 Click the “blue text” above to see the little stars
Click the “blue text” above to see the little stars Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM)
Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) TCM is often perceived in a certain way.
TCM is often perceived in a certain way.
 However, many people may not know that modern TCM can be prepared in various forms, with pills being one of them.
However, many people may not know that modern TCM can be prepared in various forms, with pills being one of them.
 Pills
Pills





Release and dissolve the medication slowly, prolonging efficacy, reducing toxicity and irritation, and minimizing adverse reactions.
Some new types of pills can be used for emergency treatment.
They are often used in the treatment of chronic diseases.
 General preparation methods for water pills
General preparation methods for water pills
1. Process Flow
Preparation of materials → Molding → Shaping → Coating → Drying → Selection of pills → Quality inspection → Packaging

 Preparation of materials
Preparation of materials
Supplies: 1 clean medicine tray, 1 paintbrush, 1 small broom (palm brush), 1 each of 5mm and 6mm diameter medicine sieves, 2 medicine trays, an appropriate amount of fine powder of medicinal herbs passed through a 100-mesh sieve, and cool boiled water or the medicinal juice specified in the prescription.
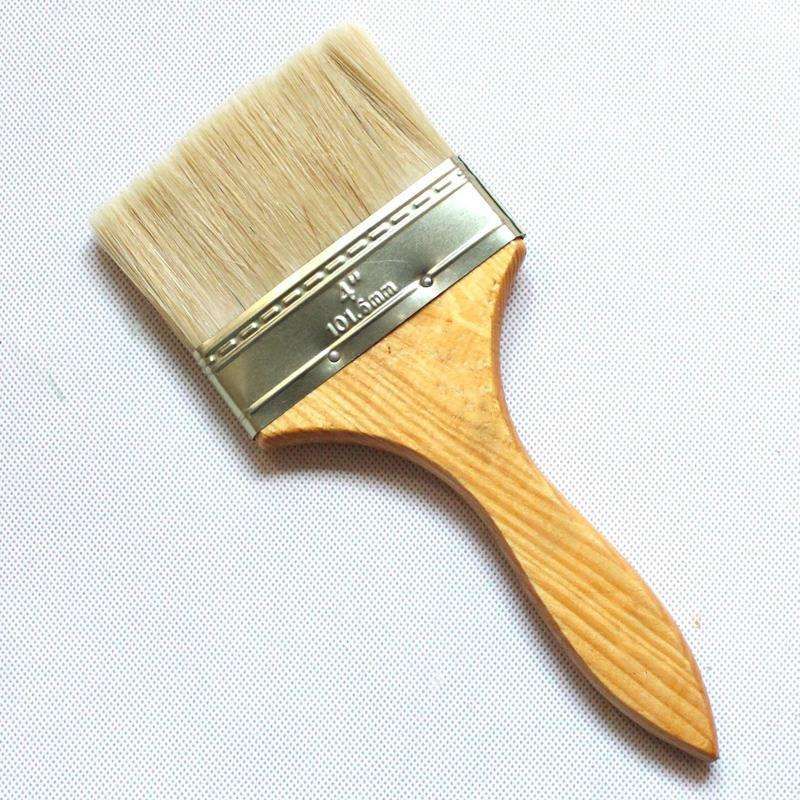
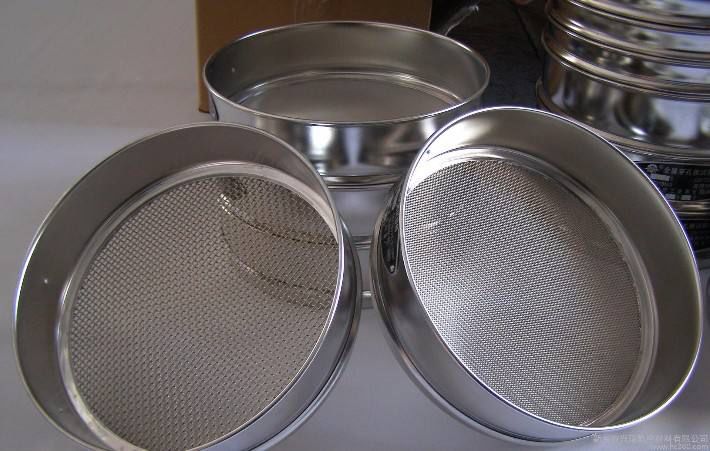
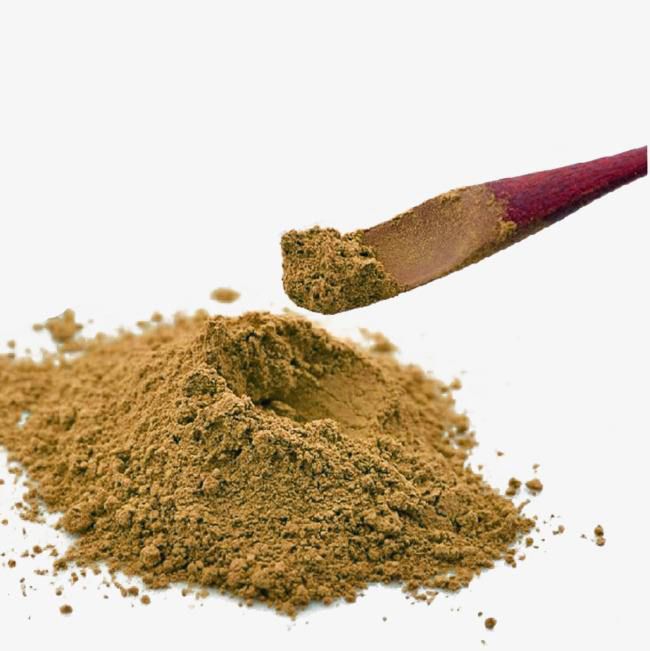
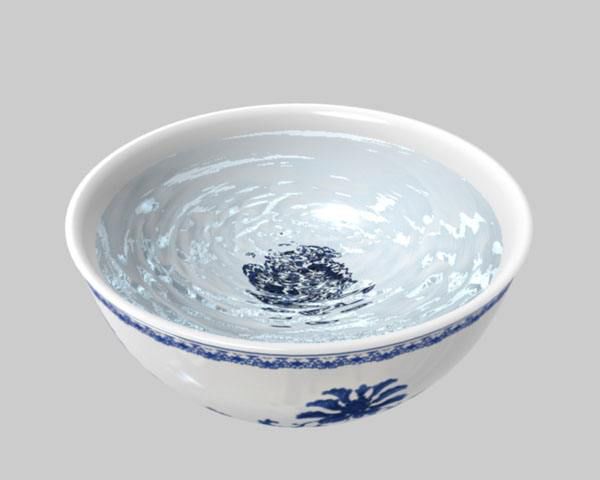






