
Introduction: In Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), observation, listening, questioning, and pulse-taking are essential. Observing the patient’s body shape, color, posture, etc., provides the physician with firsthand information. Observation is crucial!

First, here are two verses:
Kidney deficiency leads to dark circles, Lung heat shows red tips, Liver excess results in red eyes,
Cold cough shows dark cheeks, Wind causes blue eyes, Phlegm-damp leads to yellow eyes,
Excess phlegm causes swollen eyes, Cold stomach shows blue lips, Kidney failure leads to dark ears,
Dampness causes yellow skin,Liver heat leads to dry skin, Spleen heat shows red cheeks,
Mixed colors indicate dim vision, Foot injuries lead to heavy neck. Blood loss leads to dark complexion,
Diarrhea shows pale yellow face, Qi deficiency leads to puffy face, Excess sweating shows blue lips,
Pain leads to furrowed brows. Fire dryness shows dark forehead, Forehead dryness needs water replenishment,
White lips indicate cold, Red cheeks clear liver and lungs, Excess fat indicates phlegm to be removed.
Thin people have excess liver fire,Weakness indicates Qi deficiency, Throat constriction leads to choking,
Throat constriction indicates stomach cold, Diarrhea shows pale yellow face. Abdominal pain shows pale lips,
Dark blue face indicates diarrhea prevention, Round bulging eyes indicate mania, resembling a crane indicates tuberculosis,
Dark purple indicates bone steaming. Fright shows blue-black face, Stomach failure shows blue mouth,
Poisoning shows white mouth, red blood symptoms, Yellow face like dyed paper,
Intestinal wind and blood collapse,Sunken eyes indicate eye disease, Ugly nose indicates instability,
Strange black parts indicate worry, Spots also need evaluation. Suspended needle locks the seal,
Middle Jiao disease must be treated, Nose shows three bends, Hand and foot fractures indicate fright,
Excess phlegm shows bright face. Tight Qi indicates waist pain prevention, Dark nose and ears indicate impending death,
All diseases should be checked here, Don’t rush in clinical symptoms.
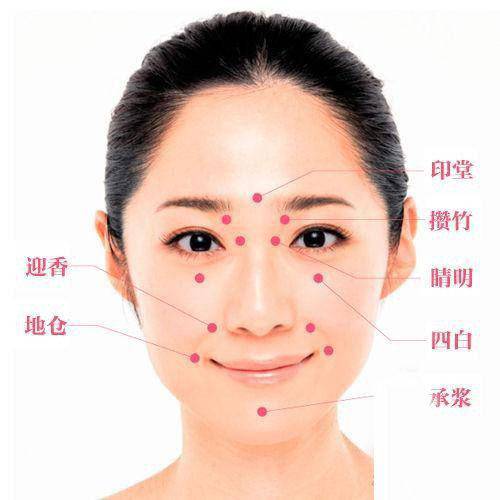
Facial Diagnosis Mnemonics
When seeing a patient, observation comes first. Vital energy is the most important. Organ positions must be remembered. Multiple shadows should be distinguished. Diseases are manifold, arising from Qi and blood. Blue complexion indicates cold pain. Glossy complexion indicates abundant Qi and blood. Red complexion indicates heat.
Red like makeup indicates false fire. Black complexion indicates liver and kidney issues. Pale white complexion indicates deficiency cold. Dull white indicates blood deficiency.
Yellow complexion indicates damp heat. Dark yellow indicates liver and kidney disease. Bright forehead indicates good spirit. Dark forehead indicates disaster.
Bright eyes indicate no major illness. Dull eyes indicate Qi deficiency. Red eyes indicate internal heat. Yellow whites indicate liver and gallbladder disease.
Missing iris indicates brain disease. Large stomach indicates poisoning. Black vertical lines indicate inflammation. Black depressions indicate organ damage.
Itchy dermatitis indicates gray around the iris. Hard blood vessels indicate white circles. Iris diagnosis is profound. Concentric circles are key.
Multiple segments form a ring. Rings interlock, representing the whole body. Eyes are like fish, precious and bright. Shiny nose indicates no major illness.
Blue nose indicates cold injury. White nose indicates blood injury. Dark nose indicates stomach Qi deficiency. Misaligned nose indicates serious illness.
Spots on the nose indicate serious illness. Bright philtrum indicates no major illness. Full tear hall indicates fullness. Dry dark indicates kidney deficiency.
