
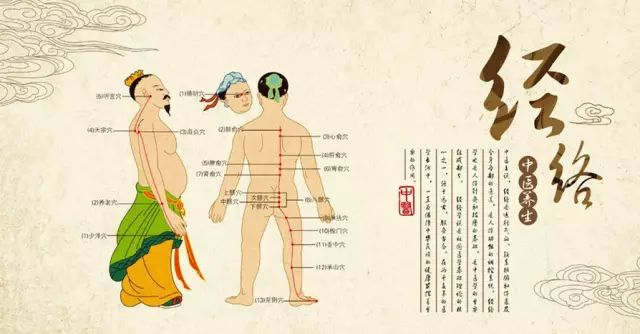
The Eight Extraordinary Meridians (Qi Jing Ba Mai) are a category of the body’s meridian pathways. They consist of the Du Mai (Governing Vessel), Ren Mai (Conception Vessel), Chong Mai (Penetrating Vessel), Dai Mai (Belt Vessel), Yang Wei Mai (Yang Linking Vessel), Yin Wei Mai (Yin Linking Vessel), Yin Qiao Mai (Yin Heel Vessel), and Yang Qiao Mai (Yang Heel Vessel). Unlike the twelve primary meridians, they do not directly correspond to the organs and do not have a paired relationship, hence they are referred to as “extraordinary meridians.” What are the Eight Extraordinary Meridians?

1Extraordinary Meridians
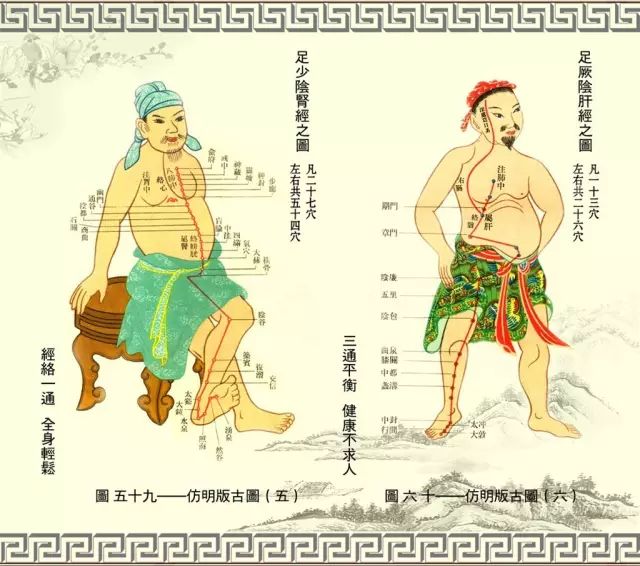
The Eight Extraordinary Meridians include the Ren Mai, Du Mai, Chong Mai, Dai Mai, Yin Qiao Mai, Yang Qiao Mai, Yin Wei Mai, and Yang Wei Mai. They differ from the twelve primary meridians as they do not directly correspond to the organs and do not have a paired relationship; their pathways are unique, hence they are called extraordinary meridians.
Functions:
1. Facilitate communication between the twelve meridians;
2. Regulate the accumulation and distribution of Qi and blood in the twelve meridians.
2Eight Meridians
1、Ren Mai: Runs along the midline of the abdomen, frequently intersecting with the three Yin meridians of the hands and feet as well as the Yin Wei Mai, thus governing all Yin meridians in the body, hence referred to as the “Sea of Yin Meridians.” The Ren Mai originates from the uterus and is related to women’s pregnancy, hence the saying “Ren governs the uterus and fetus.”
2、Du Mai: Runs along the midline of the back, frequently intersecting with the three Yang meridians of the hands and feet as well as the Yang Wei Mai, thus governing all Yang meridians in the body, hence referred to as the “Sea of Yang Meridians.” The Du Mai runs along the spine, ascends into the brain, and branches out from the spine to connect with the kidneys, having a close relationship with the brain, spinal cord, and kidneys.
