
Click the blue text above to follow us

 Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) acupuncture refers to the techniques of needling and moxibustion. Needling involves inserting fine needles into specific acupuncture points on the patient’s body, utilizing techniques such as twisting and lifting to treat diseases; moxibustion involves burning moxa (mugwort) on specific acupuncture points to apply heat stimulation for therapeutic purposes. Acupuncture is composed of “needles” and “moxibustion”, and is one of the important components of TCM..
Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) acupuncture refers to the techniques of needling and moxibustion. Needling involves inserting fine needles into specific acupuncture points on the patient’s body, utilizing techniques such as twisting and lifting to treat diseases; moxibustion involves burning moxa (mugwort) on specific acupuncture points to apply heat stimulation for therapeutic purposes. Acupuncture is composed of “needles” and “moxibustion”, and is one of the important components of TCM..
The principles of disease treatment in TCM acupuncture
1
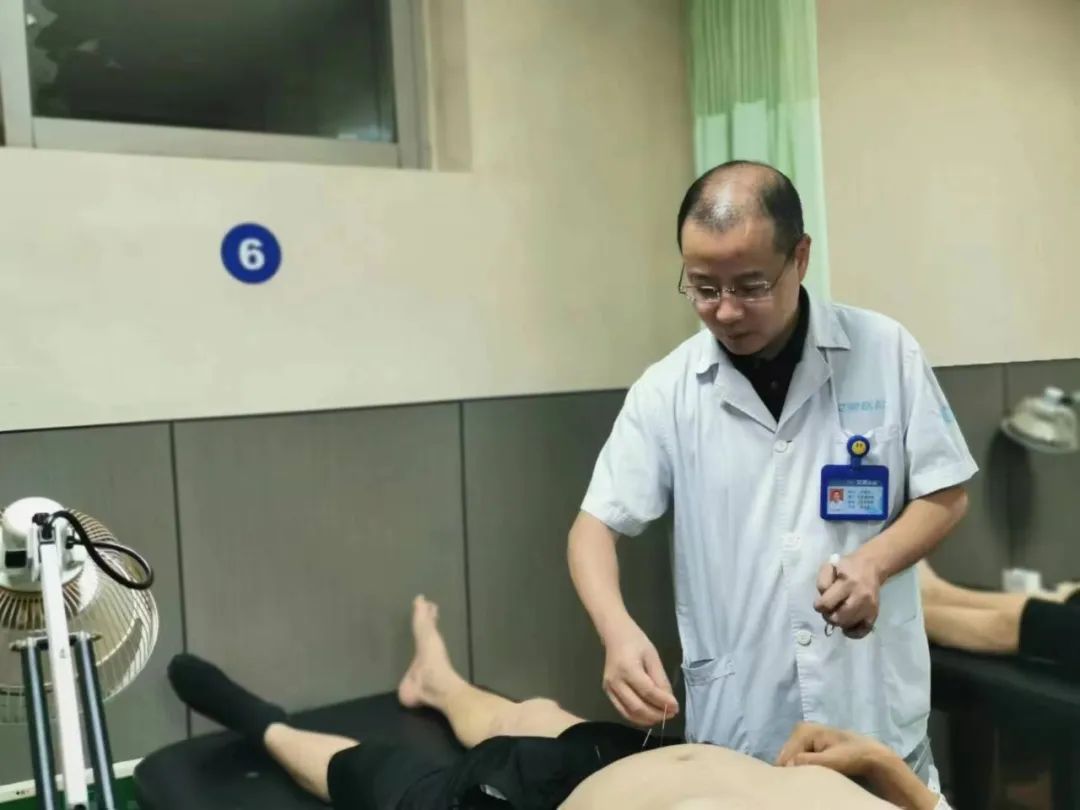 1. Harmonizing Yin and Yang: Under normal circumstances, the Yin and Yang aspects of the human body are in a relatively balanced state. The therapeutic effect of acupuncture primarily lies in harmonizing Yin and Yang, which is achieved through the combination of meridians, acupuncture points, and needling techniques. For example, toothache caused by excessive stomach fire is classified as Yang heat predominance, and treatment should focus on clearing and draining stomach fire by needling the Stomach Meridian point Neiting (内庭), using a draining technique to clear stomach heat. Conversely, stomach pain caused by cold evil harming the stomach is classified as Yin evil predominance, and treatment should focus on warming and dispersing cold by needling the Stomach Meridian points Zusanli (足三里) and Middle Cavity (中脘), using a draining technique and moxibustion to warm and disperse cold evil. Modern clinical observations and experimental studies have fully demonstrated that acupuncture has a significant regulatory effect on the functional activities of various organ tissues, especially under pathological conditions, where this regulatory effect is more pronounced. Generally, acupuncture has an inhibitory effect on overactive, excited, and spastic tissues and organs, while it has a stimulating effect on weak, inhibited, and relaxed tissues and organs. This regulation is beneficial and bidirectional, which is one of the fundamental reasons why acupuncture can treat various diseases. If we relate the pathological imbalance of tissues and organs to the theory of Yin and Yang, it can be explained using Yin and Yang, thus stating that acupuncture regulates pathological imbalances, which is essentially the regulation of Yin and Yang imbalances.2. Supporting the Right and Expelling Evil: Acupuncture has the function of supporting the right and expelling evil, specifically manifested as tonifying deficiency and draining excess. The tonification and draining effects of acupuncture are reflected in three aspects: first, the needling and moxibustion techniques, where moxibustion is often used for tonification, and bloodletting is often used for draining excess; second, the needling techniques, where ancient and modern practitioners have summarized various tonifying and draining techniques; third, the combination of acupuncture points, where extensive clinical experience has shown that many acupuncture points have different tonifying and draining effects, such as Shenque (神阙), Qihai (气海), Guanyuan (关元), Zusanli (足三里), and Mingmen (命门) points, which are often used for tonification during supportive treatment, while points like Shixuan (十宣), Zhongji (中极), and Shuigou (水沟) are often used for draining during expelling evil treatment. Modern clinical practice and experimental research have proven that acupuncture can enhance the body’s immune function, resisting various pathogenic factors, which is similar to the TCM principle of “supporting the right and expelling evil.”3. Unblocking Meridians: Acupuncture stimulates acupuncture points to unblock meridians and regulate Qi and blood, thereby achieving the purpose of treating diseases. Acupuncture for pain relief is also a result of unblocking meridians and relieving obstructions.
1. Harmonizing Yin and Yang: Under normal circumstances, the Yin and Yang aspects of the human body are in a relatively balanced state. The therapeutic effect of acupuncture primarily lies in harmonizing Yin and Yang, which is achieved through the combination of meridians, acupuncture points, and needling techniques. For example, toothache caused by excessive stomach fire is classified as Yang heat predominance, and treatment should focus on clearing and draining stomach fire by needling the Stomach Meridian point Neiting (内庭), using a draining technique to clear stomach heat. Conversely, stomach pain caused by cold evil harming the stomach is classified as Yin evil predominance, and treatment should focus on warming and dispersing cold by needling the Stomach Meridian points Zusanli (足三里) and Middle Cavity (中脘), using a draining technique and moxibustion to warm and disperse cold evil. Modern clinical observations and experimental studies have fully demonstrated that acupuncture has a significant regulatory effect on the functional activities of various organ tissues, especially under pathological conditions, where this regulatory effect is more pronounced. Generally, acupuncture has an inhibitory effect on overactive, excited, and spastic tissues and organs, while it has a stimulating effect on weak, inhibited, and relaxed tissues and organs. This regulation is beneficial and bidirectional, which is one of the fundamental reasons why acupuncture can treat various diseases. If we relate the pathological imbalance of tissues and organs to the theory of Yin and Yang, it can be explained using Yin and Yang, thus stating that acupuncture regulates pathological imbalances, which is essentially the regulation of Yin and Yang imbalances.2. Supporting the Right and Expelling Evil: Acupuncture has the function of supporting the right and expelling evil, specifically manifested as tonifying deficiency and draining excess. The tonification and draining effects of acupuncture are reflected in three aspects: first, the needling and moxibustion techniques, where moxibustion is often used for tonification, and bloodletting is often used for draining excess; second, the needling techniques, where ancient and modern practitioners have summarized various tonifying and draining techniques; third, the combination of acupuncture points, where extensive clinical experience has shown that many acupuncture points have different tonifying and draining effects, such as Shenque (神阙), Qihai (气海), Guanyuan (关元), Zusanli (足三里), and Mingmen (命门) points, which are often used for tonification during supportive treatment, while points like Shixuan (十宣), Zhongji (中极), and Shuigou (水沟) are often used for draining during expelling evil treatment. Modern clinical practice and experimental research have proven that acupuncture can enhance the body’s immune function, resisting various pathogenic factors, which is similar to the TCM principle of “supporting the right and expelling evil.”3. Unblocking Meridians: Acupuncture stimulates acupuncture points to unblock meridians and regulate Qi and blood, thereby achieving the purpose of treating diseases. Acupuncture for pain relief is also a result of unblocking meridians and relieving obstructions.
