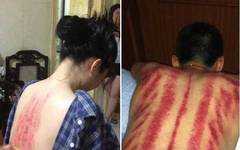
【Live Broadcast Announcement】↓↓↓
Gua Sha Symptoms — Color of Sha
Deep Red —Heat Syndrome
Bright Red —Yang Deficiency with Excess Heat
Black —Cold Syndrome
Purple —Dermatitis
Pale Blue, Purple Spots —Qi Deficiency with Blood Stasis
Blue-Purple —Severe Internal Cold
Purple-Black and Dark —Blood Stasis with Cold
Purple-Red —Wet Heat
Large Area Deep Purple —Heart Cold
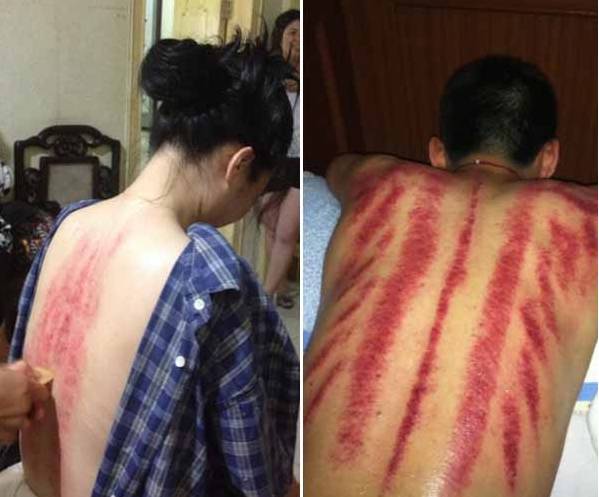
Depth of Sha into the Bone
Small Dots —Toxins Accumulated in the Epidermis
Medium Dots —Toxins Deeper into the Bone
Large Dots —Toxins Deep into the Bone Marrow

Observation Areas
1: Occipital Region
This area reflects issues in the head and neck. If there are abnormal shapes and tenderness, it may indicate headaches, cervical osteophytes, hypertension, or pharyngitis.
2: Spinal Region — Represents Sleep and Sleep Quality
3: Bilateral Shoulder and Back Region — Reflects Shoulder Issues
⑴ If there is tenderness in this area, it may indicate headaches, shoulder pain, stiff neck, and other symptoms;
⑵ If purple Sha appears, check for rheumatism;
⑶ If the muscles along the Large Intestine Meridian are too tight and have red spots, it may indicate shoulder periarthritis, with more severe Sha on the right shoulder indicating excessive desk work, while the left shoulder indicates overthinking.
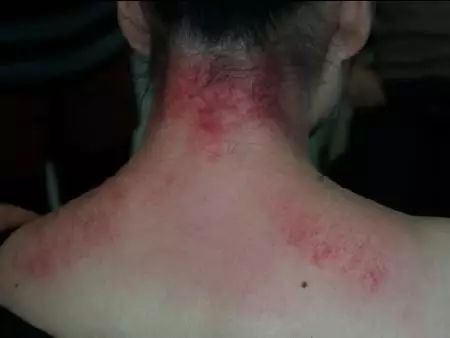
4: Heart and Lung Region (Thoracic Vertebrae 1-5, 6) — Reflects Respiratory Issues
⑴ If there is tenderness, stiffness, and red spots, it may indicate cold, chest tightness, or insufficient heart and lung function.
⑵ When there is dryness and heat in the heart and lungs: easy thirst at night, dry cough; forehead prone to acne, skin on the forehead dry; irritability; severe cases may lead to nosebleeds; tongue is pointed, red, with flushed cheeks, hot palms, red lips, and prone to spontaneous sweating (sweating even while sitting).
⑶ If heart and lung function is deficient, there may be forehead wrinkles, dry skin, pale lips, insufficient righteous qi, speaking softly despite effort, easy shortness of breath, prone to rhinitis, pale complexion, and night sweats.
