Recently, there has been a noticeable increase in patients suffering from various types of respiratory diseases caused by viruses, mycoplasmas, and bacteria. Most respiratory diseases present with symptoms such as fever and cough. Many parents consult during visits, asking, “After taking medication and receiving IV fluids, why does my child still have a persistent cough and fever? What other methods can alleviate my child’s suffering and relieve their symptoms?”
In addition to IV fluids and medication, our pediatric department has achieved good results using pediatric Gua Sha for children with recurrent fever, cough, and phlegm. Let’s learn about this unique TCM therapy for children with Dr. Yao from pediatrics.

1. What is Gua Sha?

The Gua Sha therapy is a form of external treatment in Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), guided by the theory of meridians and acupoints. It involves using specialized Gua Sha tools and techniques to scrape the skin with a certain medium, resulting in localized redness or dark red petechiae, known as “Sha”. This process aims to invigorate blood circulation and expel pathogenic factors. In simple terms, “Sha” is a form of pathogenic waste, and its emergence signifies the expulsion of these evils to improve the balance of Qi and blood.
In pediatric Gua Sha, specific acupoints are stimulated to adjust the child’s physiological functions and enhance their immunity, achieving the goals of disease prevention and treatment.

2. Characteristics of Pediatric Gua Sha
The technique is gentle, using soft pressure and alternating between rapid and slow movements to relax and open the meridians, allowing the obstructed Qi and blood to flow freely while resolving diseases with minimal or no pain, resulting in quick and effective outcomes.
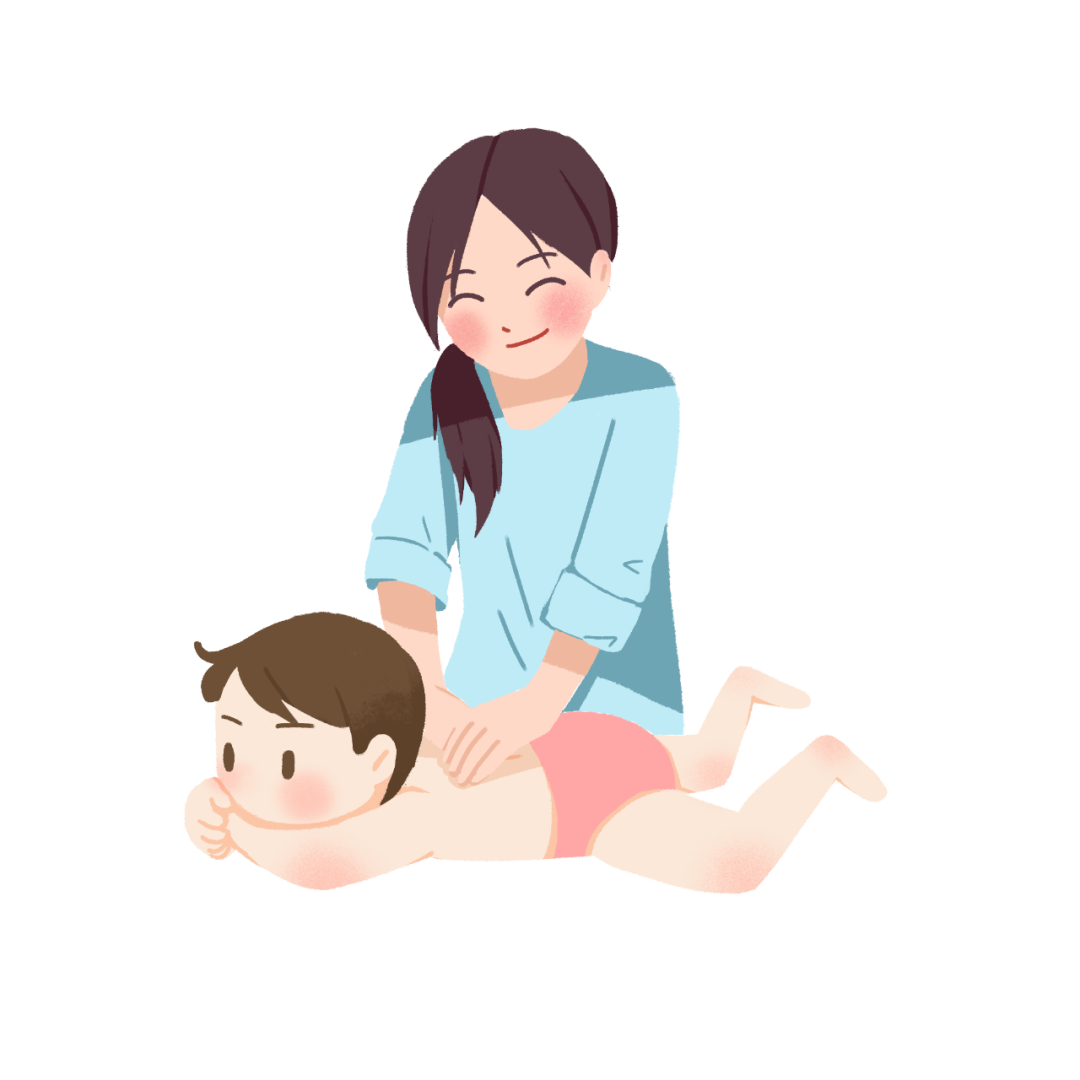
3. Applications of Pediatric Gua Sha
1. Respiratory Diseases: Fever, cough, asthma, rhinitis, snoring, and susceptibility to infections.
2. Digestive Diseases: Vomiting, constipation, anorexia, indigestion, abdominal pain, etc.
3. Halitosis, damp-heat, body coldness, and various internal heat symptoms.
4. Suitable age for pediatric Gua Sha: 4 to 12 years old.