Common Acupuncture Points for Health Preservation
2
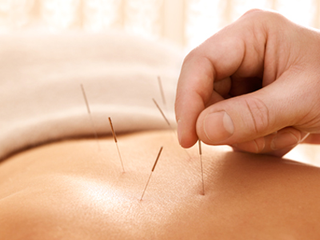 1.Zusanli (足三里): One of the health-preserving acupuncture points, known as the “Longevity Point” in ancient times. The meridian theory related to Zusanli has been confirmed by extensive modern research, showing that it regulates cortical function, cardiovascular function, gastrointestinal motility, endocrine function, and the immune system. According to TCM meridian theory, the Stomach Meridian where Zusanli is located is a channel rich in Qi and blood, running from the head to the feet, traversing the entire body, mainly distributed in the head, face, chest, abdomen, and the outer side of the lower limbs. Therefore, Zusanli can not only regulate digestive system function but also treat diseases in areas traversed by the stomach meridian, as well as various systemic diseases such as heart disease and gastrointestinal disorders. Regular cupping on Zusanli can have health-preserving effects.2.Yongquan (涌泉): The first point of the Kidney Meridian, located at the center of the sole of the foot. Dampness and toxins can easily accumulate here, making it difficult to expel, leading to blockages in Qi. Cupping at Yongquan can help expel dampness and toxins from the body and unblock the Qi of the Kidney Meridian. When kidney Qi is abundant, the body is energetic, leading to strong teeth, dark hair, clear hearing, and delayed aging.3.Sanyinjiao (三阴交): The intersection point of the three Yin meridians: liver, kidney, and spleen. The liver stores blood, the spleen governs blood, and the essence of the spleen and blood share the same source. The kidney is the foundation of pre-natal essence, while the spleen is the foundation of post-natal essence. The pre-natal essence relies on the nourishment of post-natal essence, and the post-natal essence relies on the promotion of pre-natal essence. Regular cupping at Sanyinjiao can regulate the Qi of the three Yin meridians, enhancing pre-natal essence and ensuring sufficient post-natal essence, thus achieving health and longevity.4.Baihui (百会): Also known as the meeting point of the three Yang and five meetings, located at the intersection of the midline of the head and the line connecting the tips of both ears. Cupping or regular massage at this point has significant effects on the prevention and treatment of cerebrovascular diseases. Its uplifting effect is remarkable, especially for organ prolapse. Cupping at this point often requires a haircut for better sealing, otherwise, the therapeutic effect may be compromised. The function of Baihui is to pacify the liver, extinguish wind, clear heat, open the orifices, uplift Yang, benefit Qi, and calm the mind.5.Hegu (合谷): Commonly referred to as the “Party Point.” It belongs to the Large Intestine Meridian, which runs from the hand along the outer side of the arm to the head and face. Hegu has the functions of clearing Yangming, dispelling wind and toxins, unblocking meridians, and relieving pain. Regular cupping can promote dental health and treat facial diseases. It also helps maintain smooth bowel movements, facilitating the expulsion of toxins and waste, thus promoting beauty and anti-aging effects.
