Qi Deficiency (气虚) is a term in Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) that refers to a series of pathological changes and syndromes caused by insufficient vital energy (元气). Qi is considered the most fundamental substance of the human body, formed by the essence (精气) from the kidneys, the energy (气) absorbed and transformed by the spleen and stomach from food, and the clear qi (清气) inhaled by the lungs.
Qi deficiency generally refers to symptoms such as physical weakness, pale complexion, shortness of breath, fatigue in the limbs, dizziness, sweating upon exertion, and a weak voice. It includes the deficiency of the original qi (元气), ancestral qi (宗气), and defensive qi (卫气), as well as a reduction in the functions of qi in promoting, warming, defending, consolidating, and transforming, leading to decreased or weakened bodily functions and a lowered resistance to disease.

Fundamentally, human life activities are movements of the rise and fall of vital energy. Qi deficiency is a common syndrome often caused by congenital insufficiency, malnutrition, aging, prolonged illness, major surgery, and excessive fatigue. Clinically, qi deficiency can also include syndromes such as lung qi deficiency, heart qi deficiency, spleen qi deficiency, and kidney qi deficiency.
The concept of qi deficiency is an important aspect of traditional Chinese medicine. Many foreign researchers have also expressed their views on this topic. Here are some excerpts from scholars for sharing.
The content includes the following points:
– Symptoms
– Causes
– Spleen
– Treatment
– Diagnosis
– Curing diseases
– Key points
Overview
You may not realize that you have qi deficiency, nor that your qi may be lacking. However, according to Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), balanced qi is crucial for your physical and mental health. If your qi and blood are imbalanced, it may be the reason you feel unwell.
Continue reading to learn how a deficiency of qi can affect your health and how to maintain the balance of qi.
What exactly is Qi?
According to TCM, qi is a life force that drives every activity of living organisms. It exists in everything, from physical objects like your phone to the non-material aspects of the world such as light, heat, and emotions.
There is no direct equivalent in Western medicine for the term “qi” in the human body, but it is similar to a person’s energy. Therefore, the deficiency of qi can loosely be translated as a lack of energy. However, it is much more than that.
Qi and the theory of yin and yang (the harmony of seemingly opposing forces) are two core components of TCM. It is believed that sufficient qi is needed to maintain the balance of yin and yang in the body. When a person’s qi is balanced and harmonious, they benefit from health, happiness, and satisfaction. When a person’s qi is deficient, they may experience pain, suffering, and disease.
What are the symptoms of Qi Deficiency?
Symptoms can vary widely, as each organ and process in the body has its own qi. Qi deficiency can occur anywhere in the body where there is insufficient energy to perform its functions.
Symptoms may affect the following areas:
Digestive System
In TCM, the digestive system is referred to as the “spleen” (脾), which functions differently from the organ of the same name in Western medicine. Symptoms of qi deficiency in this system include:
– Indigestion
– Physical weakness
– Abdominal bloating
– Loose stools
– Decreased or lack of appetite
– Anemia
Lungs
Symptoms of qi deficiency related to the lungs include:
– Asthma
– Weak voice or difficulty breathing
– Low immunity
– Spontaneous sweating
Heart
Symptoms of qi deficiency related to the heart include:
– Poor circulation
– Palpitations
– Lack of joy
Kidneys
Symptoms of kidney qi deficiency include:
– Decreased memory
– Hair loss
– Knee or back pain
Other Symptoms
Other symptoms may include:
– Anxiety
– Dry skin
– Brittle hair
– Muscle soreness
– Weakness
– Weight issues
– Mental fatigue
– Low mood
Qi deficiency is also considered a root cause of many common Western diseases, such as chronic fatigue syndrome, diabetes, indigestion, and dysmenorrhea.
What causes Qi Deficiency?
In TCM, various factors determine your qi and blood. It begins with your genetic makeup and is influenced by your diet, emotions, and habits after birth. It is constantly changing.
Various physical and emotional conditions are believed to weaken your qi. The most common causes are chronic stress and lack of sleep. Both conditions can elevate the stress hormone cortisol, disrupting immune function and increasing the risk of depression and fatigue. You may be able to naturally lower cortisol levels while using home remedies and TCM supplements.