Dr. Yao
Fever in Children
(1) Effects of Gua Sha
When a child has a fever, Gua Sha at the Dazhui (大椎) acupoint helps to reduce temperature. The Du Mai (督脉) is known as the sea of Yang meridians, and Dazhui is a crucial acupoint on this meridian. Stimulating it can effectively reduce fever.
(2) The Dazhui acupoint is located on the neck, below the spinous process of the seventh cervical vertebra, in the depression just below the most prominent bone when the head is lowered, level with the shoulders.


Dr. Yao

Loss of Appetite in Children
(1) Causes of Loss of Appetite
Loss of appetite in children is often due to insufficient spleen and stomach function, lack of Qi and blood, some related to congenital deficiencies, and others caused by environmental factors. TCM believes that if the spleen meridian is unblocked, the issue of loss of appetite will be resolved.
(2) Effects of Gua Sha
Gua Sha therapy can enhance the body’s Yang Qi, regulate spleen and stomach functions, replenish Qi and blood, and improve children’s loss of appetite.
4. Contraindications
1. Diseases with a tendency to bleed, such as leukemia, allergic purpura, and thrombocytopenic diseases, should not use this method.
2. Skin conditions such as burns, scalds, cracks, or sores are not suitable for Gua Sha.
3. Certain acute infectious diseases, such as hand-foot-mouth disease, cellulitis, bone tuberculosis, osteomyelitis, and erysipelas.
4. Critical conditions or weak individuals.
5. Precautions
1. Gua Sha should not be performed on an empty or overly full stomach; it is best done 40 minutes after a meal or between meals.
2. Care should be taken to keep warm and avoid exposing the child to cold. After Gua Sha, avoid direct wind or air conditioning, and wait 4-6 hours before bathing.
3. Drink warm water after Gua Sha to promote circulation and metabolism; the diet should be light, avoiding raw, cold, and fried foods.
4. Pediatric Gua Sha should be performed under the guidance of a physician and not done independently.
Pediatrics Overview

The pediatrics department is a key specialty in Meizhou City, with 57 beds (including 6 VIP rooms) and a team of 17 medical experts, including 1 chief physician, 1 associate chief physician, 4 attending physicians, 1 associate chief nurse, and 10 charge nurses.
We currently have non-invasive ventilators, high-flow nasal humidification therapy devices, fiber bronchoscopy, nasopharyngoscopy, central negative pressure suction, central oxygen supply, ECG monitors, high-frequency chest wall oscillation devices, intelligent digital multifunctional therapeutic devices, imported Jaeger pulmonary function instruments from Germany, Omron, Jiaruikang, and Baier children’s professional nebulizers, and automatic blood gas analyzers from the USA.

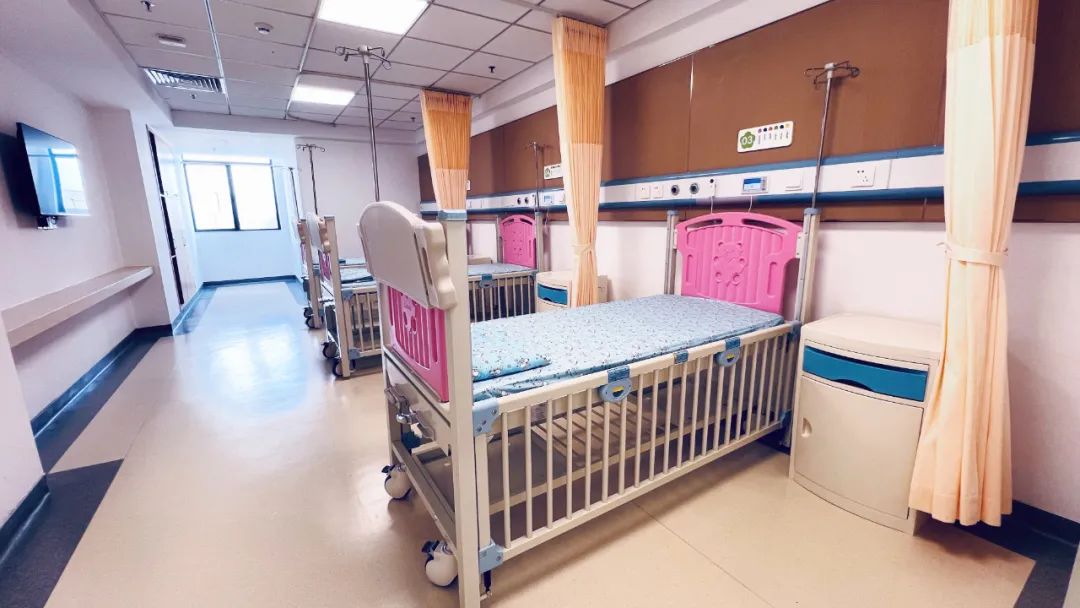
We conduct fiber bronchoscopy and alveolar lavage, routine PCR tests for pediatric respiratory pathogens, pediatric pulmonary function tests, professional nebulization therapy with compressed air pumps, high-frequency chest wall oscillation therapy, TCM targeted drug delivery therapy, herbal fumigation therapy, herbal acupoint application therapy, as well as pediatric Gua Sha, massage, and other techniques..
Consultation Phone:0753-2306168
Submitted by: Pediatrics Dr. Yao Yixian
Edited by: Li Yijun
Reviewed by: Medical Department Liao Sisen
Share, view, and like; at least I want to have one.
[Maternal and Child Health Science Popularization]