Insomnia indicates spirit injury. Flat grooves indicate lack of strength. Philtrum blisters indicate stomach fire. Crooked philtrum indicates short life.
Pale red lips indicate no major illness. White lips indicate blood injury. Blue-purple lips indicate cold pain and stasis. Bright face indicates water accumulation.
Yellow-black face indicates fatty liver. Dark ears indicate cancer prevention. Thin face indicates caution. If no illness, weight will increase.
Ten steps away, eyebrows and eyes are clear. No serious illness indicates longevity. Clear positions, five colors are clear. Knowing colors can ensure safety.

The Five Organs and Diseases
The five organs are important parts of the human body, closely related to the five viscera. If the five organs feel uncomfortable, the viscera are gradually weakening, leading to disease.1. Sudden frequent blurriness in the eyes, dryness at the corners, and unclear vision indicate liver function weakening. Pressing around the liver will feel swollen. In addition to seeking medical attention promptly, one should also pay attention to eye hygiene and avoid excessive eye strain, as improper use of the eyes can also affect the liver. 2. Constant buzzing in the ears and difficulty hearing indicate gradual kidney function decline, sometimes accompanied by foot pain, back pain, and frequent urination. Those who work too hard should especially pay attention to balancing work and rest, avoiding excessive fatigue, and reducing alcohol and spicy food intake. 3. Diminished sense of smell, frequent coughing, and sometimes even difficulty breathing indicate gradual lung function decline. Patients should first pay attention to diet, quit smoking or control smoking, and avoid being around heavy smokers. Eating more fresh fruits and vegetables and strengthening physical exercise can prevent lung complications. 4. Numbness in the lips, reduced appetite, and noticeable weight loss indicate gradual pancreatic function decline, mainly due to dietary imbalance and improper eating habits. When the pancreas is not functioning well, it also affects the stomach, leading to noticeably dry and cracked lips, numbness, and lack of taste. In addition to adjusting the diet, one should also avoid eating raw, cold, and greasy foods. 5. Dull taste, inability to taste food, accompanied by palpitations, frequent dreams, and insomnia indicate heart function damage. This is caused by excessive labor. When the mouth feels dry, the tongue coating is thick, and one cannot taste food, one should be especially vigilant to prevent heart disease.
Comprehensive Facial Diagnosis
(1) Slightly yellowish complexion with a rosy hue, full of spirit, natural expression, and slightly glossy — normal appearance. (2) Flushed complexion, excited and restless, flaring nostrils, lip herpes, painful expression, rapid breathing and pulse — acute disease appearance, such as lobar pneumonia, dysentery, acute purulent tonsillitis, acute infectious diseases, etc. (3) Facial swelling, pale eyelids, small eye fissures, and noticeable indentation on the forehead, especially severe in the morning — acute or chronic nephritis, kidney disease, etc. (4) Haggard appearance, grayish complexion, lifeless eyes, and mental fatigue — chronic wasting disease. (5) Pale complexion, swelling, wide and loose eyelids, dull and cold expression, white showing above the black eyeball, protruding eyeballs — hyperthyroidism. (6) Pale complexion, swelling, lack of expression. Thick tongue and lips. Accompanied by hoarseness, deafness, and rough skin all over — hypothyroidism. (7) Facial swelling, dark red cheeks, and cyanotic lips — often rheumatic heart disease, mitral stenosis. (8) Enlarged head, elongated face, protruding jaw, prominent cheekbones, enlarged ears and nose — acromegaly. (9) Slow response, apathetic expression, vacant gaze, little breath and speech — typhoid fever. (10) Red, round, moon-like face due to fat accumulation in the cheeks, possibly obscuring