Liver Qi stagnation, abbreviated as liver depression (肝郁, gān yù), occurs when the liver’s function of regulating Qi is disrupted. This can happen due to emotional distress, anger harming the liver, or other factors affecting the upward movement and dispersal of Qi, leading to liver stagnation. Particularly, individuals who are often irritable may accumulate turbid Qi in their bodies, which, if not expelled in a timely manner, will inevitably result in liver Qi stagnation. Liver stagnation is the source of many ailments and should not be taken lightly.

Liver Qi stagnation is one of the most common conditions among women. This is often caused by accumulated anger over time, leading to common issues such as irregular menstruation, breast tenderness, chest tightness, and pain in the ribs on both sides, all due to significant harm to the liver and the accumulation of turbid Qi in the body.
Causes of Liver Qi Stagnation
Several factors can lead to liver Qi stagnation:Family Disharmony: Frequent arguments between spouses or tense relationships with in-laws can lead to discomfort in liver Qi.Social Pressure: For instance, older unmarried women often face pressure from parents, relatives, and colleagues regarding marriage, compounded by societal criticism of their situation, leading to significant stress and discomfort in liver Qi. Work Pressure: In modern workplaces, there is no gender preference, and women face unprecedented pressure, especially white-collar workers who are torn between family and career, leading to widespread liver Qi stagnation.Poor Self-Regulation: Many women struggle to cope with issues, often fixating on the negative aspects of life and work, failing to self-soothe, which typically results in liver Qi stagnation.
Work Pressure: In modern workplaces, there is no gender preference, and women face unprecedented pressure, especially white-collar workers who are torn between family and career, leading to widespread liver Qi stagnation.Poor Self-Regulation: Many women struggle to cope with issues, often fixating on the negative aspects of life and work, failing to self-soothe, which typically results in liver Qi stagnation.
