practice, for instance, treatments for Warm Heat Disease should primarily focus on clearing heat, while treatments for Damp-Heat Disease should emphasize resolving dampness.
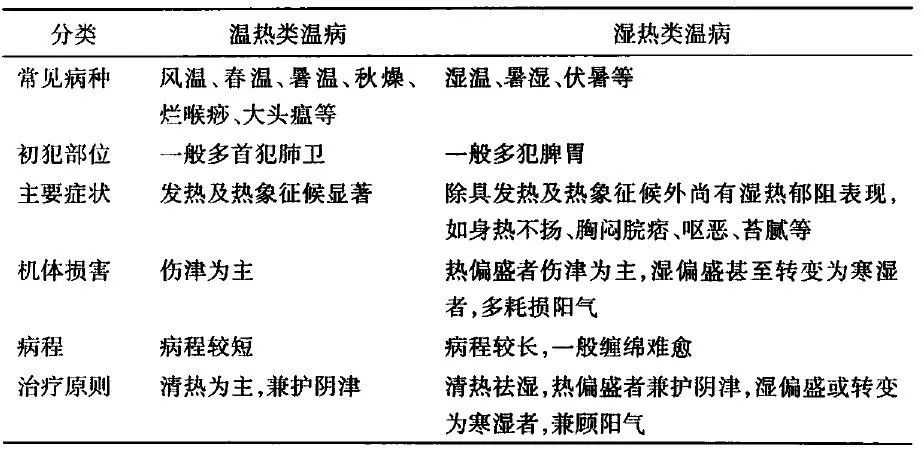
▲ Comparison of Warm Heat Disease and Damp-Heat Disease Additionally, Warm Disease can be categorized into nine types: Wind-Warmth, Warm Heat, Warm Epidemic, Warm Toxin, Summer Warmth, Damp-Warmth, Autumn Dryness, Winter Warmth, and Warm Malaria. Among these, Damp-Warmth Disease certainly falls under the category of Damp-Heat Disease, while Wind-Warmth, Warm Heat, Warm Toxin, Autumn Dryness, and Winter Warmth belong to Warm Heat Disease. Summer Warmth, Warm Epidemic, and Warm Malaria can be classified as either Warm Heat Disease or Damp-Heat Disease. For example, Summer Warmth Disease is characterized by the dominant qi of summer, where the climate is distinct from other seasons. On one hand, summer has high temperatures, and the prevalence of summer heat pathogens can lead to Summer Warmth Disease, classified as Warm Heat Disease. On the other hand, summer is often rainy, which can lead to the invasion of summer damp pathogens, resulting in Summer Warmth Disease being classified as Damp-Heat Disease.

▲ Wu Jutong’s theoretical distinctions among the nine types of Warm DiseaseDamp-Heat Disease is characterized by both heat symptoms, such as fever, red tongue, yellow coating, and rapid pulse, as well as clinical manifestations of dampness, including a heavy sensation throughout the body, thick and greasy tongue coating, and foul-smelling excretions. The most common form is Damp-Warmth Disease, which includes acute infectious diseases such as meningitis and encephalitis, all classified under Damp-Heat Disease. The manifestations of Damp-Heat Disease are extensive: in the gastrointestinal tract, it can present as fullness and discomfort in the stomach or nausea and vomiting; in the intestines, it can manifest as damp-heat diarrhea; in the liver and gallbladder, it can present as damp-heat jaundice or hypochondriac pain; in the lower jiao, it can present as damp-heat stranguria, and in women, it can manifest as damp-heat leukorrhea; on the skin, it can present as eczema, wet sores, or damp-heat arthralgia.
What is the relationship between Warm Disease and infectious diseases in Western medicine?
Some argue that Warm Disease is synonymous with infectious diseases; however, the scope of Warm Disease is broader. Infectious diseases fall under the category of infectious illnesses, while Warm Disease encompasses various infectious diseases. However, not all infectious diseases are classified as Warm Disease. For instance, Wind-Warmth Disease in Warm Disease is an infectious disease but is not contagious. Additionally, some conditions, such as heat stroke, are not infectious diseases but are caused by physical factors, yet they can present with acute fever, fitting the concept of Warm Disease and thus belong to its category. However, some infectious diseases, despite being contagious, do not fall under the category of Warm Disease. For example, tuberculosis is an infectious disease that can occur year-round, regardless of the season, and does not present with an acute fever process. In summary, there is an overlap between Warm Disease and infectious diseases, and whether a disease is classified as Warm Disease should not be determined solely by its infectious nature but rather by the concept of Warm Disease itself. 

Long press the QR code to follow us
Learn Traditional Chinese Medicine
Let’s work hard together!