the ears — often due to long-term use of adrenal cortex hormones, Cushing’s syndrome. (11) Facial muscle rigidity, expressionless during speech or movement, resembling a mask — Parkinson’s disease and encephalitis. (12) Pale grayish complexion, apathetic expression, sunken eyes, prominent cheekbones, and sharp nose — often due to severe hemorrhage, shock, acute peritonitis, etc. (13) Conjunctival hyperemia, redness in the facial and eye socket areas, neck, and chest skin, fading upon pressure — often epidemic hemorrhagic fever. (14) Dark complexion without jaundice, brownish-black with a hint of gray — often cirrhosis or late-stage liver cancer. (15) Mouth corners drooping towards the healthy side, inability to whistle or puff cheeks, enlarged eye fissures, inability to close eyelids, tearing, and disappearance of forehead wrinkles — often facial nerve inflammation. (16) Nodular hyperplasia and patches on the face, merging into large uneven nodules, partial or complete loss of eyebrows and eyelashes, resembling a lion’s face — often leprosy. (17) Thin and pale face, rosy cheeks, noticeable low-grade fever in the afternoon — active pulmonary tuberculosis. (18) Dull yellow complexion, flat nose, almond-shaped eyes, swollen eyelids, wrinkled forehead, thick lips, extended tongue, fatigue — congenital idiocy. (19) Haggard face due to diarrhea or vomiting, sunken eyes, prominent nose, and clear cheekbones — severe dehydration. (20) Face resembling a “black person,” with black-blue pigmentation on gums and buccal mucosa — chronic adrenal cortical insufficiency. (21) Deep wounds from trauma, difficulty opening mouth after several days, facial muscle spasms, appearing to smile but not genuinely — often tetanus. (22) Laughing foolishly, constantly looking in the mirror, making faces, thinking strangely, emotional responses are childish, and behavior is disordered — juvenile-type schizophrenia. (23) Manic laughter — mental illness, such as reactive psychosis, hysteria, arteriosclerotic psychosis, mania, etc. (24) Foolish laughter — often seen in congenital idiocy due to chromosomal abnormalities, as well as in cases of maternal exposure to radiation, viral infections during pregnancy, and other congenital developmental disorders; difficult labor and sequelae of encephalitis and meningitis. (25) Forced laughter — often a sequel to multiple cerebrovascular accidents, also seen in multiple sclerosis, often accompanied by forced crying, speech, and swallowing difficulties. (26) Strange laughter, winking, pouting, tongue sticking out, frowning, and eye rolling — often seen in patients with chorea. (27) Dull laughter, often with open mouth, drooling, and unconscious laughter — often seen in elderly diffuse cerebral arteriosclerosis. (28) Fake laughter, enlarged eye fissures, flat nasolabial folds, drooping mouth corners, and facial asymmetry — facial nerve paralysis. (29) Long-term abnormal facial color and lack of spirit — should seek hospital examination and treatment. (30) Sudden yellowing of the face — may indicate jaundice hepatitis, cholecystitis, or hookworm disease. (31) Cyanosis of the face — often respiratory diseases, such as tuberculosis, emphysema, pneumonia, chronic bronchitis, etc. (32) Gradual darkening of the face — may indicate cirrhosis. (33) Swelling of the eyelids — indicates “water retention” or lack of sleep; if swelling is more severe in the morning, it indicates heart or kidney issues. (34) White patches on the cheekbones or facial area — may indicate vitiligo or cancer. (35) Yellow skin, dull hair, and easy tangling — indicate thyroid secretion disorders. (36) Excessively pale skin — may indicate anemia. (37) Red skin — indicates high red blood cell content or issues with the heart, liver, and intestines. (38) Half-moon white patches on the eyelids — may indicate high cholesterol levels in the blood. (39) Changes in moles on the face, such as darkening, enlargement, or irregular edges — may indicate skin cancer.