Characteristics of Liver Qi Stagnation
One aspect is Qi stagnation, where Qi is trapped within the body, leading to feelings of depression and oppression, commonly described as feeling “stifled” or “angry inside.” Prolonged liver Qi stagnation can generate heat, resulting in excessive liver fire, irritability, and a short temper. Some individuals may sigh frequently and feel unhappy, risking serious health issues; others may become impulsive, lashing out at minor inconveniences, causing distress to themselves and others.Many women report being aware of their poor health and wanting to take blood-nourishing supplements, but they experience mouth ulcers or insomnia after taking them. Some believe this is due to “deficiency not accepting nourishment,” but these issues are often caused by liver fire; if liver fire is obstructing, how can nourishment be absorbed?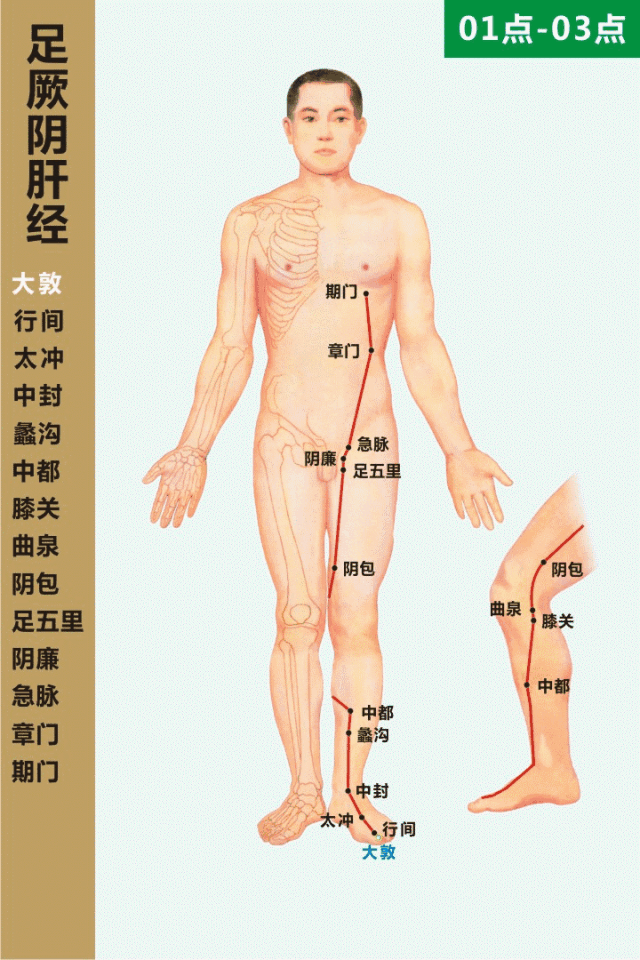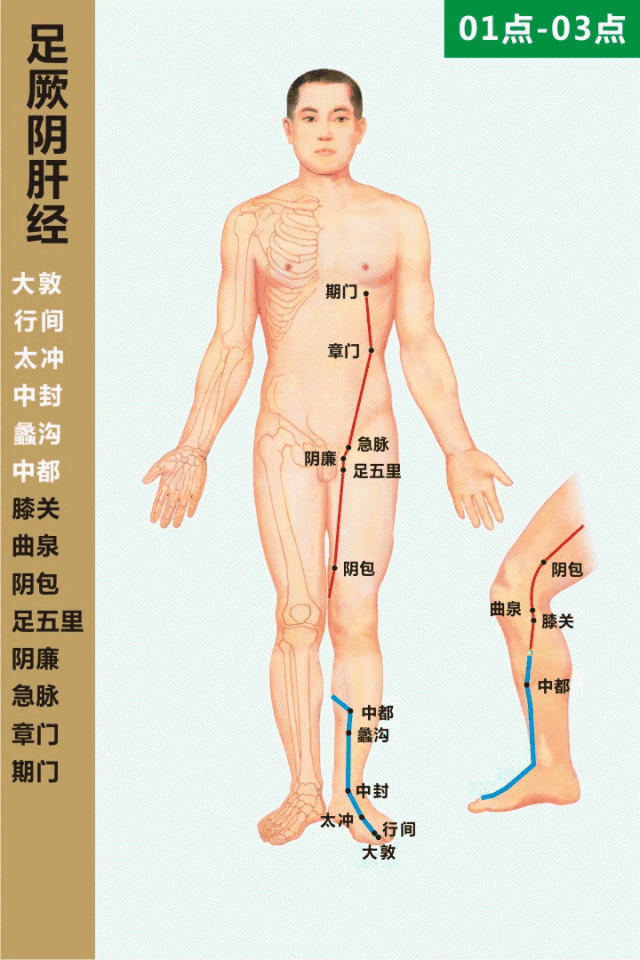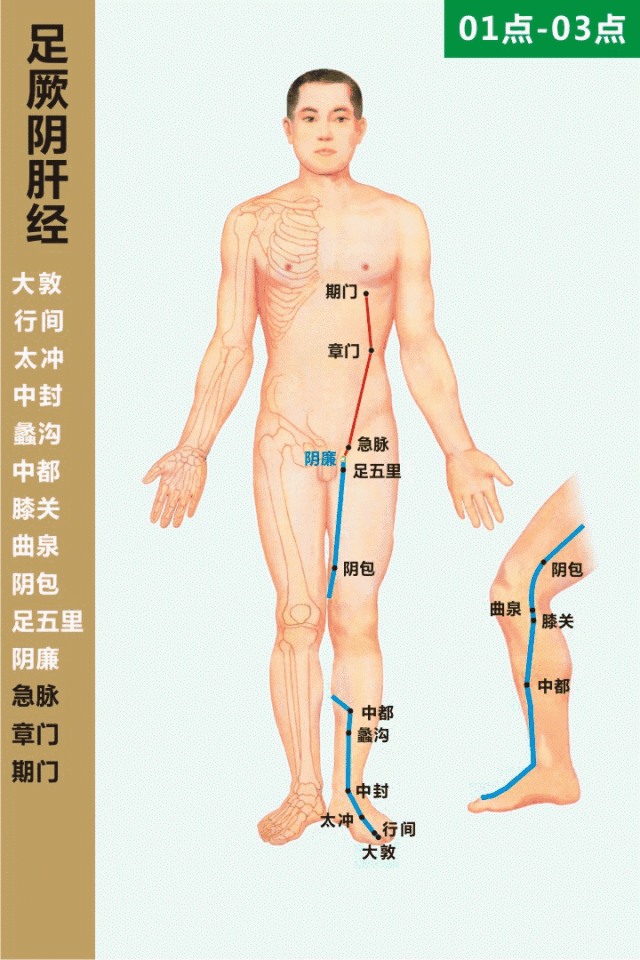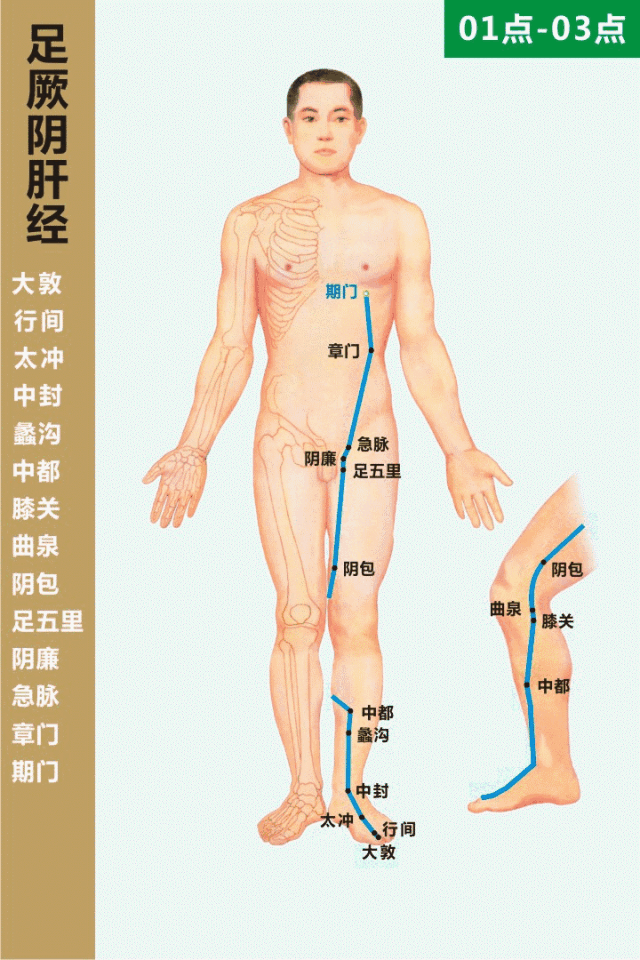 The consequences of liver Qi stagnation are severe and beyond imagination; it can lead to blood stasis, weak temper, dampness accumulation, and even yin deficiency with yang excess. In summary, the “crimes” of liver Qi stagnation are numerous. Vice President Wang Guowei of Beijing Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital stated on Beijing TV’s “Health Hall” program that “all diseases stem from the liver.” Today, many people suffer from liver Qi stagnation, especially women who juggle family responsibilities, career demands, child-rearing, and filial duties, making it difficult to avoid liver Qi stagnation.
