1. Comprehensive Holographic Observation Diagnosis
1
Through facial color diagnosis:
1. Yellow: Indicates potential issues with the spleen and stomach, and digestive system;
2. White: Indicates potential issues with the lungs and respiratory system;
3. Red: Indicates potential issues with the cardiovascular system;
4. Blue: Indicates potential issues with the liver and gallbladder, and immune system;
5. Black: Indicates potential issues with the kidneys and bladder.
2
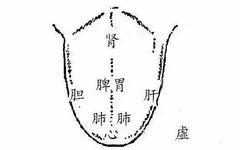
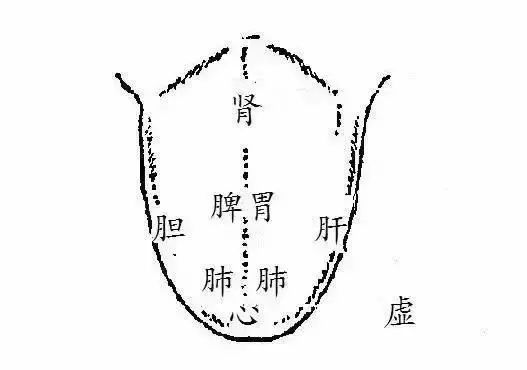
Through tongue observation for health diagnosis:
The tongue of a healthy person is pink. If a person is unhealthy, it can be observed from the tongue:
1. A thick coating indicates poor spleen and stomach function;
2. A bluish root indicates kidney issues;
3. Imprints on the sides of the tongue indicate liver issues;
4. A pale tongue indicates heart issues, suggesting insufficient blood supply to the myocardium, poor blood circulation, and symptoms of anemia;
5. A dark purple tip indicates excessive heart fire, blood stasis, and blood viscosity;
6. Numerous small red spots on the tip may indicate myocarditis;
7. A blunt tip with a deep groove in the center may indicate diabetes.
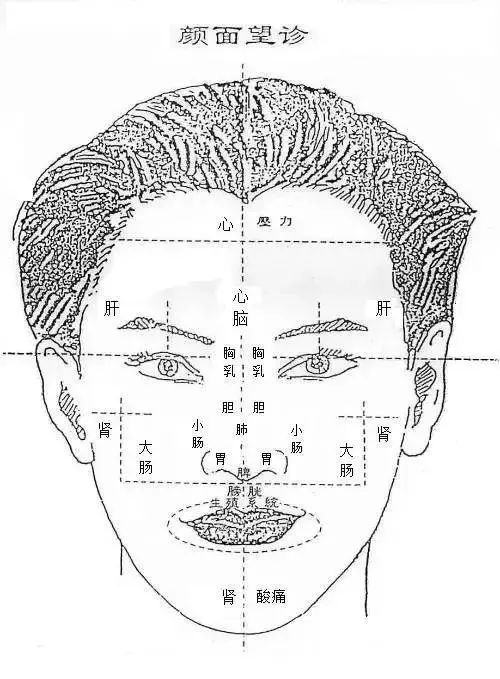
Facial diagnosis is primarily divided into eight major areas:
“Heart, Lungs, Liver, Kidneys, Spleen, Small Intestine, Large Intestine, Reproductive”
3
Heart
Reflex area (1): On the forehead from 1/3 to the hairline (the hairline circle)
1. The appearance of acne or a color difference in this area indicates significant physiological stress;
2. The presence of spots indicates heart disease (e.g., myocardial insufficiency);
3. The presence of moles indicates congenital heart function insufficiency;
Reflex area (2): At the bridge of the nose between the corners of the eyes
4. The appearance of horizontal lines or prominent horizontal lines indicates arrhythmia or poor heart condition;
5. If deep horizontal lines appear and there are also deep vertical lines on the tongue, it may indicate severe heart disease;
6. People with heart issues often have a face full of red blood vessels, resembling many small insects crawling on the face, indicating poor blood circulation.
