TCM Tongue Diagnosis: Illustrated Guide to Four Types of Sublingual Vessels
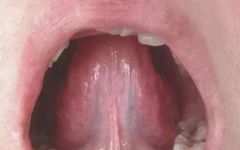
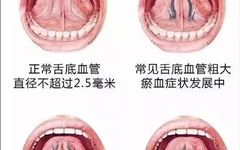
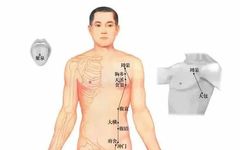
Subscribe to topics and read quality articles Click on Qihuang Ming Shi → Top right corner of the homepage → Set as a star ★ Sublingual Vessels The sublingual vessels are the longitudinal veins located on both sides of the lingual frenulum, primarily reflecting the state of Qi and blood circulation. Common abnormal manifestations of … Read more