The consequences of liver Qi stagnation are severe and beyond imagination; it can lead to blood stasis, weak temper, dampness accumulation, and even yin deficiency with yang excess. In summary, the “crimes” of liver Qi stagnation are numerous. Vice President Wang Guowei of Beijing Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital stated on Beijing TV’s “Health Hall” program that “all diseases stem from the liver.” Today, many people suffer from liver Qi stagnation, especially women who juggle family responsibilities, career demands, child-rearing, and filial duties, making it difficult to avoid liver Qi stagnation.
How to Determine if You Have Liver Qi Stagnation
Just as solving a case requires evidence, self-diagnosis also requires careful consideration. The most critical evidence for liver Qi stagnation can be found on the tongue. Generally, a normal tongue is oval-shaped, while a person with liver Qi stagnation has a pointed tongue, often with a red tip and edges—this is a key clue for liver Qi stagnation.To confirm liver Qi stagnation, you will also need the following “evidence”:Bitterness in the Mouth: Many women notice a bitter taste in their mouth, especially in the morning. Dry Throat: A feeling of dryness in the mouth and throat, as if there is no saliva, although some may still have visible saliva on their tongue. Feeling of a Lump in the Throat: A sensation of something stuck in the throat, like a bayberry pit, which cannot be coughed up or swallowed, known as “plum pit Qi.” Dizziness: Some women frequently experience dizziness, either all day or in sudden episodes, and some may also have headaches. Poor Appetite: “Liver wood counteracting spleen earth” means that liver Qi stagnation can lead to various spleen and stomach issues, such as lack of appetite, bloating, and stomach pain. Body Temperature Fluctuations: Feeling hot when dressed and cold when undressed, or feeling hot in a warm room but cold outside. Irritability: Individuals with liver Qi stagnation often feel irritable and easily angered. Nausea and Vomiting: Due to “liver wood counteracting spleen earth,” leading to upward reversal of stomach Qi, causing feelings of gas, belching, acid reflux, or even vomiting. Chest Tightness: A feeling of tightness in the chest, sometimes diagnosed as heart