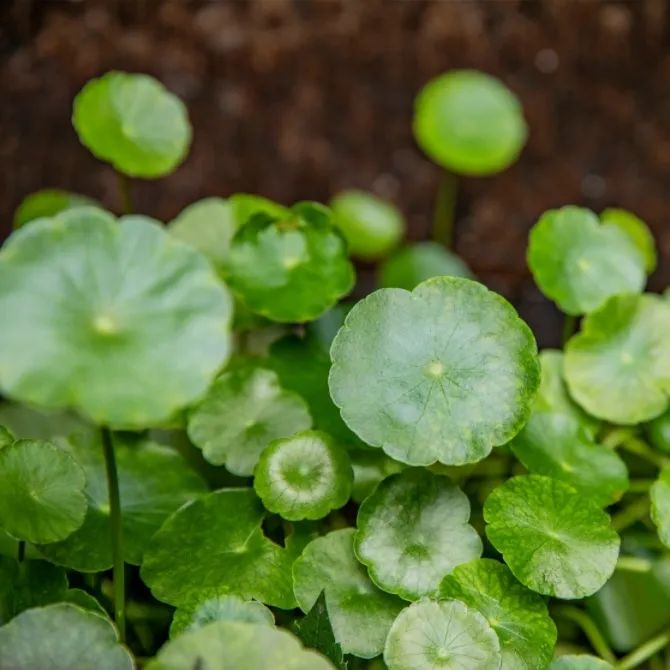

Jin Qian Cao (金钱草)
– Herbal Name –
Category: Diuretic and Dampness-Resolving
· Overview ·
Jin Qian Cao, known as Lysimachia christinae, is the dried whole herb of the plant belonging to the Primulaceae family. It is distributed in Yunnan, Sichuan, Guizhou, southern Shaanxi, Henan, Hubei, Hunan, Guangxi, Guangdong, Jiangxi, Anhui, Jiangsu, Zhejiang, and Fujian provinces. It has the effects of resolving dampness and jaundice, promoting urination, and detoxifying to reduce swelling.
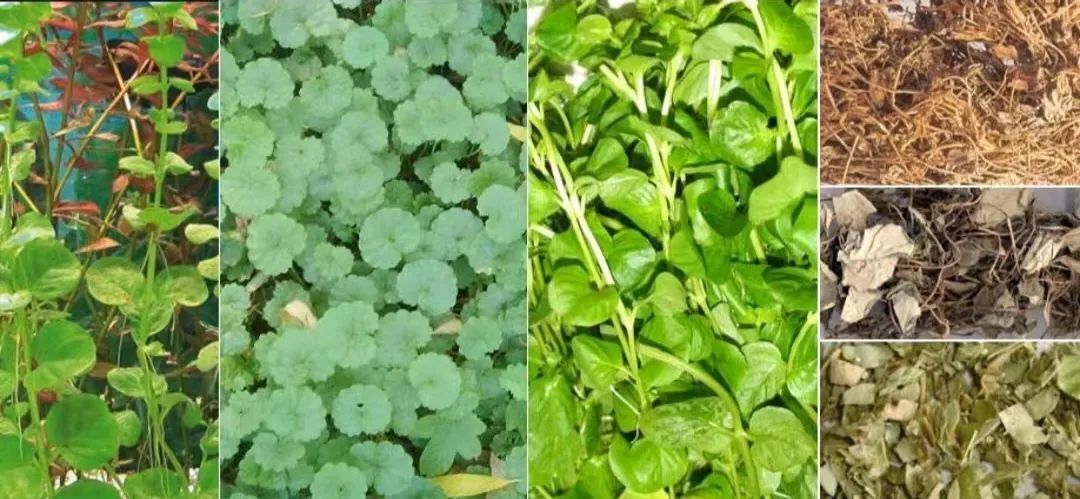

· Herbal Properties ·
1
Parts Used

The dried whole herb of the plant.

Taste and Properties
2
Sweet, salty, slightly cold in nature. Enters the Liver (肝), Gallbladder (胆), Kidney (肾), and Bladder (膀胱) meridians.
3
Dosage

15-60g.

Preparation Method
4
Collection and Processing:
Harvested in summer and autumn, impurities removed, and dried.
Preparation Method:
Remove impurities, wash quickly, cut into sections, and dry.
· Functions and Indications ·
Jin Qian Cao is used for damp-heat jaundice, gallbladder distension and pain, stone lin syndrome, heat lin syndrome, painful and difficult urination, and for treating carbuncles, sores, and snake bites.
Damp-heat jaundice, gallbladder distension and pain:
-
Used for damp-heat jaundice, often combined with Yin Chen (茵陈) and Zhi Zi (栀子).
-
For liver and gallbladder stones, gallbladder distension and pain, can be used alone or combined with Yin Chen, Da Huang (大黄), and Yu Jin (郁金).
Stone lin syndrome, heat lin syndrome:
-
Can be used in large doses as a decoction instead of tea, or combined with Hu Po (琥珀), Hai Jin Sha (海金沙), and Ji Nei Jin (鸡内金).
Carbuncles, sores, snake bites:
-
Fresh herb can be crushed for juice to take internally or applied externally, or combined with Pu Gong Ying (蒲公英), Ye Hua (野花), and Zi Hua Di Ding (紫花地丁).
· Precautions ·
Jin Qian Cao is a slightly cool herb; individuals with a weak constitution, frequent cold stomach pain, cold hands and feet, or prone to diarrhea should avoid using it without professional guidance. Pregnant and breastfeeding women must have a professional assessment before use.
Note:
This content is for reference only and should not be used as a basis for diagnosis or treatment. Please follow medical advice!

If you like this article, remember to click the “Looking” button at the bottom right of the article, or share it with your friends!Want to maintain your health daily?Follow us!

 ⊙ Note: This public account is a platform for sharing and exchanging knowledge about Traditional Chinese Medicine. The articles are for learning and reference only. If medication is involved, please do so under the guidance of a licensed physician.This article contains images sourced from copyright libraries and Jiu Daifu; some images are from the internet and are for educational exchange only. Copyright belongs to the original authors. If there is any infringement, please notify for removal.
⊙ Note: This public account is a platform for sharing and exchanging knowledge about Traditional Chinese Medicine. The articles are for learning and reference only. If medication is involved, please do so under the guidance of a licensed physician.This article contains images sourced from copyright libraries and Jiu Daifu; some images are from the internet and are for educational exchange only. Copyright belongs to the original authors. If there is any infringement, please notify for removal.
⊙ For business cooperation, contact WeChat: tudi1970