3、Chong Mai: Ascends to the head and descends to the feet, traversing the entire body; it serves as a crucial junction for Qi and blood, regulating the Qi and blood of the twelve meridians, hence referred to as the “Sea of the Twelve Meridians” and also known as the “Sea of Blood.” It is related to women’s menstruation.
4、Dai Mai: Originates from the lateral costal region, descends obliquely to the Dai Mai point, encircling the body like a belt, thus restraining the meridians that run vertically.
5、6、Yin Qiao Mai, Yang Qiao Mai: “Qiao” implies agility and quickness. They nourish the eyes, control the opening and closing of the eyelids, and facilitate movement of the lower limbs.
7、8、Yin Wei Mai, Yang Wei Mai: “Wei” implies connection. The function of the Yin Wei Mai is to “connect all Yin meridians”; the function of the Yang Wei Mai is to “connect all Yang meridians.”
Physiological Functions of the Eight Extraordinary Meridians
1. Further strengthen the connections between the twelve meridians: For example, the Du Mai governs all Yang meridians; the Ren Mai connects all Yin meridians; the Dai Mai restrains the vertical meridians. The Yin and Yang Qiao Mai govern the left and right sides of the body; the Yin and Yang Wei Mai connect the exterior and interior Yin and Yang. Thus, the Eight Extraordinary Meridians further enhance the connections among various parts of the body.
2. Regulate the Qi and blood of the twelve meridians: When the Qi of the twelve meridians is abundant, it is stored in the Eight Extraordinary Meridians; when the Qi and blood of the twelve meridians are insufficient, the Eight Extraordinary Meridians can “overflow” to provide timely supplementation.
3. The Eight Extraordinary Meridians have a close relationship with the liver, kidneys, and other organs, as well as with the uterus in women, the brain, and the marrow, having certain connections in both physiological and pathological contexts.
Pathways and Physiological Functions of the Eight Extraordinary Meridians
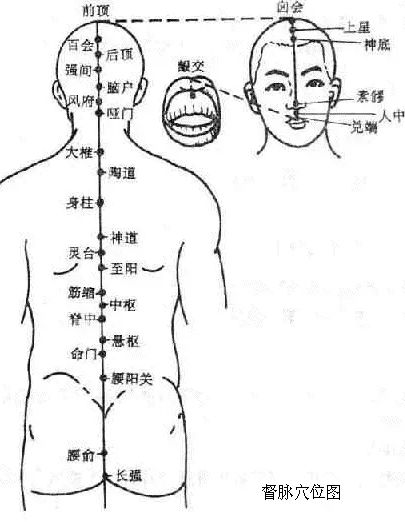
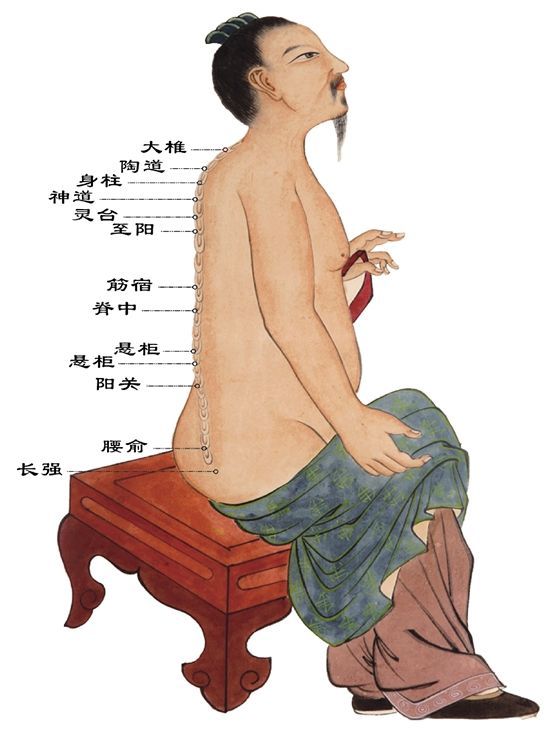
1Pathway and Physiological Functions of the Du Mai
1. Pathway: The Du Mai originates from the lower abdomen, exits at the perineum, travels to the tailbone at the Changqiang point, ascends along the spine, passes through the nape to the Fengfu point, enters the brain, belongs to the brain, runs along the midline of the head, ascends to the Baihui point at the top of the head, descends through the forehead to the Suliao point at the tip of the nose, passes through the philtrum, and reaches the Gingjiao point at the center of the upper gums.