1.Zusanli (足三里): One of the health-preserving acupuncture points, known as the “Longevity Point” in ancient times. The meridian theory related to Zusanli has been confirmed by extensive modern research, showing that it regulates cortical function, cardiovascular function, gastrointestinal motility, endocrine function, and the immune system. According to TCM meridian theory, the Stomach Meridian where Zusanli is located is a channel rich in Qi and blood, running from the head to the feet, traversing the entire body, mainly distributed in the head, face, chest, abdomen, and the outer side of the lower limbs. Therefore, Zusanli can not only regulate digestive system function but also treat diseases in areas traversed by the stomach meridian, as well as various systemic diseases such as heart disease and gastrointestinal disorders. Regular cupping on Zusanli can have health-preserving effects.2.Yongquan (涌泉): The first point of the Kidney Meridian, located at the center of the sole of the foot. Dampness and toxins can easily accumulate here, making it difficult to expel, leading to blockages in Qi. Cupping at Yongquan can help expel dampness and toxins from the body and unblock the Qi of the Kidney Meridian. When kidney Qi is abundant, the body is energetic, leading to strong teeth, dark hair, clear hearing, and delayed aging.3.Sanyinjiao (三阴交): The intersection point of the three Yin meridians: liver, kidney, and spleen. The liver stores blood, the spleen governs blood, and the essence of the spleen and blood share the same source. The kidney is the foundation of pre-natal essence, while the spleen is the foundation of post-natal essence. The pre-natal essence relies on the nourishment of post-natal essence, and the post-natal essence relies on the promotion of pre-natal essence. Regular cupping at Sanyinjiao can regulate the Qi of the three Yin meridians, enhancing pre-natal essence and ensuring sufficient post-natal essence, thus achieving health and longevity.4.Baihui (百会): Also known as the meeting point of the three Yang and five meetings, located at the intersection of the midline of the head and the line connecting the tips of both ears. Cupping or regular massage at this point has significant effects on the prevention and treatment of cerebrovascular diseases. Its uplifting effect is remarkable, especially for organ prolapse. Cupping at this point often requires a haircut for better sealing, otherwise, the therapeutic effect may be compromised. The function of Baihui is to pacify the liver, extinguish wind, clear heat, open the orifices, uplift Yang, benefit Qi, and calm the mind.5.Hegu (合谷): Commonly referred to as the “Party Point.” It belongs to the Large Intestine Meridian, which runs from the hand along the outer side of the arm to the head and face. Hegu has the functions of clearing Yangming, dispelling wind and toxins, unblocking meridians, and relieving pain. Regular cupping can promote dental health and treat facial diseases. It also helps maintain smooth bowel movements, facilitating the expulsion of toxins and waste, thus promoting beauty and anti-aging effects.
Precautions
3
 1. Acupuncture should not be performed when overly hungry, overly full, overly fatigued, or intoxicated.2. Maintain a relaxed mood before acupuncture, avoiding excessive tension.3. Avoid makeup, scraping the tongue, or using perfume to prevent affecting the doctor’s accurate assessment of your condition.4. Visit the restroom before acupuncture to avoid discomfort from leaving needles (referring to leaving needles in the acupuncture point without movement to enhance the sensation and effect, generally for 10-20 minutes) or stimulating the bladder when treating the abdomen.5. After acupuncture, maintain skin cleanliness; there is no need for special disinfection, just avoid contact with dirty water, oil, or other unclean substances to prevent infection at the needle site.
1. Acupuncture should not be performed when overly hungry, overly full, overly fatigued, or intoxicated.2. Maintain a relaxed mood before acupuncture, avoiding excessive tension.3. Avoid makeup, scraping the tongue, or using perfume to prevent affecting the doctor’s accurate assessment of your condition.4. Visit the restroom before acupuncture to avoid discomfort from leaving needles (referring to leaving needles in the acupuncture point without movement to enhance the sensation and effect, generally for 10-20 minutes) or stimulating the bladder when treating the abdomen.5. After acupuncture, maintain skin cleanliness; there is no need for special disinfection, just avoid contact with dirty water, oil, or other unclean substances to prevent infection at the needle site.

Source: Acupuncture Therapy Department
Editor: Huang Yuzeng
Reviewed by: Song Weiqiang

Warm Reminder
To ensure the safety of patients, please wear a mask throughout your visit and maintain a safe distance of more than 1 meter from others. Our hospital is a veteran-friendly hospital, offering medical discounts for veterans and their families.


