01
╱ Definition of Zou Guan ╱
01
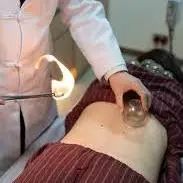
Zou Guan therapy is one of the modern developments of cupping therapy, integrating the effects of warm acupuncture, cupping, gua sha, massage, and pharmacotherapy, with wide clinical applications.
02
Zou Guan therapy involves attaching a fire cupping device to the skin and using a back-and-forth pulling technique to relieve the subcutaneous and fascial tissues. The mechanical force generated by the negative pressure transforms into biological stimulation, promoting the release of cellular factors in the body, thereby producing therapeutic effects.
02
╱ Mechanism of Zou Guan ╱
01
From the perspective of Western medicine, Zou Guan therapy primarily relies on the negative pressure and thermal stimulation at the suction site to cause rupture of subcutaneous capillaries, leading to blood leakage, which in turn stimulates the release of neurotransmitters and immune-active substances, achieving the goal of improving the body’s environment, increasing metabolism, and promoting cellular recovery.
02
From the perspective of Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), Zou Guan therapy can help to unblock meridians, promote qi and blood circulation, and regulate the internal organs. It is particularly suitable for conditions such as myofascial pain syndrome, frozen shoulder, colds, neuritis, lumbar disc herniation, facial nerve paralysis, insomnia, and cervical spondylosis, which are characterized by meridian obstruction and blood stasis.
03
╱ Operation of Zou Guan ╱

01
Before performing Zou Guan therapy, apply an appropriate amount of lubricant (such as gua sha oil, petroleum jelly, carnation oil, essential oils, medical glycerin, liquid paraffin, moisturizing cream, or coupling agents) to the treatment area. Then, use the flash fire method to secure the cupping device, holding it with one or both hands and applying slight force to repeatedly push and pull the cupping device along a specific path until the skin becomes red or shows sha marks.
02
To remove the cup, the practitioner should hold the cup slightly tilted with one hand while using the thumb or index finger of the other hand to press along the edge of the cup to create a gap between the cup and the skin, allowing air to enter the cup for removal.
04
╱ Precautions ╱

01
The operator should inform the recipient in advance about the reactions and potential risks of Zou Guan therapy, such as sha marks, local discomfort, hematomas, or blisters. The operator should also observe the recipient’s mental state; if there is excessive tension or fear, the operation should be stopped immediately. Advise the recipient to avoid wind and cold after cupping.
02
Do not use on patients with hypoglycemia, intoxication, cachexia, convulsions, or extreme tension; contraindicated for those with thrombocytopenic purpura, hemophilia, or other coagulation disorders; avoid using on acute traumatic fractures; contraindicated for pregnant women on the abdomen and lower back; avoid areas over the apex of the heart, superficial arterial pulsations, and varicose veins.
References:
[1] Chen Bo, Chen Zelin, Guo Yi, et al. Research on Zou Guan Therapy – The Three Parts of Tian Ren Di Zou Guan Method [J]. Chinese Acupuncture, 2010, 30(9): 777–780.
[2] Yu Hailong, Chen Bo, Chen Zelin, et al. Analysis of Suitable Conditions for Zou Guan Therapy [J]. Journal of Tianjin University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2012, 31(1): 50–53.
[3] Zhao Yijing, Liu Peidong, Chen Zelin, et al. Preliminary Observation on the Effect of Different Parameters of Governing Vessel Zou Guan on Local Skin Blood Flow in Sub-healthy Individuals [J]. Journal of Tianjin University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2015, 34(1): 18–22.
[4] Liu Ting. Research and Formulation of WFAS Standard “Cupping Operation Specifications” [D]. Tianjin University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022.
[5] Shuman. Study on the Efficacy of Zou Guan Therapy for Chronic Low Back Pain and Related Molecular Mechanisms Promoting Tissue Regeneration [D]. PLA Medical Academy, 2019.
[6] Zhou Liwu, Chen Yuchuan, Feng Yaming. Introduction to Zou Guan Techniques [J]. Chinese Folk Therapy, 2007, (1): 13.
PS: The editor advises readers not to attempt this at home and to seek treatment from a legitimate medical institution to prevent accidents.
Image source from the internet, please delete if infringing!

Editor, Layout|Li Jiashan
Review|Liu Qi