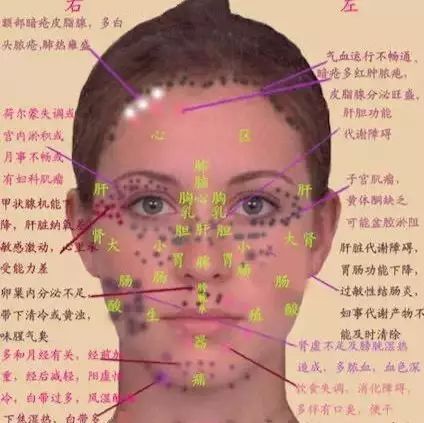
Facial Features:
The face of an infant is clean, and only after weaning and starting solid food does it show the capabilities of the heart, liver, spleen, stomach, and kidneys. As one ages, the conditions displayed on the face become more varied, including acne, spots, scars, and wrinkles; generally, adolescents show acne, middle-aged individuals show wrinkles, and the elderly show spots.Specific Features: 1. Cardiovascular pressure zones mostly show acne, spots, and wrinkles. 2. Liver zone: shows crow’s feet and spots. 3. Gallbladder zone: appears bluish. 4. Lung zone: appears dark, indicating poor lung function. 5. Brain zone: shows vertical lines (between the inner sides of the eyebrows, or three lines, or two lines) indicating poor cardiovascular health; a red glabella indicates thick blood lipids, often associated with hypertension. 6. Heart zone: shows horizontal lines (one, two, or several lines) indicating heart issues. Nose lines often indicate insufficient blood supply. 7. Spleen and stomach zone: abnormal color (or red nose) indicates disharmony of the spleen and stomach. 8. Reproductive zone: abnormal color appears bluish, often indicating endocrine disorders. 9. Kidney zone: appears dark, indicating kidney deficiency. Red bumps indicate back pain and general soreness, while sunken areas on the side of the cheeks indicate kidney deficiency, and small ears indicate kidney deficiency. 10. Large intestine and small intestine zones: spots and “dark-colored” red dots indicate poor liver function. 11. Chest and breast zone: dark color corresponds to one side. 12. Bladder zone: appears dark and black, with acne; bladder issues may arise.
Comprehensive Body Supplementation:
1. General Overview 1. Moles and blemishes on the face indicate congenital organ function deficiencies. 2. Spots on the face indicate chronic diseases formed by long-term chronic consumption (3-5 years). 3. Acne on the face indicates current inflammatory lesions in the organs (short-term formation). 4. Full facial acne and spots indicate endocrine disorders or decreased liver immune function.
2. Specific Discussions1. Psychological Stress: The reflective area is on the upper third of the forehead to the hairline (the hairline circle); if acne (bumps) appears here, or if the forehead color differs, it indicates significant psychological stress. If spots appear, it indicates heart disease (e.g., myocardial weakness); moles indicate congenital heart function deficiencies. 2. Heart: The reflective area is on the bridge of the nose between the corners of the eyes; if horizontal lines or prominent horizontal lines appear here, it indicates arrhythmia or poor heart condition; if deep horizontal lines appear and there are also deep vertical lines (grooves) on the tongue, it may indicate severe heart disease. Heart disease generally correlates with poor small intestine function and can lead to diseases of blood vessels, brain, thyroid, and parathyroid. Wrinkles on the lower lip indicate coronary heart disease, and purple lips indicate heart disease. 3. Brain: The reflective area is between the eyebrows; if vertical lines appear here, especially deep and red, it indicates insufficient blood supply to the brain, headaches, neurasthenia, frequent dreams, poor sleep, palpitations, and irritability. 4. Lungs: (respiratory system, throat, trachea, tonsils, etc.): The reflective area is between the eyebrows and the lower third of the forehead. If the middle of the forehead is sunken and the color is dark, bluish, or spotted, it indicates lung disease and difficulty breathing; if there are acne spots, it indicates recent colds or sore throats. If there are moles, spots, or whiteness at the eyebrow area, it indicates pharyngitis, tonsillitis, chest tightness, or lung disease. A bulge above the eyebrows also indicates lung disease. Individuals with poor lung function generally have poor large intestine excretion. 5. Chest (Breast): The reflective area is between the corners of the eyes and the bridge of the nose. If this area appears dark or bluish in men, it indicates chest tightness and shortness of breath. If this area appears dark or bluish in women, it indicates breast tenderness during menstruation. If there are moles or acne-like protrusions on the inner side of the upper eyelid, it indicates lobular hyperplasia in women, and in men, it indicates pleurisy. If there are small bumps at the corners of the eyes in women, it indicates breast hyperplasia or breast tumors. 6. Liver: The reflective area is between the eyebrows and above the temples, and the lower third of the forehead, as well as the middle section of the bridge of the nose (the highest point of the nose). If these areas appear dark or spotted, and the person is relatively young or wealthy, it may indicate fatty liver. If these areas or one of them has acne (bumps), it indicates excess liver fire. If spots appear at the temples, it indicates weakened liver function. If spots appear at the highest point of the nose, it may indicate excessive liver fire, emotional instability, or menopause. If both areas have noticeable spots and the complexion is dark and dull, indicating poor appearance and thinness, it suggests liver disease (hepatitis or cirrhosis). A mole in the center of the eyebrows, yellowing of the eyeballs, and a very yellow complexion indicate hepatitis B. A blue line from the bridge of the nose to the tip may indicate cancer or tumors! 