Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) believes that the spleen and stomach are responsible for the transformation and transportation of food and fluids, serving as the source of qi and blood production. When invaded by dampness, the absorption of food and fluids is obstructed, leading to insufficient yin blood and fluids, resulting in a condition known as yin deficiency and fluid deficiency. This condition can cause an imbalance of yin and yang in the body, manifesting symptoms such as insufficient yin fluids and internal heat due to yin deficiency.
To improve this condition, it is essential to nourish yin and generate fluids. Today, I would like to share a wonderful formula consisting of two herbs: Huang Jing (Rhizoma Polygonati) and Yu Zhu (Polygonatum Odoratum).
One part Huang Jing and one part Yu Zhu will help you tonify qi, nourish yin, and quench thirst.
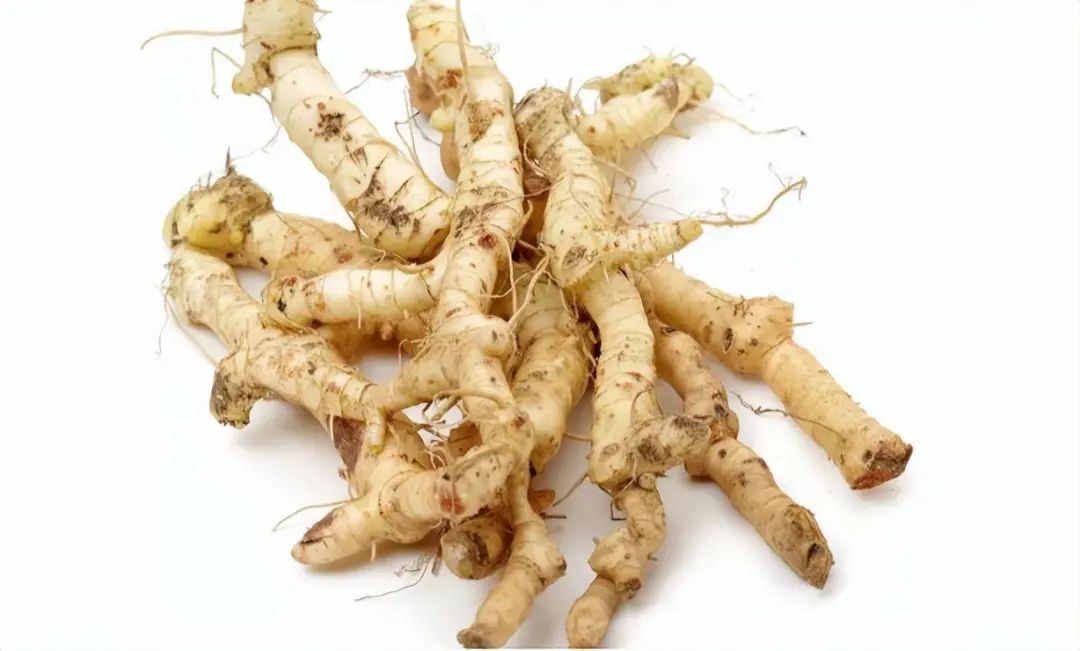