2. Branches: The first branch, along with the Chong and Ren meridians, originates from the uterus, exits at the perineum, and at the tailbone, it connects with the Kidney meridian and the Bladder meridian. The second branch ascends directly from the lower abdomen through the navel, travels upward to the heart, reaches the throat, and connects with the Chong and Ren meridians, then encircles the lips and reaches the center below the eyes. The third branch, originating from the inner canthus of the eye, ascends to the forehead, converges at the top of the head, connects with the brain, then branches down the back of the neck, along the inner scapula, beside the spine, reaching the waist, and enters the muscles on both sides of the spine, connecting with the kidneys.
3. Physiological Functions
(1) Regulates the Qi and blood of the Yang meridians, serving as the “Sea of Yang Meridians”: The Du Mai runs along the back, which is Yang, indicating its role in commanding and supervising the Qi of all Yang meridians. Additionally, all six Yang meridians intersect with the Du Mai at the Dazhui point, demonstrating its regulatory function over the Yang meridians, hence the saying “governs all Yang meridians in the body.”
(2) Reflects the functions of the brain, kidneys, and spinal cord: The Du Mai belongs to the brain and connects with the kidneys. The kidneys produce marrow, and the brain is considered the sea of marrow. The relationship between the Du Mai, brain, kidneys, and spinal cord is very close.
(3) Governs reproductive functions: The Du Mai connects with the kidneys, which are associated with reproductive functions, hence its relevance to reproductive health.
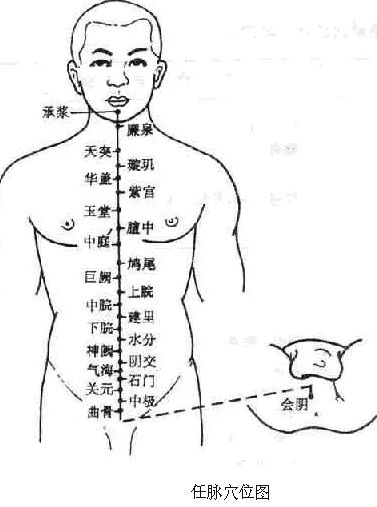
2Pathway and Physiological Functions of the Ren Mai
1. Pathway: The Ren Mai originates from the uterus, exits at the perineum, travels through the Yin Palace, ascends along the midline of the abdomen, passes through the throat (Tiantu point), reaches the inner lower lip, divides to encircle the lips, intersects with the Du Mai at the Gingjiao point, and then ascends through the nostrils to the lower eye socket (Chengqi point), connecting with the Yangming meridian of the foot.
2. Branches: It traverses from the uterus along the spine, ascending along the back.
3. Physiological Functions
(1) Regulates the Qi and blood of the Yin meridians, serving as the “Sea of Yin Meridians”: The Ren Mai runs along the midline of the abdomen, which is Yin, indicating its role in overseeing and governing the Qi of all Yin meridians. Additionally, the three Yin meridians of the foot intersect with the Ren Mai in the lower abdomen, and the three Yin meridians of the hand connect with the Ren Mai through the three Yin meridians of the foot, thus the Ren Mai regulates the Qi and blood of the Yin meridians, hence the saying “governs all Yin meridians.”
(2) Regulates menstruation and supports fetal development: The Ren Mai originates from the uterus, playing a role in regulating menstruation and promoting women’s reproductive functions, hence the saying “Ren governs the uterus and fetus.”