issues. However, individuals with heart problems should first address liver Qi stagnation if their tongue is pointed. Rib Pain: A persistent feeling of pain in the ribs. Insomnia and Vivid Dreams: Insomnia can stem from either blood deficiency or liver Qi stagnation, with vivid dreams being a common symptom of liver Qi stagnation. Low Mood: Feelings of sadness, sighing, and sensitivity. Cold Hands and Feet: While many know that cold extremities can result from yang deficiency, blood deficiency, or blood stasis, few recognize that liver Qi stagnation can also cause cold hands and feet. If cold extremities accompany the above symptoms, consider the possibility of liver Qi stagnation.All of the above are criteria for diagnosing liver Qi stagnation. If at least one or two symptoms match, and the tongue is pointed, it is reasonable to conclude liver Qi stagnation.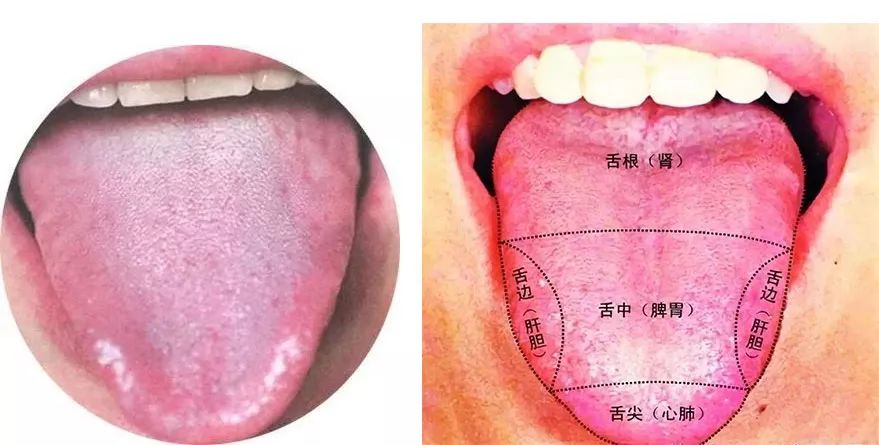 In fact, even without examining these symptoms, women can often sense their own emotional state, whether they have encountered distressing events, felt anger, or experienced significant work pressure. These personal insights are crucial for diagnosing liver Qi stagnation.
In fact, even without examining these symptoms, women can often sense their own emotional state, whether they have encountered distressing events, felt anger, or experienced significant work pressure. These personal insights are crucial for diagnosing liver Qi stagnation.
Cupping and Moxibustion for Liver Qi Stagnation
To regulate liver Qi stagnation, the combination of moxibustion and cupping is highly effective. The specific acupoints for moxibustion and cupping are as follows:
1
Taichong (太冲, Tàichōng) Point
The Taichong point is located on the liver meridian (足厥阴肝经, zú jué yīn gān jīng) on the dorsum of the foot, in the depression at the junction of the metatarsal bones. Cupping followed by moxibustion at this point can help regulate Qi, soothe the liver, invigorate blood circulation, and promote the smooth flow of Qi and blood.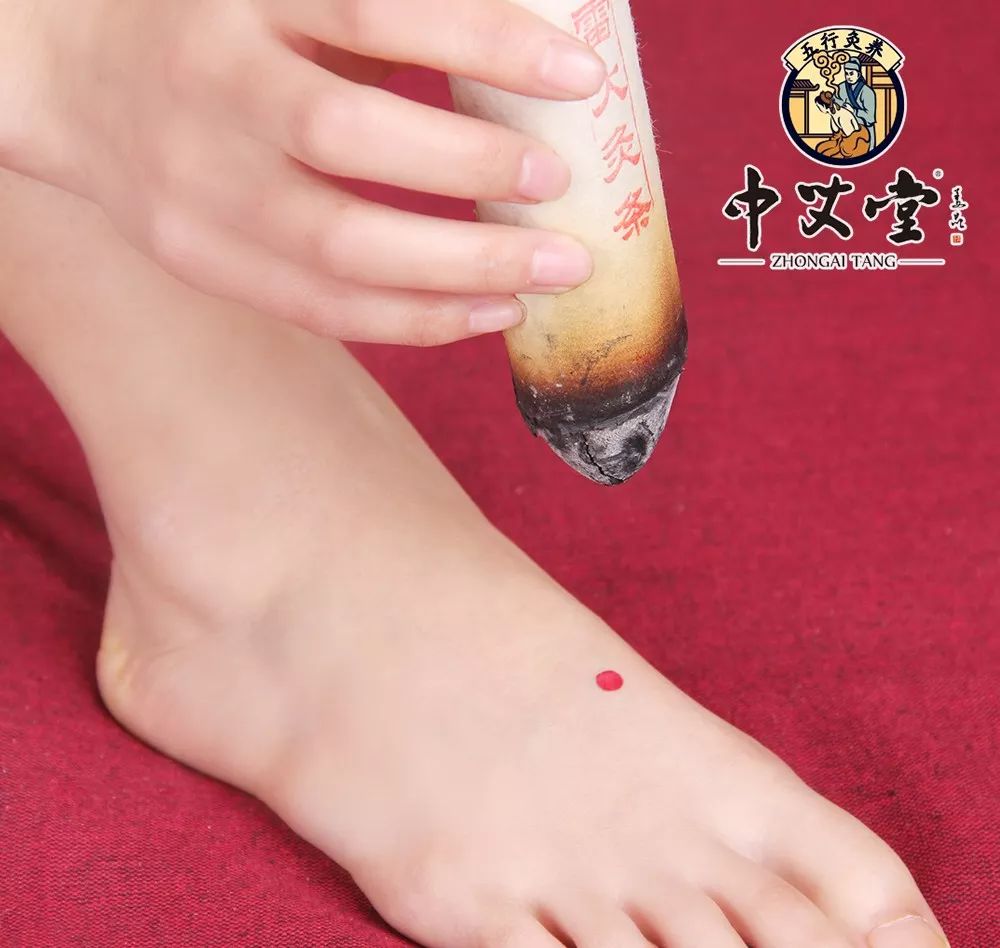