Huang Jing
Huang Jing
Huang Jing has a sweet taste and a neutral nature, entering the spleen, lung, and kidney meridians. It is known for its ability to nourish yin, moisten the lungs, tonify the kidneys, and benefit the spleen and qi, making it a dual tonic for both qi and yin.
The term Huang Jing refers to its dried rhizome, which is used as both a food and medicinal herb. The fleshy roots of Huang Jing only begin to grow in the third year, growing only one segment per year, thus it absorbs the essence of the land.
From the text of Baopuzi: “Obtaining the qi of the earth and acquiring the essence of heaven and earth”
Ancient scholars believed that Huang Jing belongs to the category of medicinal herbs that absorb the essence of the earth, hence it is referred to as “Wu Ji Zhi” in the Wufu Jing. Additionally, because Huang Jing can be chewed and eaten to satiate hunger, the famous physician of the Southern and Northern Dynasties, Tao Hongjing, also called it “the food of immortals”.
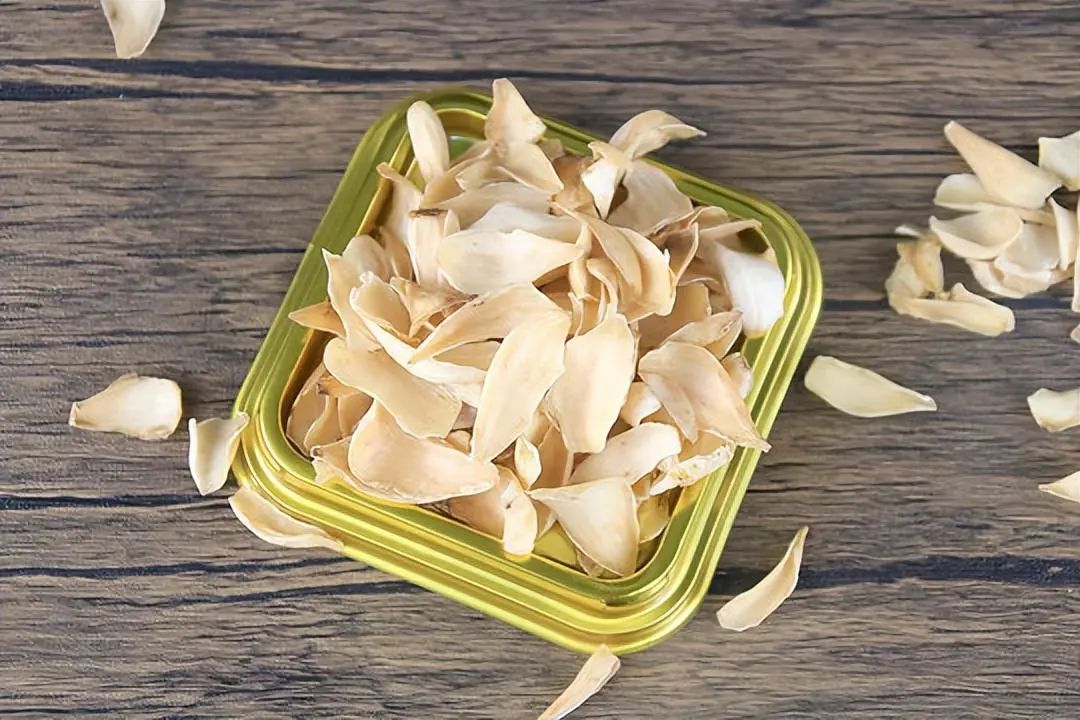

Yu Zhu
Yu Zhu
Yu Zhu has a sweet taste and a slightly cold nature, entering the lung and stomach meridians. It is known for its effects of clearing heat, moistening the lungs, nourishing yin, extinguishing wind, benefiting the five organs, nourishing qi and blood, and providing a balanced and moistening effect while also dispelling wind-heat.
It nourishes without being greasy, and it is neither too cold nor too dry. It acts on the spleen and stomach, thus long-term use does not harm these organs. Furthermore, Yu Zhu has anti-aging and skin moisturizing properties.
The first ancient text on Chinese medicine, the Shennong Bencao Jing, classifies herbs into three grades: upper, middle, and lower. Upper-grade herbs are non-toxic and primarily used for tonifying and replenishing, suitable for long-term use, and Yu Zhu is one of these upper-grade herbs.
Yu Zhu has the effects of clearing heat, nourishing yin, and generating fluids, and is commonly used in clinical practice to treat symptoms such as dry mouth and thirst caused by excessive heat in the upper jiao. Huang Jing tonifies qi, nourishes yin, and moistens the lungs, making it useful for treating fatigue and dry cough. The combination of these two herbs tonifies the spleen, benefits qi, nourishes yin, and generates fluids, greatly aiding in the improvement of yin deficiency and fluid deficiency.

Remember to follow us!
to follow us!
Editor’s Recommended Articles
1. A simple herbal remedy can tonify lung qi, spleen qi, and kidney qi, boosting immunity
2. Waking up naturally at 3-5 AM? It may be due to lung qi deficiency; consider these three herbs to tonify lung qi and improve insomnia
3. So precious! Over 800 folk remedies, there’s no illness that can’t be treated; save for future reference!
4. Understanding each herbal resource compilation
Like is a form of encouragement Share to spread joy