5: Spleen and Stomach Region (8, 9-11, 12) — Reflects Digestive Issues
⑴ If there are abnormalities, purple-black color or tenderness and swelling, it may indicate diseases caused by poor liver function.
⑵ If the spleen is weak, the eye circles may appear purple-red, skin dull, pale complexion, loose skin, dry lips, peeling, bland taste, weight loss, and weakness.
⑶ If the spleen is damp, water retention may cause a yellowish complexion, bags under the eyes, dark acne, and a swollen upper body, with teeth marks on the tongue and pale tongue coating.
⑷ If the stomach is weak, dark circles may appear black, with poor digestion, thinness, dry and red tongue, and thirst; if the stomach is very poor, there may be no tongue coating.
6: Liver and Gallbladder Region (5, 6-8, 9)
If there are tender points, abnormal spots, stiffness, pain, swelling, and purple-black color, it may indicate indigestion, gastrointestinal bloating, acute or chronic gastroenteritis, and low back pain.
7: Lumbar and Kidney Region (12-L5) — Reflects Endocrine Issues
⑴ If there are tender points, stiffness, swelling, and purple-black color, it may indicate cystitis, kidney deficiency, kidney dysfunction, diabetes, edema, low back pain, frequent urination, and lumbar strain.
⑵ Excessive secretion of male hormones: acne around the mouth, coarse hair, oily skin, irritability, and heat in the internal organs.
⑶ Excessive secretion of female hormones: yellowish skin around the mouth, dry skin, yellowish complexion, lack of luster, prone to spots, irritability, and menopausal syndrome.
8: Sacral Region
If the skin color appears dark, with soreness and swelling, it may indicate sciatica, menstrual irregularities, and uterine inflammation.
9: Shoulder, Scapula, and Extremities Region
If there are abnormal shapes, tenderness, and swelling, it may indicate hand and foot diseases, knee pain, and limb swelling, and vascular sclerosis.
Fundamentals of TCM Nursing Practice and Learning Guidance, 6th Edition, Wang Jun, Chief Editor Quality Nursing Products23
Quality Nursing Products23
Observe the Shape
1: Flake —Superficial, issues only at the surface
2: Small Dots —Damp Heat or Cold Damp, representing long-term accumulation; if not eliminated, may lead to internal wind damp or arthritis
3: Medium Dots —Precursor to pathology
4: Large Dots —Response to pathology
5: Blisters —Wind Damp or Internal Wind Damp has formed
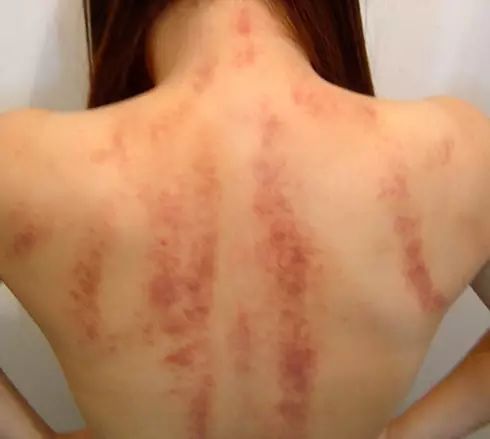
Identification of Sha Symptoms
Back Heart and Lung Region —Cold, chest tightness, chest pain, weak heart and lung function; eat more (almonds, honey, pears)
Liver and Gallbladder Region —Chronic fatigue, insufficient sleep, severe cases may lead to liver cirrhosis; eat more (red and green foods)
Spleen and Stomach Region —Indigestion, gastrointestinal bloating, excessive stomach acid, low back pain; eat more (yellow foods such as millet, soybeans, corn, pumpkin)
Kidney Water Region —Cystitis, strong taste, low back pain, prone to edema
Sacral Region —Menstrual irregularities, weak uterine function, dysmenorrhea, gynecological diseases, sciatica
Bilateral Shoulder Region —Chronic shoulder pain, headaches, stiff neck, limb pain, severe cases may lead to vision impairment
Shoulder, Scapula, and Extremities Region —Numbness in hands and feet, knee pain, poor ovarian function, limb swelling
Bright red dots indicate a mild condition at the surface.