2
Qimen (期门, Qīmén) Point
The Qimen point is the alarm point of the liver meridian, located in the sixth intercostal space, four inches lateral to the midline (directly below the nipple). Moxibustion at this point can soothe the liver and strengthen the spleen, regulate Qi, and invigorate blood circulation. Cupping can also be performed at the liver shu (肝俞, gān shū) and diaphragm shu (膈俞, gé shū) points to achieve similar effects, primarily treating chest and rib pain. Rubbing the sides of the ribs with both hands can also help soothe the liver and relieve stagnation.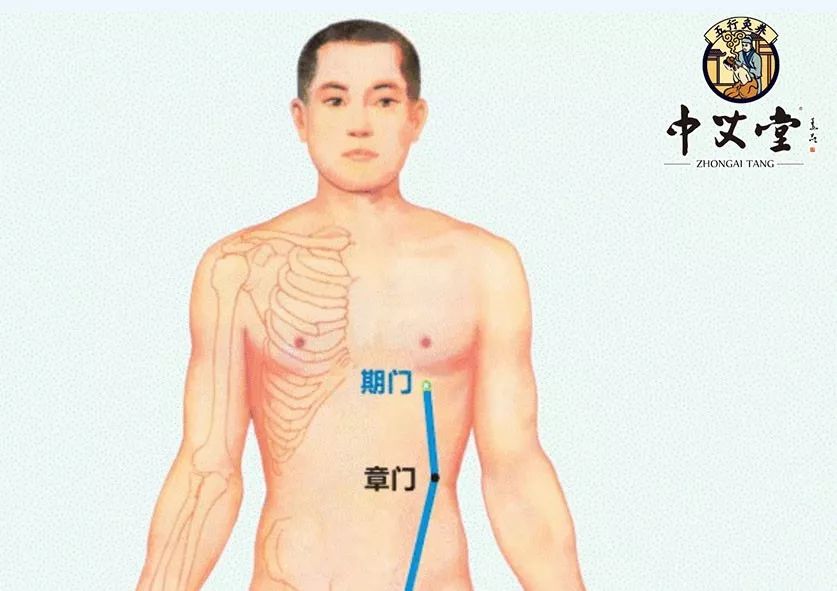
3
Shanzhong (膻中, Shānzhōng) Point
Located at the fourth intercostal space along the midline (between the nipples), cupping at this point can invigorate blood circulation, open the chest, regulate Qi, and alleviate cough and asthma. Even massaging this point can yield good results, relieving symptoms such as chest tightness, cough, and vomiting. Cupping at these points should be done for 5-10 minutes if there are no significant discomforts.Generally, a course of treatment consists of 10 sessions, with cupping performed every five days and moxibustion every other day. The color of the cupping marks reflects individual constitution and health status: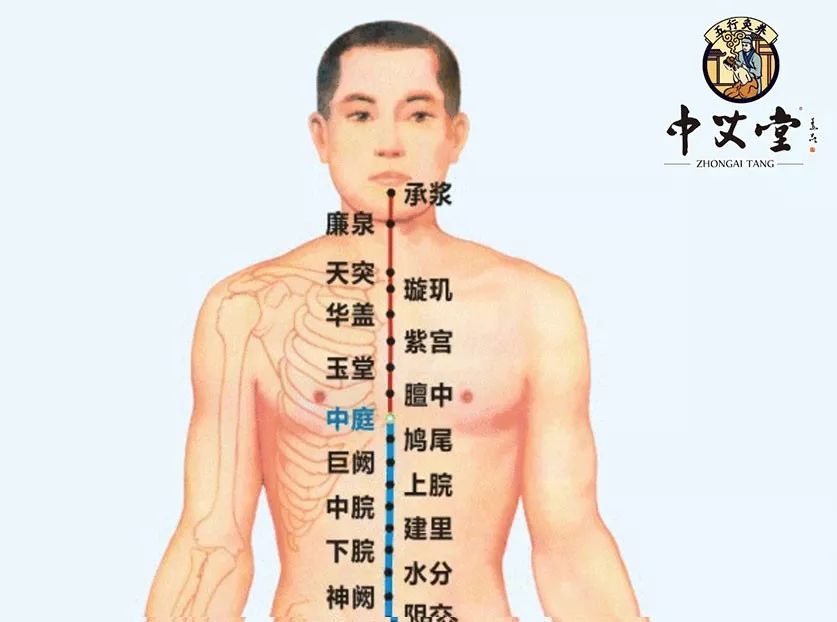 Dark purple cupping marks indicate blood stasis in the body.Dark red cupping marks suggest the presence of stasis heat and more severe conditions.Pale and slightly swollen cupping marks indicate yang deficiency leading to water retention.Prominent surface patterns and enlarged pores with slight itching suggest wind and dampness invasion.During cupping, one may experience localized tightness, coolness, or swelling; if there is no significant discomfort, the cupping marks will naturally fade within 3-5 days without special treatment.As modern life increases work and social pressures, liver Qi stagnation and irritability are common issues. Through this article, I hope everyone has gained a better understanding of the manifestations of liver Qi stagnation and how to alleviate these symptoms. In daily life, we should also learn to maintain a positive emotional state, relax our minds, and engage in appropriate exercise to lead a healthier life.