Traditional Chinese Medicine
Click the blue text above to follow us

Dampness is a common physical condition we often discuss. When symptoms such as dizziness, heaviness in the limbs, loss of appetite, and a thick, greasy tongue coating appear, we usually conclude that the individual has excessive dampness in the body and begin recommending various damp-dispelling products.
However, did you know that in Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), dampness is categorized into two types: Damp-Heat and Damp-Cold? The causes and symptoms of these two conditions differ significantly. Therefore, it is essential to distinguish between them during the damp-dispelling process to achieve effective results. So, what are the differences between Damp-Heat and Damp-Cold, and how can we differentiate them?

Differences Between Damp-Heat and Damp-Cold

Damp-Heat refers to the simultaneous presence of dampness and heat, which can occur due to hot and humid weather in summer and autumn, or from prolonged dampness transforming into heat, or from a “Yang-Heat constitution” causing dampness to transform into heat. Therefore, the coexistence of dampness and heat is quite common.
Damp-Cold, according to TCM theory, suggests that the human body is a balanced organic whole, and weakness fundamentally arises from an imbalance of Yin and Yang. The cold constitution is characterized by an excess of Yin energy within the body, leading to a disturbance in the balance of Yin and Yang. Specific manifestations include: organ prolapse, weakened digestive and absorption functions, resulting in reduced heat absorption by the body, which presents as a cold nature.
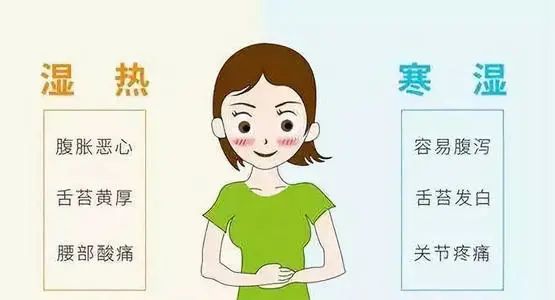
Three Ways to Distinguish Between Damp-Heat and Damp-Cold

1. Check Urine Condition
Individuals with a Damp-Heat constitution tend to have yellow urine with a strong odor, which is a symptom caused by damp-heat issues; whereas those with a Damp-Cold constitution have urine that is clear and resembles natural water.
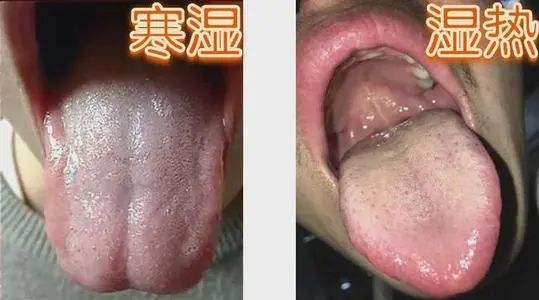
2. Observe Tongue Coating
People with a Damp-Heat constitution typically have a yellow, thick tongue coating and a noticeably red tongue; while those with a Damp-Cold constitution have a white tongue coating with tooth marks.
3. Assess Physical Sensation
Individuals with a Damp-Heat constitution often feel very stuffy and may frequently experience oral ulcers and acne due to damp-heat; whereas those with a Damp-Cold constitution tend to be more sensitive to cold, often experiencing cold hands and feet even in the heat of summer.
Additionally, dampness does not act alone; it can transform into Damp-Heat when exposed to heat and into Damp-Cold when exposed to cold… Over time, this can have adverse effects on the body.
Differences Between Damp-Heat and Damp-Cold:
① Mouth
Damp-Heat: Red tongue body, thick greasy yellow coating, dry mouth with a bitter taste.
Damp-Cold: Pale tongue body, white coating.
② Constitution
Damp-Heat: Heat-sensitive, palms and soles easily sweat and feel hot.
Damp-Cold: Cold-sensitive, hands and feet are often cold year-round.
③ Complexion
Damp-Heat: Oily complexion, prone to acne and pimples, red face and ears.
Damp-Cold: Pale or bluish complexion, lacking color.
Methods to Eliminate Dampness

Whether you have a Damp-Heat or Damp-Cold constitution, you can try the following methods to eliminate dampness, which are very effective!
Method 1: Get More Sunlight
Getting more sunlight not only warms the body but also helps dispel dampness within. Absorbing ultraviolet rays and replenishing sufficient Yang energy can naturally combat excessive dampness in the body.
Method 2: Massage Acupoints
1. Yin Ling Quan (Yin Mound Spring) Point
Location: Located on the inner side of the lower leg, in the depression below the tibia.
Function: Strengthens the spleen and benefits the stomach, enhancing the spleen’s ability to transform and transport dampness, promoting diuresis and reducing edema.
2. Di Ji (Earth’s Foundation) Point
Location: Located on the inner side of the lower leg, at the posterior edge of the tibia.
Function: Effectively dispels dampness from the body and is also good for regulating Qi and blood.
3. Ji Quan (Extreme Spring) Point
Location: Located at the center of the armpit.
Function: Effectively opens the meridians of the heart, thus helping to dispel dampness and detoxify.
Method 3: Exercise More
Regular exercise and sweating can help eliminate accumulated waste and toxins from the body. Aim for at least 30 minutes of exercise daily, whether it’s jogging, brisk walking, cycling, or yoga; as long as you sweat appropriately, the body’s dampness can be expelled.
If you have health concerns, feel free to add us on WeChat for consultation. Please leave a message indicating your age, symptoms, and thoughts after adding.

© Zheyan Looks at TCM

Long press the QR code below to follow us


Discussing Medicine and Philosophy, Inheriting the Wisdom of Qi Huang
Exploring the Depths, Seeking Hidden Truths

Reprint with source indicated
Some content sourced from the internet, copyright belongs to the original author

WeChat|xiayu99



Like this article
If interested, please click the bottom right corner, there is youto see

