Click the blue text

Follow us
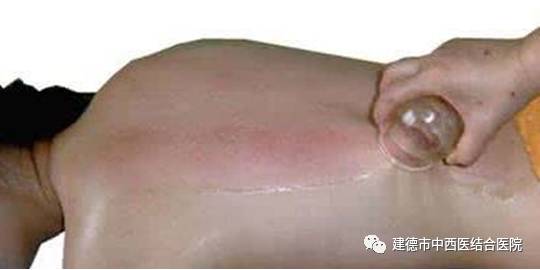
Cupping Therapy
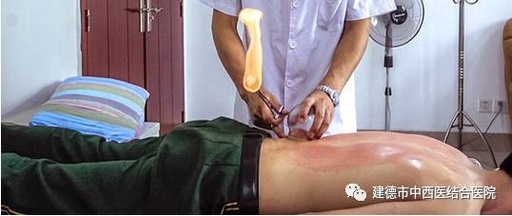
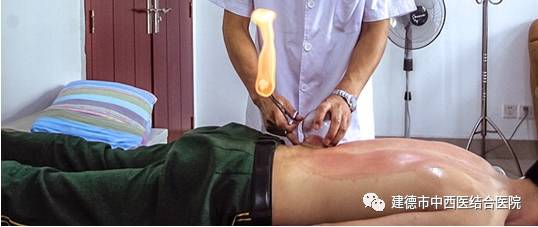
Also known as sliding cupping, this technique involves applying a layer of lubricant such as petroleum jelly or lard to the skin or the rim of the cup before suctioning. The cup is then applied to the selected area of the skin using the flash fire method or dripping alcohol method. The practitioner holds the cup with the right hand while using the left hand to stretch the skin, moving the cup up, down, or sideways.
The practitioner moves the cup back and forth over the area until the skin becomes red, congested, or even bruised. By controlling the speed, frequency, and density (area) of the cupping, the practitioner can adjust the intensity and direction of the suction, achieving selective and enhanced stimulation. This can help regulate the functions of the internal organs and meridians, playing a role in disease prevention and treatment. Conditions such as low back pain, shoulder periarthritis, colds, fevers, hypertension, bronchitis, asthma, chronic gastroenteritis, and acne can all benefit from this therapy.
Cupping therapy is an excellent method for addressing heatstroke, as it promotes internal blood circulation and helps eliminate toxins from the body. This is particularly beneficial for individuals suffering from heatstroke. While it has subjective benefits for the body, it should not be performed too frequently; once a week is generally sufficient. If there are no unusual bodily symptoms, it is best to avoid cupping.
Dr. Li Guohong reminds:
1. After cupping, it is best to avoid exposure to cold, as this can cause significant harm to the body. 2. Do not take a shower immediately after cupping, especially not with cold water. 3. If there are any skin injuries or blisters, avoid spicy and irritating foods.
Contraindicated populations
Individuals with leukemia, skin allergies or ulcerated areas, large blood vessels, areas around the eyes, pregnant women, those with menstrual disorders, and children under six years old.
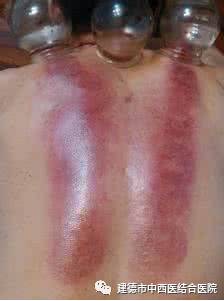
Scientific knowledge: “Reflections of Cupping Marks”
1
Dark purple or black cupping marks: Generally indicate insufficient blood supply and poor circulation with blood stasis.
2
Purple cupping marks with patches: Generally indicate cold congealing and blood stasis.
3
Scattered purple spots: Indicate qi stagnation and blood stasis.
4
Bright red cupping marks: Generally indicate yin deficiency, qi and blood deficiency, or excess fire due to yin deficiency.
5
Dark red cupping marks: Indicate high blood lipids and the presence of heat pathogens.
6
Grayish-white cupping marks that feel cold to the touch: Generally indicate deficiency cold or damp pathogens.
7
Cupping marks with skin texture or slight itching: Indicate wind or damp conditions.
8
Moisture on the inner wall of the cup: Indicates dampness in that area.
9
Blisters appearing on cupping marks indicate heavy internal dampness; if the blisters contain blood, it reflects damp-heat toxicity.
If you need assistance, please consult: 58305791 (Rehabilitation Department), 13989852320 (Dr. Li)