

Ancient Natural Therapy
— Gua Sha
Natural therapy refers to a traditional medical system that does not require drug treatment, aiming to prevent and promote the body’s “self-repair” process to achieve the purpose of disease prevention and treatment. This concept is based on natural medicine, which believes that the human body inherently possesses natural healing abilities. The focus of natural therapy is on disease prevention and helping the body restore or enhance its innate resistance to disease. Traditional natural therapy advocates harmonious coexistence with nature on physical, psychological, moral, and spiritual levels. Therefore, doctors who respect traditional natural therapy center their treatments around air, water, soil, heat, and space, such as dietary therapy and hydrotherapy.


What is Gua Sha

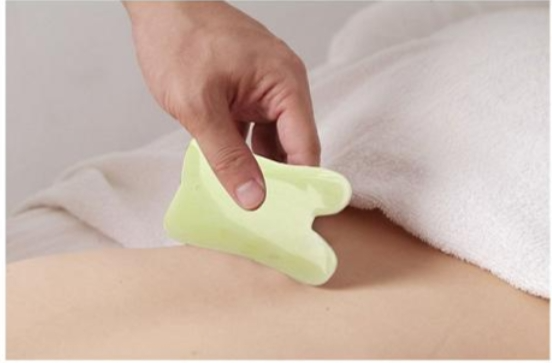
Gua Sha (Skin Scraping) is one of the traditional natural therapies in China. It is based on the TCM theory of the skin and uses scraping tools made of materials such as buffalo horn or jade to scrape the skin in related areas. Through beneficial stimulation, it fully utilizes the function of the ying wei (nutritive and defensive qi), causing congestion at the acupuncture points and improving local microcirculation to achieve the purpose of unblocking the meridians and invigorating blood circulation.
Gua Sha can expand capillaries, increase sweat gland secretion, and promote blood circulation, providing immediate effects for conditions such as hypertension, heat stroke, and muscle soreness caused by wind-cold bi syndrome. Thus, it serves to strengthen the body’s defenses and expel pathogens, preventing and treating diseases.


TCM Theory of the Skin

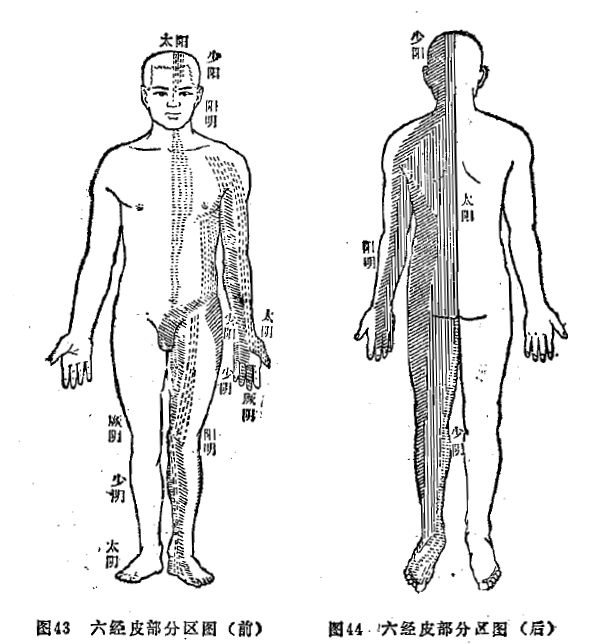
The skin is the part of the twelve meridian system that is distributed on the body surface. Simply put, the skin is the surface part of the twelve meridian system and is the outermost part of it. If we use modern anatomical terms, it corresponds to the superficial fascia layer of the fascial system. The Su Wen (Plain Questions) states: “The skin is the part of the meridians.” This means that the twelve meridians and their collaterals have corresponding distribution areas on the skin surface. Since there are twelve meridians, there are twelve corresponding areas on the skin surface, referred to as the twelve skin areas. The Su Wen states: “To understand the skin areas, one must refer to the meridians.” However, there is no clear record in ancient literature regarding the specific locations of the twelve skin areas on the body surface.


Mechanism of Action

1. Promote blood circulation
2. Regulate autonomic nervous function
3. Regulate immune function
4. Regulate endocrine function
5. Improve microcirculation


Precautions

1. Understand the condition and determine the scraping area; it is not necessary to force the appearance of sha (red marks).
2. Ensure warmth in the room during Gua Sha.
3. Avoid bathing within 30 minutes after Gua Sha.
4. It is best to drink a cup of warm water and rest for 15-20 minutes after Gua Sha.
If you have friends who wish to experience and receive treatment as mentioned above, you are welcome to visit the first floor of the Rehabilitation Treatment Area at the First People’s Hospital of Chenzhou for consultation.

Text | Rehabilitation Treatment Department Li Tailiang
Editor | Ma Xiao
Review | Sun Wei, Zhang Lingling

