
Colds are a common ailment in daily life.
Over-the-counter cold medications are a staple in most households.
Often, taking medication can alleviate symptoms of a cold.
However, sometimes medication does not seem to work, or may even worsen the condition.
This raises the question of whether the “medication is inappropriate for the symptoms”.

It turns out that
there is a distinction between Wind-Cold and Wind-Heat colds.
Not all cold medications are suitable for every type.
Today, let’s explore
how to use medications for different types of colds.
Cold Medication Tips
It is not easy for non-professionals to distinguish between Wind-Heat and Wind-Cold colds. Misunderstanding the nature of the cold can lead to ineffective treatment, which is why some people feel better after taking medication while others do not.
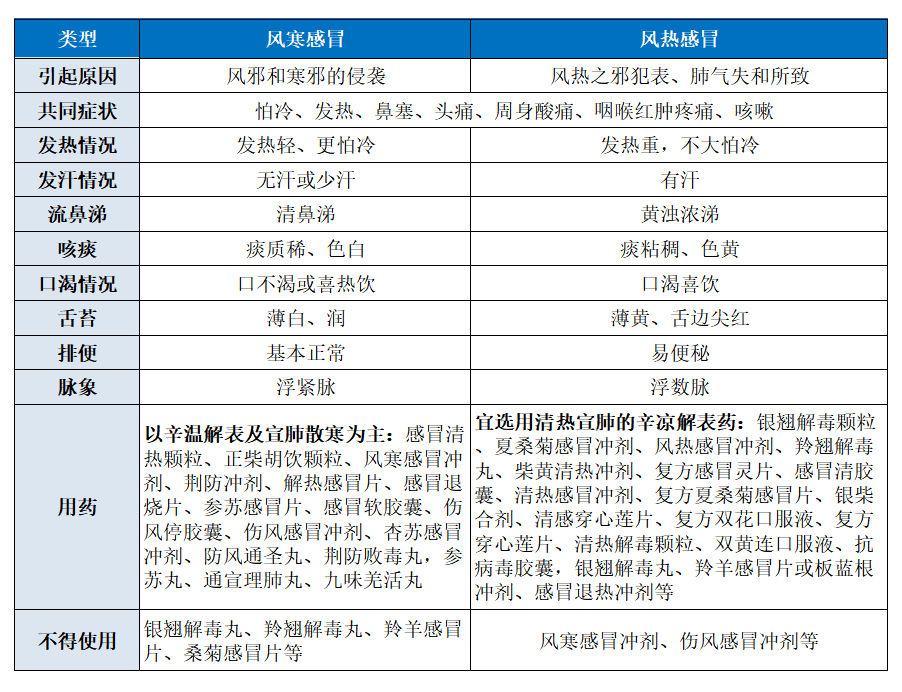
Generally, Wind-Cold colds are primarily caused by the invasion of Wind and Cold pathogens. Patients typically experience nasal congestion, sneezing, coughing, and headaches, along withchills, low fever, no or little sweating, headaches, body aches, clear nasal discharge, thin white phlegm, sweating, sore throat with redness and swelling, no thirst or preference for hot drinks, and a thin white tongue coating. The pulse is usually floating and tight, and patients often feel comfortable only when bundled in many layers or under heavy blankets.
The key to treating Wind-Cold colds is to induce sweating (known in TCM as “xīn wēn jiě biǎo”), with primary methods including sauna, soaking feet in hot water (preferably with some alcohol), covering with thick blankets, drinking ginger syrup, ginger and scallion water, or ginger porridge.

For medicinal treatment of Wind-Cold colds, the focus should be on warming and dispersing the exterior and dispersing cold from the lungs. Suitable medications include Ganmao Qingre Granules, Zheng Chaihu Decoction Granules, Wind-Cold Cold Powder, Jingfang Granules, Fever-Reducing Cold Tablets, Cold-Reducing Tablets, Shen Su Cold Tablets, Cold Soft Capsules, Cold Stopping Capsules, Wind-Cold Cold Powder, Xing Su Cold Powder, Fang Feng Tong Sheng Pills, Jing Fang Bai Du Pills, Shen Su Pills, Tong Xuan Li Lung Pills, and Jiu Wei Qiang Huo Pills. However, do not use Yin Qiao Jie Du Pills, Ling Qiao Jie Du Pills, Ling Yang Cold Tablets, or Sang Ju Cold Tablets, as they may worsen the condition or prolong recovery.
Wind-Heat colds are caused by the invasion of Wind-Heat pathogens and disharmony of lung qi. Symptoms includehigh fever, slight aversion to wind, headache, sweating, sore throat with redness and swelling, cough, sticky or yellow phlegm, nasal congestion, yellow nasal discharge, thirst with a preference for drinking, red tongue edges, thin white and slightly yellow tongue coating, and constipation.
Wind-Heat colds are more common in summer and autumn due to external Wind-Heat invasion. Symptoms of Wind-Heat colds include:
sore throat, which usually occurs before other cold symptoms, with phlegm typically being yellow or black.
Purulent nasal discharge, usually yellow.
Yellowish tongue coating, which may also be white, with a generally red tongue.
Constipation.
Fever, thirst, and irritability.
The pulse is usually floating and rapid, with a stronger and faster pulse than normal.