4
Brain
Reflex area: Between the eyebrows
1. The appearance of deep vertical lines and redness in this area indicates insufficient blood supply to the cardiovascular system, headaches, neurasthenia, vivid dreams, poor sleep, palpitations, and irritability;
2. If this area is red and shiny, it usually indicates high blood pressure.
5
Lungs
Reflex area: Between the eyebrows and below the forehead, at the Yintang position
1. If the Yintang area is red, it indicates recent upper respiratory infections;
2. If the Yintang is dark, especially black, it may indicate pathological changes, and a hospital check-up is advised;
3. If the center of the forehead is significantly concave and the color is dark, bluish, or spotted, it indicates lung disease and difficulty in breathing;
4. If there are acne spots, it indicates recent colds or sore throat;
5. If there are moles or white spots at the eyebrow area, it indicates pharyngitis, tonsillitis, or chest tightness and shortness of breath, or lung disease;
6. A bulge above the eyebrows also indicates lung disease.
6
Liver
Reflex area: The triangular area from the center of the eyebrows to the tail of the eyebrows, and the middle section of the bridge of the nose is also the liver area
1. If these two areas are dark or spotted, it may indicate fatty liver;
2. If there are acne spots in these areas, it indicates excessive anger;
3. If there are spots at the temples, it indicates weakened liver function;
4. If there are spots in the middle section of the bridge of the nose, it may indicate excessive anger, emotional instability, or menopause;
5. If both areas have prominent spots and the complexion is dark and dull, indicating a very thin person, it may indicate hepatitis or cirrhosis;
6. A mole in the center of the eyebrows and yellowing of the eyeballs, along with a very yellow complexion, indicates hepatitis B;
7. Soft, thin, dull nails with vertical lines that are prone to breakage indicate poor liver function;
8. A face full of dark spots indicates congenital liver function insufficiency.
7
Gallbladder
Reflex area: On both sides of the middle section of the bridge of the nose
1. If this area has red blood vessels, acne, or a bitter taste in the mouth upon waking, it indicates mild inflammation of the gallbladder;
2. If there are spots or shadows, it may indicate cholecystitis;
3. If there are vertical lines in this area or if vertical lines appear when smiling, it indicates gallbladder issues;
4. If there are moles or spots in this area, it indicates congenital gallbladder function insufficiency;
5. If you place your right hand under the right rib (where the gallbladder is located) and hit the back of your right hand with your left fist, if it hurts, it indicates cholecystitis;
6. If the pain is severe, it may indicate gallstones. People with gallbladder issues may be overweight;
7. A pair of prominent spots or moles under the eyes indicates gallstones. Dark circles under the eyes also indicate poor gallbladder function.
8
Kidneys
Reflex area: The area where a vertical line from the outer corner of the eye intersects with a vertical line from the middle of the ear down to the chin
1. If there are bumps or dark spots in this area, it is not due to lack of cleanliness or sun exposure, indicating poor kidney function;
2. If this area has red blood vessels, acne, or spots, it indicates kidney deficiency, often accompanied by fatigue and soreness in the lower back and legs;
3. If there are deep and large spots in this area, it may indicate kidney stones. If black moles or bumps appear on the ears, it may indicate kidney stones;
4. If there are moles or bumps in this area, it indicates congenital kidney function insufficiency, which may also cause soreness in the lower back, legs, and back;
5. Deep crow’s feet at the corners of the eyes and vertical lines near the ears indicate declining kidney function;
6. The chin is the area of kidney soreness. If there are red spots or bumps in this area, it indicates lower back soreness, often due to nephritis.