(Some materials in this article are sourced from the internet, and copyright belongs to the original authors. Images are authorized by Shetu Network. If there is any infringement, please contact us for removal!)Author|Ze LanEditor|XU GaiTraditional Moxibustion Center, your moxibustion expert!
Dark purple cupping marks indicate blood stasis in the body.Dark red cupping marks suggest the presence of stasis heat and more severe conditions.Pale and slightly swollen cupping marks indicate yang deficiency leading to water retention.Prominent surface patterns and enlarged pores with slight itching suggest wind and dampness invasion.During cupping, one may experience localized tightness, coolness, or swelling; if there is no significant discomfort, the cupping marks will naturally fade within 3-5 days without special treatment.As modern life increases work and social pressures, liver Qi stagnation and irritability are common issues. Through this article, I hope everyone has gained a better understanding of the manifestations of liver Qi stagnation and how to alleviate these symptoms. In daily life, we should also learn to maintain a positive emotional state, relax our minds, and engage in appropriate exercise to lead a healthier life.(Some materials in this article are sourced from the internet, and copyright belongs to the original authors. Images are authorized by Shetu Network. If there is any infringement, please contact us for removal!)Author|Ze LanEditor|XU GaiTraditional Moxibustion Center, your moxibustion expert! END
END
Traditional Moxibustion Center submission email:
Related articles review (click the text to jump):
☃ Moxibustion on these two height-increasing points can help children grow 5-10 cm!
For more related articles, please search in the public account
☃ Article search guide