Blue-purple, dark red spots indicate a long-term, severe condition with toxins in the skin and bone marrow.
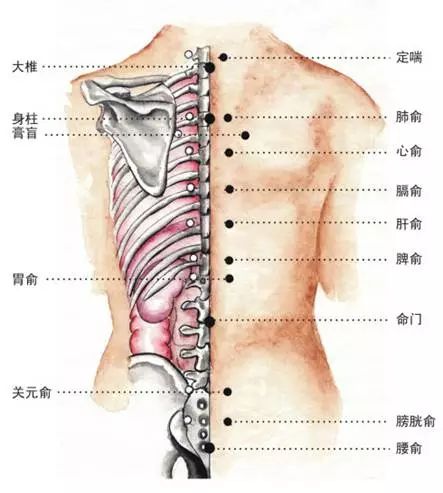
Lie Down and Observe the Dazhui (Great Vertebra) —If it is large and particularly protruding, it indicates severe deformity.
Feel Body Temperature —If cool, it indicates heavy internal cold; if warm, it is acceptable.
Press on the Cervical Vertebrae and Shoulder Neck —If pressing is painful or sore, it indicates shoulder periarthritis; if pushing the shoulder neck is blocked, it indicates meridian obstruction.
Press Jianjing (GB21), Tianzong (SI11), and the Shoulder Blade Gap —After pressing, if there is soreness, numbness, swelling, pain, or weakness, it indicates shoulder issues.
Push the Bladder Meridian — Divided into Three Sections.For the lung, stomach, and gynecological areas. If the lung area turns deep red, it indicates internal heat. If the stomach area is dark or red, it indicates stomach cold or heat. If there are Sha particles in the gynecological area, it indicates gynecological issues such as uterine cold, pain, and low back pain.
Press Lumbar Acupoints — If sore, swollen, or painful.It indicates lumbar muscle strain; if the lumbar area feels cool after rubbing, it indicates heavy internal cold, suggesting uterine cold.
Overall Back Push —If the back feels very cool and the shoulder blade area is very sore, it indicates excessive internal cold and toxin accumulation. It is recommended to use Gua Sha or cupping to treat the pain; if untreated, it will increase internal cold and toxins will not be expelled smoothly.
This may lead to cervical spondylosis (dizziness, brain hypoxia, limb numbness, overall weakness, and ultimately decreased immunity, leading to inability to work normally. If combined with treatment, the body can accelerate blood circulation through massage, expelling toxins through the lymphatic system, improving cervical spondylosis and shoulder periarthritis, effectively alleviating pain and enhancing immunity).
Gua Sha “Scraping the Shoulder and Neck” — If the Sha particles are coarse, numerous, and black-red, with blisters, it indicates heavy toxins, slow blood circulation, and reduced lymphatic detoxification. If the shoulder blade area is black-red or has blisters, it indicates shoulder periarthritis, which should be treated immediately; otherwise, severe cases may lead to numbness in the arms, loss of sensation, and impaired mobility, affecting work.
Scraping the Bladder Meridian, if the lung area is black-red or has blisters, it indicates throat inflammation and significant internal inflammation; it is recommended to drink warm water, otherwise, it may lead to tonsillitis or gynecological issues. If the stomach area is black-red or has blisters, it indicates stomach cold or excessive stomach heat.
After scraping the spine, it can be immediately observed whether the spine has deformed. If the spine is deformed, immediate treatment is necessary.
Gua Sha Techniques
Direct Scraping Method
First, use a hot towel to wipe the area to be scraped, then apply the corresponding Gua Sha medium to that area, and use the Gua Sha tool to directly touch the patient’s skin, scraping repeatedly until Sha marks appear on the surface of the skin.
Indirect Scraping Method
Place a thin cloth on the area to be scraped, then use the Gua Sha tool to scrape directly on the cloth. This method is very effective in protecting the skin and is mainly used for children and the elderly.