9
Spleen and Stomach
Spleen reflex area: At the tip of the nose;
Stomach reflex area: At the wings of the nose, with the depressions on both sides being the duodenum area
1. Pale lips without redness, dry lips that are prone to cracking, indicate poor spleen and stomach function;
2. A red nose tip, rosacea, red blood vessels, black spots, and bumps indicate poor spleen and stomach function;
3. A white nose tip without redness, especially pale, indicates spleen deficiency and may lead to anemia. A yellow nose tip also indicates spleen deficiency, with symptoms such as excessive sweating, aversion to wind, fatigue, and poor appetite;
4. If the nostrils are always dirty, dark, and oily, resembling a lack of cleanliness, or if there are bumps, it indicates poor stomach function;
5. If the nostrils are red, it indicates stomach fire, leading to hunger and bad breath. If there are severe red blood vessels, it usually indicates gastritis;
6. If the nostrils are grayish-blue, it indicates stomach cold, and when shaking hands, the fingertips feel cold, indicating abdominal pain and diarrhea due to wind-cold;
7. Spots or moles in the spleen area may indicate spleen enlargement, while spots and moles in the stomach area may indicate ulcers and other pathological changes.
Abdominal pain before meals usually indicates gastritis.
Abdominal pain one to two hours after meals is usually due to gastric ulcers, with tenderness in the middle or slightly to the left of the abdomen.
Abdominal pain two to four hours after meals is usually due to duodenal ulcers, with pain in the area near the ribs, resembling a needle-like sensation, and severe cases may cause pain to the back, with tenderness slightly to the right of the abdomen.
10
Small Intestine
Reflex area: Below the cheekbone, towards the inner side
If this area has red blood vessels, acne, spots, moles, or blemishes, it indicates poor small intestine function, often leading to loose stools.
11
Large Intestine and Rectum
Large intestine reflex area: Below the cheekbone, towards the outer side, from the eyes to the outer corners down to the mouth corners
1. If this area has red blood vessels, acne, spots, moles, or blemishes, it indicates dysfunction of the large intestine, often leading to dry stools and constipation;
2. If this area has crescent-shaped spots, it indicates constipation or hemorrhoids;
The large intestine area appears dark red and uneven, indicating colitis.
Rectum reflex area: At the intersection of the lower part of the nose and the vertical line from the outer corner of the eye
4. If there are spots here, it indicates hemorrhoids; if this area is red or has white spots, it may indicate rectal cancer.
12
Bladder
Reflex area: On both sides of the philtrum at the base of the nose
1. If this area is red, with red blood vessels, acne, or sores, it indicates cystitis, which may lead to symptoms such as red and yellow urine, frequent urination, etc. Cystitis can also cause lower back pain;
2. If there are wrinkles in the bladder area, it may indicate kidney atrophy, and red acne indicates inflammation, while black moles may indicate pathological changes.
13
Reproductive System
Reflex area: Around the philtrum and lips
1. If a woman has moles or spots below her lips, and the kidney reflex area is smooth, it indicates a retroverted uterus and lower back pain;
2. If a woman has moles or spots around her lips, and the kidney reflex area is also poor; or if a woman’s lips are bluish, dark, or pale, and the kidney reflex area is also poor, these two conditions usually indicate coldness in the body;
3. If there are bumps in the philtrum, it usually indicates uterine disease;
4. If a man has moles or spots around his lips, and the kidney reflex area is also poor, it indicates reproductive system issues;
5. If a man’s upper lip is uneven, with grooves and vertical lines, it indicates male sexual dysfunction.
14
Chest and Breasts
Reflex area: The slope of the bridge of the nose between the eyes
The presence of moles and spots in the breast area may indicate breast hyperplasia and tumors.
Originating from TCM thinking.
