Click the blue text for more exciting information
Blood Stasis Syndrome (Xue Yu Zheng) is a term in Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM). Although the term “blood stasis” or “stagnant blood” does not appear in the “Huangdi Neijing” (Inner Canon of Huangdi), related terms such as “evil blood”, “retained blood”, “hemorrhagic blood”, and “blood mass” are used to describe the condition characterized by the obstruction of stagnant blood, primarily manifested through symptoms such as pain, masses, bleeding, purple tongue, and a choppy pulse. Blood that has left the meridians and has not been expelled or dissipated in time, or blood flow that is obstructed and accumulates within the meridians or organs, losing its physiological function, is classified as blood stasis.
Blood Stasis Syndrome is not a disease name in itself; it is usually associated with other diseases. For example: many vascular diseases such as coronary heart disease or ischemic stroke are considered to fall under the category of “blood stasis syndrome” in TCM; dysmenorrhea of the blood stasis type, and qi stagnation with blood stasis type low back pain also belong to the category of “blood stasis syndrome”.

The characteristic of blood stasis syndrome is that after the formation of stagnant blood, the blood not only loses its normal nourishing function but also affects the circulation of qi and blood locally or throughout the body, leading to pain, bleeding, or visceral accumulation, resulting in adverse consequences such as “stagnant blood not being removed, new blood not being generated”.1. Symptoms of Blood Stasis SyndromeBlood stasis syndrome manifests as: pain like needle pricks, fixed, tender to touch, worsening at night. Surface masses are purple, and abdominal masses are hard and immovable. Bleeding is dark purple or mixed with clots, and stools are black and tarry. The complexion is dark, lips and nails are cyanotic, purple spots under the eyes, skin is rough, abdominal veins are prominent, and skin shows thread-like red lines. Women may experience amenorrhea or menorrhagia. The tongue is dark purple with purple spots, and the sublingual veins are engorged, or there are cyanotic streaks on the tongue edges, with a choppy pulse, or intermittent pulse, or no pulse.
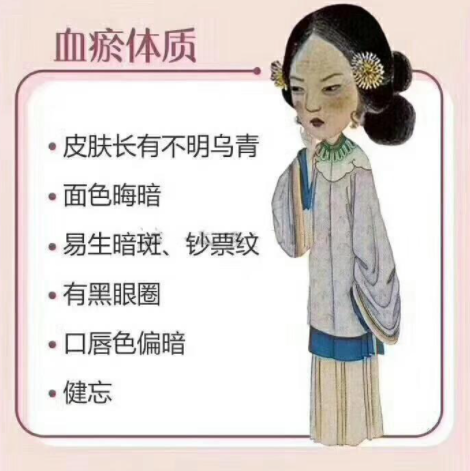
Stasis in the Heart— may present with palpitations, chest tightness, cyanosis of lips and nails;Stasis in the Lung— may present with chest pain, coughing blood;Stasis in the Gastrointestinal Tract— may present with vomiting blood, black stools;Stasis in the Liver— may present with painful masses;Stasis in the Uterus— may present with lower abdominal pain, dysmenorrhea, dark purple menstrual flow;Stasis in the Skin— may present with swollen, painful, and cyanotic skin.2. Is Blood Stasis the Same as Stagnant Blood?1. Blood stasis refers to: sluggish and stagnant blood flow; dead blood obstructing the blood vessels; blood vessels being blocked and not flowing; blood leaving the meridians and accumulating in four pathological states, which belong to the category of pathogenesis.2. Stagnant blood refers to: blood that has coagulated and is not flowing, which is a pathological product of blood stasis. Once stagnant blood forms, it will affect the normal circulation of blood and can lead to and exacerbate the pathological state of blood stasis.In fact, blood stasis and stagnant blood are both distinct and interconnected, with a causal relationship between the two.

3. How to Diagnose and Treat Blood Stasis Syndrome?In TCM diagnosis, it is essential to integrate the four diagnostic methods: observation, listening, inquiry, and palpation.1. Observation: observe the spirit, color, tongue quality, lips and cheeks, and eyes.2. Listening: stagnant blood causes qi and blood to be unblocked, leading to stabbing pain; if the pain is unbearable, there may be groaning sounds.3. Inquiry: ask about cold and heat, sweating, pain, chest and abdomen, thirst, menstruation and childbirth, trauma, and urination.4. Palpation: qi and blood flow, qi stagnation and blood stasis, if blood stasis occurs, the pulse is often deep and choppy.In terms of treatment, commonly used herbal formulas for invigorating blood and resolving stasis, in addition to herbal prescriptions, acupuncture, tui na (Chinese therapeutic massage), and cupping are often employed to improve blood viscosity and rheology, increase blood flow, correct blood circulation and microcirculation disorders, achieving the effect of “unblocking the blood vessels”.

4. The Dangers of Blood Stasis SyndromeTCM believes that stagnant blood obstructs the flow of qi and blood, and sluggish circulation can lead to insufficient blood supply to the heart, which over time can gradually develop into coronary heart disease, causing chest tightness and pain. If stagnant blood is not effectively treated for a long time, it can form masses locally, and if these masses form in the uterus, they can become uterine fibroids. Stagnant blood not only obstructs the flow of qi and blood but also affects the metabolism of qi and blood; if stagnant blood is not removed, new blood cannot be generated, leading to amenorrhea.Therefore, if blood stasis syndrome is not treated in a timely manner, it can have serious consequences, causing stabbing pain, bruising; leading to anxiety and forgetfulness; accelerating aging; and increasing the risk of coronary heart disease, cerebral infarction, uterine fibroids, amenorrhea, and other diseases.Beijing Dongsi Traditional Chinese Medicine HospitalHealth Begins with Traditional Chinese Medicine
▼

Consultation Phone: 010-84046477Hospital Address: No. 62, Dongsi Sixth Alley, Dongcheng District, Beijing