7. Gallbladder: The reflective area is on the outer side of the high point of the bridge of the nose. If this area has red blood vessels, acne, or if the mouth tastes bitter upon waking, it indicates mild inflammation of the gallbladder; if spots appear, it may indicate cholecystitis. If this area has vertical folds or shows vertical lines when smiling, it indicates gallbladder issues. If there are moles, it indicates congenital gallbladder function deficiencies. If one places the right hand under the right rib (the gallbladder is located here) and strikes the back of the right hand with a fist, if it hurts, it indicates cholecystitis; if the pain is severe, it may indicate gallstones. Individuals with gallbladder issues may be overweight. A pair of noticeable spots or moles under the eyes indicates gallstones. Dark eye bags also indicate gallbladder issues. 8. Kidneys: The reflective area is where a vertical line from the outer corner of the eyes intersects with a line dropped from the middle of the ears down to the chin. If this area has red blood vessels, acne, or spots, it indicates kidney deficiency, generally accompanied by fatigue, soreness in the lower back and legs. If this area has deep and large spots, it may indicate kidney stones. If this area has disease or lumps, it indicates congenital kidney function deficiencies, which can also lead to diseases of the bladder, reproductive system, and gonads. Deep crow’s feet at the corners of the eyes and vertical folds near the ears also indicate kidney deficiency. If this area has disease or moles and the brain area has deep vertical lines, it indicates hypertension or suggests future cerebrovascular disease. 9. Bladder: The reflective area is on both sides of the philtrum below the nose. If this area is red, has red blood vessels, acne, or sores, it indicates cystitis, which may cause red and yellow urine and slight urgency; cystitis can also cause lower back pain. In women, cystitis may sometimes be related to gynecological issues. If the bridge of the nose is red but there is no frequent or urgent urination, and the entire bridge of the nose is red, it indicates rhinitis. 10. Spleen: The reflective area is at the tip of the nose. If the tip of the nose is red or has rosacea or is enlarged, it indicates spleen heat or spleen enlargement, generally accompanied by a heavy head, cheek pain, and irritability. If the tip of the nose is yellow or white, it indicates spleen deficiency, which may cause excessive sweating, aversion to wind, lethargy, and lack of appetite. 11. Stomach: The reflective area is at the wings of the nose. If the wings of the nose are red, it indicates stomach fire, leading to hunger and bad breath. If there are red blood vessels and it is severe, it generally indicates gastritis. Stomach pain before meals generally indicates gastritis. Abdominal pain one to two hours after meals indicates gastric ulcers, with tenderness in the middle of the abdomen or slightly to the left; abdominal pain two to four hours after meals indicates duodenal ulcers, with pain located between the ribs near the heart, similar to a needle prick, and in severe cases, the pain may radiate to the back, with tenderness in the abdomen slightly to the right. If the wings of the nose are grayish-blue, it indicates stomach cold; when shaking hands, one can feel the person’s fingertips are cold, indicating that the person suffers from wind-cold stomach pain and diarrhea. If the wings of the nose are sunken, it generally indicates a history of stomach pain, which can lead to atrophic gastritis, with a high possibility of developing gastric cancer. Thin wings of the nose with deep grooves indicate atrophic gastritis. 12. Small Intestine: The reflective area is below the cheekbones, slightly inward. If this area has red blood vessels, acne, spots, moles, or blemishes, it indicates poor absorption function of the small intestine, generally leading to thinness. 13. Large Intestine: The reflective area is below the cheekbones, slightly outward. If this area has red blood vessels, acne, spots, moles, or blemishes, it indicates poor excretion function of the large intestine, generally leading to dry stools, constipation, or diarrhea; if this area has crescent-shaped spots, it indicates constipation or hemorrhoids. The intersection of the lower line of the nose and the outer corner of the eyes is the rectal reflex area; if there are spots here, it indicates hemorrhoids; if this area is red or has white spots, there is a possibility of rectal cancer. 