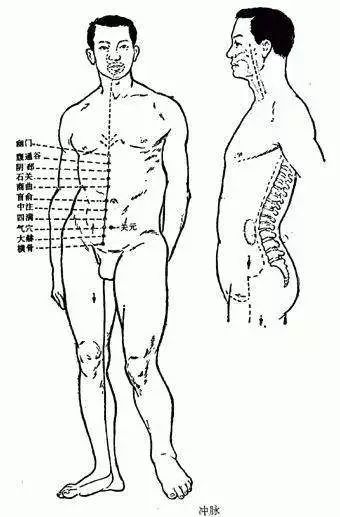
3Pathway and Physiological Functions of the Chong Mai
1. Pathway: The Chong Mai originates from the uterus, exits at the perineum, and divides into two branches. The ascending branch (the main trunk of the Chong Mai) runs along the anterior abdominal wall, five cun beside the navel, ascends, connects with the Kidney meridian, spreads in the chest, then ascends through the throat, encircling the lips; the descending branch runs along the posterior abdominal wall, ascending within the spine. The descending branch exits from the perineum, descends along the inner thigh to the space between the big toe.
2. Physiological Functions
(1) Regulates the Qi and blood of the twelve meridians: The Chong Mai ascends to the head and descends to the feet, traversing the entire body, serving as a crucial junction for the Qi and blood of all meridians. When the Qi and blood of the meridians and organs are abundant, the Chong Mai can store and accumulate them; when they are insufficient, the Chong Mai can provide infusion and supplementation to maintain the normal physiological activities of the body’s tissues and organs. Hence, it is referred to as the “Sea of the Twelve Meridians,” “Sea of the Five Zang and Six Fu,” and “Sea of Blood.”
(2) Governs reproductive functions: The Chong Mai originates from the uterus, also known as the “Blood Chamber” or “Sea of Blood.” It plays a role in regulating menstruation. The Chong Mai is closely related to reproductive functions; for women, “when the Chong Mai is abundant, menstruation occurs regularly, leading to conception.” Conversely, if the Chong Mai is deficient, it can lead to reproductive dysfunction.
(3) Regulates the ascending and descending of Qi: The Chong Mai connects with the Kidney meridian, belongs to the Yangming, and communicates with the Jueyin and Taiyang. The Chong Mai has the function of regulating the ascending and descending of Qi in certain organs (mainly the liver, kidneys, and stomach).
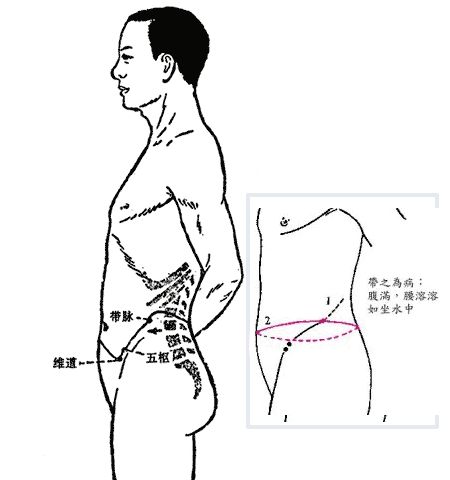
4Pathway and Physiological Functions of the Dai Mai
1. Pathway: The Dai Mai originates from the lateral costal region, descends obliquely, intersects with the Dai Mai point of the Gallbladder meridian of the foot, encircles the body, and at the Dai Mai point, it further descends obliquely along the upper edge of the hip bone to the lower abdomen.