 Molding
Molding
The powder used for molding should be selected from the prescription with a certain degree of stickiness. The amount of powder should be determined based on the nature of the herbs in the prescription and the total amount of powder to achieve the desired size of the finished pills, generally 2%-6% of the total powder. For herbs that are loose, high in fiber, and absorb water easily, a larger amount of powder should be used; for herbs that are sticky and absorb less water, a smaller amount should be used.
Method of operation: First, use a brush to dip a small amount of water and evenly brush one side of the medicine tray, then sprinkle an appropriate amount of medicinal powder. Use a small broom to gently brush the powder that adheres to the tray, tilting and rotating the tray to concentrate the powder on the other side. Then, use the brush to apply a small amount of water evenly to the tray, rotating it so that the initially moistened powder moves to the wet area. At this point, brush off the powder and sprinkle a little more powder on the wet particles, continuing to rotate the tray so that the moist powder rolls around and adheres evenly to the tray surface. Repeat this process until small round pills of uniform size, approximately 0.5mm to 1mm in diameter, are formed.
 Pill formation
Pill formation
Place the qualified small particles in the medicine tray, and using the same method as before, apply water and add medicinal powder to form pills of appropriate size, smooth and shiny. During the pill formation process, basic techniques such as rolling, kneading, flipping, and colliding should be alternated.
Rolling: Rotate the medicine tray to make the pills move in a circular motion, allowing the added water and powder to adhere evenly to the surface of the pills, making them smooth, round, and dense.
Kneading: Make the pills rotate slightly on one side of the tray, allowing water and powder to adhere to the surface. This is often done when water or powder is first added.
Flipping: Make the pills perform a push-pull flipping action on the tray. The goal is to distribute the sprinkled powder evenly and separate any pills that are stuck together.
Colliding: Forcefully pull the pills from above the tray downwards, impacting their edges to make them round and dense.
 Drying
Drying
Pills formed through the above process have a high moisture content and are prone to mold; they should be dried promptly.The 15th edition of the “Chinese Pharmacopoeia” stipulates that the moisture content of water pills should not exceed 9%, and that of honey water pills should not exceed 12%. Unless otherwise specified, water pills and honey water pills should be dried at temperatures below 80°C, and those containing volatile components should be dried at temperatures below 60°C. Drying is often done using an oven.

2. Precautions
1. Molding
When molding, pay attention to: ① The initial position for applying water and powder should be fixed; ② Water should be applied evenly, avoiding pooling; ③ Water and powder should be added in small amounts multiple times; ④ If there is powder sticking on the tray, it can be brushed into a paste when adding water, and small particles can roll on top to ensure they adhere to the small particles.
2. Pill formation
During pill formation, pay attention to:
① Control the amount of water and powder added.② After adding powder, gently form the pills to avoid dust loss and unevenness. After adding water, apply force to prevent sticking.③ Non-shaped and larger pills can be mixed with water to form a paste, then reformed into pills.④ To ensure uniform pill size, tilt the tray slightly and gently shake it; larger pills will roll down, allowing powder to be added to smaller pills, achieving a more uniform size.
3. Drying
Common issues during oven use: ① Uneven thickness of pills, unstable oven temperature, and failure to stir the material in time can cause “burnt pills”. ② During the drying process, especially in the initial stage, if moisture evaporates too quickly, the contraction effect increases, causing the pills to compress and harden. ③ At excessively high temperatures (> 80°C), starches in the wet pills can gelatinize, increasing stickiness, which is detrimental to pill dissolution. High temperatures can also damage active ingredients, affecting the quality of the medicine.
Solutions: When placing pills in a stainless steel tray, ensure an even thickness, and stir the material in a timely manner during drying. If conditions allow, install a fan in the drying box to ensure uniform temperature throughout. The drying temperature for wet pills should gradually increase from low to high until it reaches the specified temperature for each type.



Improvements in Molding Methods
① Use cooked millet or dodder seeds as molds. The amount of millet should be based on 50g/kg, and can be adjusted based on the desired size of the pills; issues may arise if the prescription does not include millet or dodder seeds.
② Wet granules for molding: Mix the medicinal powder with water to form a soft material, pass it through a No. 2 sieve, and use rotation and impact to make it compact and smooth, thus forming the mold. However, the uniformity of the mold cannot be guaranteed, and it may easily stick together.


Scan to follow
Interesting souls are waiting for you