14. Reproductive System: The reflective area is around the philtrum and lips. If a woman has moles or blemishes below her lips, and the kidney reflective area is relatively clean, it indicates a retroverted uterus and lower back pain. If a woman has moles or blemishes around her lips, and the kidney reflective area is also poor, or if the area around her lips is bluish, dark, or white, and the kidney reflective area is also poor, these two situations generally indicate sexual coldness. If a woman has a mole in the philtrum, it generally indicates uterine disease. If a man has moles or blemishes around his lips, and the kidney reflective area is also poor, it indicates reproductive system issues. If a man over 40 has a thicker upper lip, it may indicate prostate enlargement; if the upper lip has acne that recurs, it may indicate prostatitis. If a man’s upper lip is uneven with grooves, it indicates male sexual dysfunction; if both sides of the upper lip are red, it may also indicate prostatitis. Appendix:(1) Moles on the upper eyelid indicate dizziness. (2) Any reflective area with moles or blemishes indicates that ancestors suffered from diseases in that area. (3) Diabetes: A pitted tip of the nose with red blood vessels in the kidney area and red wings of the nose. Large eyelids with swelling and cracked lips, with a red line in the middle of the tongue, may indicate diabetes. (4) Dark circles around the eyes indicate insufficient blood supply to the brain, easily leading to trigeminal neuralgia and poor sleep. (5) If there are two blue veins in the throat, it indicates rheumatic arthritis. (6) Spots on the entire face indicate thrombocytopenia. If symptoms appear on the forehead near the hairline, it indicates poor cardiovascular function or significant mental stress. If there are moles, it indicates congenital cardiovascular dysfunction. If there are bumps or redness, blueness, purpleness, blackness, or darkness, it indicates current or long-term cardiovascular dysfunction or significant mental stress. If there are spots or pigmentation, it indicates long-term cardiovascular dysfunction or long-term mental stress. The area between the eyebrows and the outer half of the eyebrows, drawn in circles, represents the respiratory system (lungs, throat). The outer half of the eyebrows, drawn in circles, including the temples, represents the liver. The area below the eyes and above the cheekbones represents the gallbladder. The area at the bridge of the nose between the eyes represents the cardiovascular system. The area between the eyes and the sides of the bridge of the nose represents the chest cavity in men and the mammary glands in women, with both genders viewed crosswise. Another location for the liver is at the midpoint of the bridge of the nose, while the gallbladder is located on both sides of the midpoint of the bridge of the nose, as the liver and gallbladder are interconnected. The tip of the nose represents the spleen, while the wings of the nose represent the stomach. The area from the lower cheekbones to the lower end of the tip of the nose, parallel to the outer side, represents the large intestine. The inner side of the small U-shaped area represents the small intestine. The area from the cheekbones to the ears, including the ears and cheeks, represents kidney function. The philtrum represents the bladder. The area around the mouth represents the reproductive system. The chin represents the kidneys or body soreness; full facial acne indicates significant mental stress.
Facial Features Indicating Difficult or Impossible Treatment
Any of the following “death” features should be approached with caution: 1. Black color appearing on the glabella, nose tip, and both corners, difficult to survive for three days. 2. Hair dry and standing, difficult to survive for 15 days. 3. Blue energy descending from the hairline to the glabella, regardless of the severity of the illness, death within 60 days; to the bridge of the nose, death within a month; to the philtrum, difficult to survive for seven days. 4. A white line appearing from the glabella to the ears or nose indicates a fatal condition. 5. Lifespan appears withered black, pale white, or deep blue, indicating certain death. (Note: complexion is the first intuitive impression, do not scrutinize too closely) 6. Black forehead, heavy head, stiff neck, and downward gaze also indicate an incurable person. 7. Long-term severe illness with fixed dilated pupils indicates impending death. 8. Entire nose appears withered and black, also indicates incurability. 9. The life gate (in front of the ears) connected to the nose with a white horizontal line or purple-black indicates death. 10. Black energy entering the philtrum also indicates death. 11. Dry corners of the mouth, white-yellow, difficult to survive for seven days. 12. Blue lips and black tongue like pig liver indicate nine out of ten diseases lead to death.
(Note: complexion is the first intuitive impression, do not scrutinize too closely; rely on intuition for diagnosis, and have confidence.)
Copyright Statement:
1.Source: Dream Back to Salhu, edited by Yang Lai.
2. Copyright belongs to the relevant rights holders, respecting knowledge and labor, please retain copyright information when reprinting. If there are any improper uses, please feel free to contact us for negotiation. Contact (WeChat): 936532881
▶ We welcome everyone to submit articles, submission email [email protected]