Pinching Method
According to the technique, it can be divided into pinching, pulling, squeezing, tapping, and pressing methods;
Pinching Method
Also known as the pulling method, commonly referred to as “pinching lumps” in folk practice, involves applying Gua Sha medium to the area to be scraped. The practitioner bends the fingers, using the middle and index fingers to hook the skin, then pinches the skin and muscle, sliding outward with force and then releasing.
Pinch and release repeatedly, making a “popping” sound, and can be performed continuously 6-7 times on the same area. The pinched area will show Sha marks, causing local bruising and blood spots as a method of removing Sha.
This method does not require any tools, only the fingers.
The pinching method is flexible and can be applied to various conditions; for headaches, fever, and fatigue, one can perform it on oneself, making it a very practical self-therapy.
Pulling Method
On a specific area or acupoint of the patient, use the thumb and index finger to pull the skin forcefully, causing purple-red or dark red Sha spots to appear, achieving therapeutic effects, known as the pulling method.
The pulling method has been passed down in folk practice for a long time. Whenever feeling damp heat causing Sha symptoms or discomfort, it is common to repeatedly pinch and pull the patient’s skin until local bruising occurs.
During pulling, the patient can sit or lie down, fully exposing the skin. The practitioner uses the thumb and index finger to wet with cold water, pulling up a portion of the skin and subcutaneous tissue, then pulling and twisting to one side, and then quickly releasing.
One can also use the thumb, index, and middle fingers to pinch and pull the skin, continuously twisting in a certain direction, repeating several times until the pulled skin becomes red and hot. If the condition is severe, the pulling force can be increased until red spots appear.
The pulling method exerts a strong pulling force on the skin, often causing local and systemic reactions; the pulled area may feel pain, but afterward, the whole body feels relaxed and comfortable.
Pressing and Rubbing Method
Use the flat edge of the scraping board to perform large area scraping on the patient’s body.
Use fingers to press on a specific area or acupoint of the patient while making circular or spiral movements, combining pressing and rubbing techniques.
This method does not belong to Gua Sha techniques but is a massage technique, often used in conjunction with Gua Sha in treatment and health care, enhancing efficacy and compensating for the shortcomings of Gua Sha.
In Gua Sha treatment, it is mainly used for the head, face, abdomen, joints, and extremities.
Needling Method
Use a needle to prick the surface of the patient to treat diseases. However, this Gua Sha method should not be attempted at home; it must be performed by professionals to avoid harming oneself.
Before needling, prepare 75% alcohol, disinfecting cotton swabs, and a sterilized three-edged needle or a sewing needle, or a 916 injection needle.
The practitioner first disinfects the local skin with a cotton swab, then pinches the skin at the pricking site with the left hand, and with the right hand, quickly pierces and pulls outward, pricking each area three times, while using both hands to expel purple-dark blood, repeating 5-6 times, and finally cleaning with a disinfecting cotton ball.
Bloodletting Method
This method is suitable for superficial veins in the elbow pit, popliteal fossa, and temples (this method is difficult and should be performed by professionals).
Also known as the pricking method, it involves pricking veins or acupoints to draw blood for treatment, called bloodletting therapy.
During treatment, the patient should be in a comfortable position, fully exposing the treatment area. If bloodletting from a vein, the patient’s left arm should be tied near the heart with a cloth or tourniquet, and the patient should clench their fist. Then, disinfect the skin with iodine cotton balls, followed by 75% alcohol.
Then, needle to draw blood. When bleeding from acupoints, depending on the condition, after disinfecting the skin, use a three-edged needle or sewing needle to prick directly.
Bloodletting can be divided into blood-letting and pricking methods. It is similar to the needling method but with stronger stimulation, often used in severe emergency cases.
This method is mainly applied to the head, neck, back, and temples. It is simple, easy to master, and effective.
Source: Health and Longevity Pavilion
Recommended Reading
Library:Exclusive Quality Library for Nurses
Video Channel: Nursing Tips and Expert Live Broadcasts
Buy Books:Nursing Books, click “Read Original” below
Follow: WeChat public account categorized by nursing departments