For treating Wind-Heat colds, it is advisable to select cooling and dispersing medications that clear heat and disperse the exterior. Suitable medications include Yin Qiao Jie Du Granules, Summer Sang Ju Cold Powder, Wind-Heat Cold Powder, Ling Qiao Jie Du Pills, Chai Huang Qing Re Powder, Compound Cold Ling Tablets, Cold Qing Capsules, Qing Re Cold Powder, Compound Summer Sang Ju Cold Tablets, Yin Chai Mixture, Qing Gan Chuan Xin Lian Tablets, Compound Shuang Hua Oral Liquid, Compound Chuan Xin Lian Tablets, Qing Re Jie Du Granules, Shuang Huang Lian Oral Liquid, Antiviral Capsules, Yin Qiao Jie Du Pills, Ling Yang Cold Tablets, or Ban Lan Gen Powder, Cold Fever-Reducing Powder, etc. However, do not use Wind-Cold Cold Powder or Wind-Cold Cold Powder, as this may worsen the condition.
In summary:
Common colds are self-limiting diseases, and most people can recover on their own within a few days even without medication.When using traditional Chinese medicine to treat colds, it is essential to follow TCM principles and apply the appropriate treatment based on individual, environmental, and temporal factors to ensure a speedy recovery.

References:
[1] A survey on the usage of traditional Chinese medicine for colds – A case study in Shijiazhuang, Hebei Province. Guangming Traditional Chinese Medicine 2022, 37(8): 1483-1486.
[2] Differentiation and treatment of Wind-Cold and Wind-Heat colds. Inner Mongolia Traditional Chinese Medicine. 2012, (46): 16.
[3] Attention to symptom-based medication selection for cold-related traditional Chinese medicine. Heilongjiang Medicine. 2013, (26): 292-294.
For more medication-related questions, please consult the pharmacy outpatient department.
Pharmacy Outpatient Department The pharmacy outpatient department currently consists of clinical pharmacists and senior pharmacists from various specialties, covering areas such as anti-infection, cardiovascular, digestive, endocrine, pediatrics, critical care, respiratory, oncology, and maternal and child health.Consultation Hours: Monday to Friday (excluding Thursday afternoons for business study): 8:00 AM – 12:00 PM, 3:00 PM – 6:00 PM.Location:29th window on the right side of the outpatient pharmacy on the first floor of the outpatient building.Consultation Method:You can make an online appointment or register on-site for consultation.Service Content:Pharmacists provide relevant pharmaceutical services, establish outpatient medication records for patients, issue “consultation opinion letters”, and conduct pharmaceutical follow-ups.For more medication-related questions,you can also scan the following QR code for consultation.
The pharmacy outpatient department currently consists of clinical pharmacists and senior pharmacists from various specialties, covering areas such as anti-infection, cardiovascular, digestive, endocrine, pediatrics, critical care, respiratory, oncology, and maternal and child health.Consultation Hours: Monday to Friday (excluding Thursday afternoons for business study): 8:00 AM – 12:00 PM, 3:00 PM – 6:00 PM.Location:29th window on the right side of the outpatient pharmacy on the first floor of the outpatient building.Consultation Method:You can make an online appointment or register on-site for consultation.Service Content:Pharmacists provide relevant pharmaceutical services, establish outpatient medication records for patients, issue “consultation opinion letters”, and conduct pharmaceutical follow-ups.For more medication-related questions,you can also scan the following QR code for consultation.

Content Source: Pharmacy Department, Shen Weipei, Zeng Zheng, Xiang Changyi, Huang Zhengguang, Jiang Xia
Editor: Lan Xinmin
Proofreader: Tan Lingyu
Reviewer: Lan Feiyan
Warm Reminder
Publicity Matrix of the First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi Medical University
WeChat Public Service Account, Subscription Account, Video Account, Douyin Account, Weibo Account, Toutiao Account:
Service Account: Guangxi Medical University First Affiliated Hospital Internet Hospital – appointments, intelligent guidance, online diagnosis, prescriptions, and test result inquiries.
Subscription Account: First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi Medical University – for more information about the hospital, department updates, and health education.
 Service Account
Service Account Subscription Account
Subscription Account Video Account
Video Account Douyin Account
Douyin Account Weibo Account
Weibo Account Toutiao Account
Toutiao Account

Click to Share

Click to Save

Click to Like

Click to View

