Click Above Blue Text Follow!
Blue Text Follow!
Inheriting Traditional Chinese Medicine culture, we aim to be your health steward.
Cupping therapy, also known as sliding cupping, involves applying a layer of lubricant such as petroleum jelly or lard to the skin or the rim of the cup before the cupping process. The cup is then applied to the selected area of the skin using the flash fire method or dripping alcohol method to create suction. The practitioner holds the cup with the right hand while using the left hand to stretch the skin, moving the cup up, down, or sideways. The cup is slid back and forth over the area until the skin becomes red, congested, or even bruised, at which point the cup is removed. The sliding cupping technique is a method within the traditional cupping therapy of TCM, extending the simple suction of cupping into a dynamic sliding friction force. This combines the negative pressure suction of the cup with the friction force during sliding cupping, creating a combined effect on the skin surface. By controlling the speed, frequency, and density (area) of the sliding cupping, it is possible to adjust the intensity and direction of the combined force, achieving selective and enhanced stimulation to regulate the functions of the internal organs, meridians, and blood flow, thus playing a role in disease prevention and treatment.
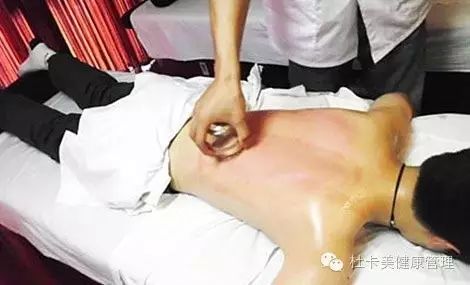
Cupping therapy utilizes various cups as tools, employing methods such as burning or suction to remove air from the cup, creating negative pressure that allows it to adhere to specific areas of the body. This technique aims to support the body’s positive energy, expel pathogenic factors, balance yin and yang, unblock meridians, regulate internal organs, dispel cold and dampness, and promote blood circulation, serving as a physical external treatment for various diseases.
Reflections on Cupping Marks
1. Dark purple-black cupping marks: Generally indicate insufficient blood supply and poor circulation with blood stasis.
2. Purple cupping marks with spots: Generally indicate cold congealing and blood stasis syndrome.
3. Cupping marks with scattered purple dots of uniform depth: Indicate qi stagnation and blood stasis syndrome.
4. Bright red cupping marks: Generally indicate yin deficiency, qi and blood deficiency, or yin deficiency with excess heat.
5. Dark red cupping marks: Indicate high blood lipids and the presence of heat pathogens.
6. Gray-white cupping marks that feel cool to the touch: Often indicate deficiency cold or damp pathogens.
7. Cupping marks with skin texture or slight itching: Indicate wind pathogens or dampness syndrome.
8. Water vapor on the inner wall of the cup: Indicates the presence of dampness in that area.
9. Cupping marks with blisters: Indicate heavy internal dampness; if the blisters contain blood-tinged fluid, it reflects damp-heat toxicity.