Other causes may include:
– Food sensitivities
– Hormonal imbalances
– Environmental factors (especially polluted air)
– Unresolved emotional issues
– Relationship problems
What is the relationship between Qi and the Spleen?
Western and Eastern medicine have very different views on the role of the spleen in the body. In Western medicine, it is considered part of the immune system but is not deemed a vital organ, as people can live without it if necessary.
However, in Eastern medicine, the spleen is believed to play a fundamental role in the body, being central to digestion and the distribution of food, as it extracts qi from what we eat. Therefore, if you experience energy deficiency issues, it is often a primary suspect.
How is Qi Deficiency treated?
Treatment will depend on the type of qi deficiency, its duration, and its causes. Blood tests may also be conducted to rule out causes more suited to conventional medicine or to address them in conjunction with conventional medicine.
Treatment methods may include:
Nutrition Therapy
Much of a person’s qi comes from the food they choose and the air they breathe, so nutritional advice is often given to treat qi deficiency. This typically includes eliminating raw and cold foods, such as ice cream and fruits, which are believed to weaken digestive capacity.
Cooking food using heat methods such as steaming, baking, or roasting can enhance qi strength. It is also generally advised to remove junk food, fried foods, and dairy from the diet. Warm foods such as grains, pumpkin, and chicken, as well as spices like fennel, chili, and ginger, should be consumed regularly. Learn more about yin-yang nutrition.
Thoroughly chewing food is also recommended to help preserve the energy of the spleen.
Herbal Medicine
Many herbs used in TCM are known as adaptogens, which claim to help the body and mind adapt to stress. This helps restore normal immune system protection and communication. Some of the most commonly used herbs in this regard include:
– Aloe Vera (芦荟)
– Magnolia Bark (木兰树皮)
– Pine Bark (松树皮)
– Rhodiola (拉芙玛)
– Cordyceps (冬虫夏草)
– Rhodiola Rosea (红景天)
– Astragalus (黄芪)
Lifestyle Changes
Western culture tends to reward and glorify those who are always on the go and busy, while TCM advocates the opposite. It is often recommended to slow down one’s lifestyle, avoid multitasking, and not do too many things at once to achieve a balance of qi and blood.
For example, it is advised not to eat while watching TV or checking emails on your phone, but rather to focus solely on eating and enjoying the food.
How is Qi Deficiency diagnosed?
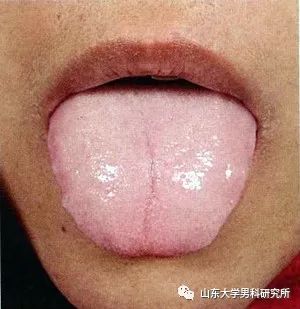
TCM practitioners typically conduct a detailed inquiry into the medical history and perform a physical examination to identify patterns of disharmony. TCM often pays special attention to the condition of the tongue, which is considered a powerful indicator of a person’s harmony or disharmony.
A pale tongue may indicate a deficiency of qi and blood. Once the patterns of disharmony and their sources are identified, the practitioner will develop a treatment plan.
Can addressing my Qi Deficiency cure my diseases?
It is difficult to determine the effectiveness of treatment, as research in this area is limited.
Many people have reportedly experienced improvements in their symptoms. Issues such as infertility and digestive problems have shown relief after treating qi deficiency.
Some studies suggest that balancing qi can inhibit the growth of cancer cells. Other studies indicate it can improve survival rates in cancer patients and alleviate symptoms such as pain, fatigue, and nausea.
However, it is important to discuss the research behind traditional medical treatments with your doctor. There is more evidence to draw from.
What should I do if I suspect I have Qi Deficiency?
If you have any symptoms related to qi deficiency, seeking TCM treatment may provide safe, natural, and effective relief in some cases. However, a prudent approach is to request blood tests to rule out any causes that may be best treated by Western medicine or in conjunction with it.
Ref: https://www.healthline.com/health/qi-deficiency
Stay tuned:
Liu Zhaoxu Urology and Andrology Science Popularization Studio
Shandong University Urology PhD Team
Shandong University Institute of Urology
Chinese Doctor Urology Website