2. 19 Key Experiences in Holographic Pulse Diagnosis:
1. The head corresponds to the distal end of the cun pulse. The neck projects to the middle of the cun pulse. 2. The chest cavity and organs project to the entire cun pulse. 3. The liver, gallbladder, spleen, and pancreas project to the distal end of the guan pulse. 4. The kidneys and adrenal glands correspond to the proximal end of the guan pulse. The pelvic organs correspond to the chi pulse. 5. The skin, muscles, etc., project to the edges of the pulse. 6. The radial edge corresponds to the lateral and posterior soft tissues of the body and related painful conditions; the ulnar edge corresponds to the pulse energy of the anterior abdominal tissues, reflecting organs near the midline. 7. A weak chi pulse indicates cold limbs and poor intestinal function. Menstrual, reproductive, and sexual function issues. A strong guan and chi pulse indicates strong sexual function; any weakening indicates dysfunction. 8. Referred pain from internal organs often reflects on the body surface and appears as edge pulses. 9. The shape of internal organs is round, and the pulse energy at the cun pulse is a point (pulse halo point); the shape of internal organs and muscles is linear, and the shape of the cun pulse halo is linear. In the early stage of organ inflammation (hyperemia phase), the pulse halo is floating. 10. The pulse position of solid organs is often deep, and during pathological changes, their pulse strength is often strong. Hollow organ pulse positions are often floating and weak. 11. When the pulse position is deep, weak, or absent, it often indicates weakened organ function, reduced size, or surgical removal. 12. In the early stages of nerve compression, the pulse strength may increase; in the later stages, the corresponding organ’s pulse energy will weaken, related to nerve function damage (e.g., lumbar disc herniation), with aseptic inflammation of the lumbar muscles, fascia, and nerves presenting as pulse shapes with edge pulses, and the spinal pulse sensation is also edge pulse but in a deep position. 13. In normal individuals, the left chi pulse is always weaker than the right chi pulse. 14. The left cun reflects the heart and throat; the right cun reflects the lungs and trachea, the middle cun reflects the tonsils, thyroid, and lymph nodes; the spleen and stomach are on the left, and the liver and gallbladder are on the right; the right guan chi pulse has the widest sensing range, menstruation is sensed in the right guan chi pulse, the rectal pulse position is at the lower end of the chi pulse, the reproductive pulse position is at the right chi end, and the urinary and prostate pulse positions are at the lower ends of both chi pulses, with the upper and lower limbs overlapping at the radial edge of the chi pulse, and the cervical and occipital areas at the radial edges of both cun pulses. 15. A strong left guan pulse often indicates spleen enlargement or cervical lymphadenopathy. 16. A strong left guan pulse with weak chi pulses indicates the need to rule out mesenteric lymphadenitis. 17. The pulse pattern of diabetes is characterized by arterial and left chi pulse halo points; based on the strength of the left chi pulse halo points, one can generally infer the blood sugar levels and treatment effects. The pulse pattern of gout is similar to that of diabetes; based on the size of the left guan pulse halo points, one can generally judge the uric acid levels and treatment effects. 18. A turbid pulse and a deep right guan pulse indicate fatty liver. A string-like left and right guan pulse with strong force like broad beans often indicates cirrhosis and liver-spleen enlargement. 19. A strong and solid guan chi pulse indicates ipsilateral lumbar disc herniation; bilateral cun pulses with edge pulses indicate cervical spondylosis; unilateral cun edge pulses indicate ipsilateral shoulder periarthritis.
— Previous Review, Click to Read —
The Seven Critical Points of the Human Body: Areas Not to Be Messed With

Step-by-Step Guide to Pulse Diagnosis: 7 Character Mnemonics + Plain Language Explanation!

How to Tell if Your Kidneys Are Healthy Just by Looking at Your Face! Two Nourishing Soups and Three Exercises for Kidney Health

On December 28th, 【Shijiazhuang】 Liu Tao’s Heart-Mind Unique Needle, Three Talents and Five Elements, Eight Trigrams Needle Method

Where There Is Flow, There Is No Pain! Fourteen Common Symptoms of Meridian Blockage

TCM Course on Difficult and Miscellaneous Diseases, Lasting Six Days!! Techniques, Needle Methods, Mindset, Secret Recipes, and Classic Formulas

If you find today’s content valuable, please click the “Like” button in the lower right corner and share it with your friends.