2. Physiological Functions: It restrains the vertical meridians and governs women’s leukorrhea.
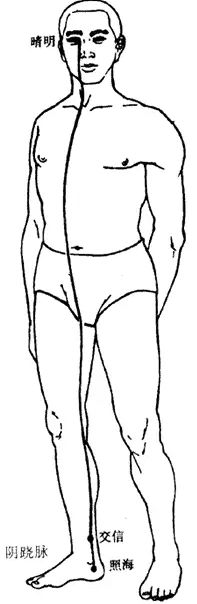
5Pathway and Physiological Functions of the Yin Qiao Mai
1. Pathway: The Yin Qiao Mai originates from the inner side of the heel of the foot, at the Zhaohai point of the Kidney meridian, ascends through the inner ankle, along the inner thigh to the anterior genital area, ascends along the anterior trunk to the chest, enters the Jueyin, ascends beside the Adam’s apple to the Renying point of the Yangming meridian, reaches beside the nose, and connects with the inner canthus of the eye, ascending with the Taiyang and Yang Qiao Mai.
2. Physiological Functions: It controls the opening and closing of the eyes and the movement of the muscles.
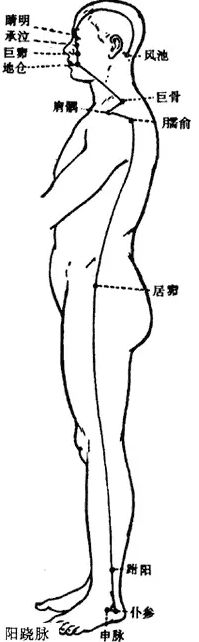
6Pathway and Physiological Functions of the Yang Qiao Mai
1. Pathway: The Yang Qiao Mai originates from the outer side of the heel of the foot, at the Shenshu point of the Bladder meridian, ascends along the outer ankle, travels upward along the outer edge of the lower limb to the abdomen. It runs along the posterior outer side of the chest, through the shoulder, neck, and forward to the forehead, distributing to the side of the head and the back of the neck, connecting with the Du Mai.
2. Physiological Functions: It controls the opening and closing of the eyes and muscle movement.
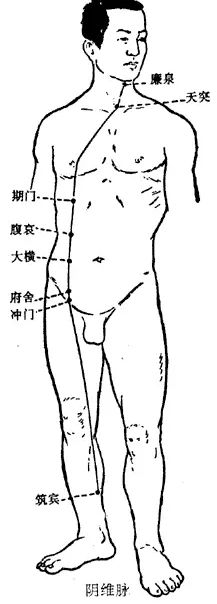
7Pathway and Physiological Functions of the Yin Wei Mai
1. Pathway: The Yin Wei Mai originates from the five cun above the inner ankle of the foot at the Zhubin point of the Kidney meridian, ascends along the inner side of the lower limb, reaches the abdomen, travels alongside the Spleen meridian of the foot to the lateral costal region, connects with the Liver meridian of the foot, ascends to intersect with the Tian Tu point of the Ren Mai, and terminates at the Lian Quan point in the throat.
2. Physiological Functions: The “Wei” in Wei Mai implies connection and binding. The Yin Wei Mai serves to connect the Yin meridians.
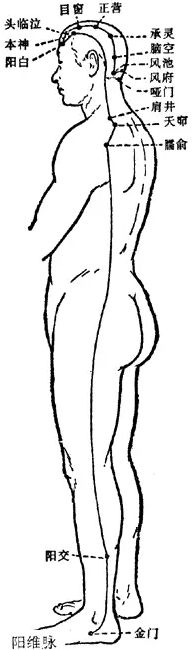
8Pathway and Physiological Functions of the Yang Wei Mai
1. Pathway: The Yang Wei Mai originates from the Jinmen point of the Bladder meridian, passes over the outer ankle, ascends alongside the Shaoyang meridian, travels upward along the outer edge of the lower limb, through the posterior outer side of the trunk, from the back of the armpit to the shoulder, through the neck, forward to the forehead, distributing to the side of the head and the back of the neck, connecting with the Du Mai.
2. Physiological Functions: It connects the Yang meridians.
Recommended Articles
1. This chart is an essential tool for learning TCM meridians; do not keep it private, share it with friends!
2. Finding acupoints is simple with this chart!

