Cupping therapy, known as “Ba Huo Guan” in Chinese, is a traditional method of treatment that has been passed down through generations in China, gaining popularity and trust among people. It is considered safe, has no side effects, and can prevent and treat diseases while enhancing physical health. Although many have experienced cupping, there is still a lack of understanding about it and what precautions to take. Below, we will provide a brief introduction to cupping therapy.

Cupping therapy, historically known as “Jiao Fa” (角法), is also referred to as “Suction Tube Therapy” or “Cupping”. It is based on the theory of meridians in Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) and utilizes cups as tools. By using fire or suction methods to remove air from the cups, a negative pressure is created, allowing the cups to adhere to acupuncture points (腧穴, shùxué) or specific areas of the body. This causes local skin congestion and even bruising, aiming to adjust bodily functions and achieve disease prevention and health enhancement through external treatment methods in TCM.
History of Cupping Therapy
Cupping therapy has a history of over two thousand years. As early as the pre-Qin period, people used animal horns (such as cow or sheep horns) to create hollow tubes. After puncturing abscesses, they would use these tubes to draw out pus and blood for therapeutic effects. Since animal horns were used as tools, this method was called “Jiao Fa”. The earliest written record of this practice can be found in the “Fifty-Two Disease Formulas” (《五十二病方》) from the Western Han dynasty: “For hemorrhoids located beside the orifice, larger ones like jujubes, smaller ones like jujube pits: use a small horn to suck it out, as if it were two dou of cooked rice, and then open the horn.” This passage describes the treatment of hemorrhoids using the “Jiao Fa” method, which includes the use of tools, operation sites, suction methods, and duration, aligning with the four essential elements of cupping therapy, marking the earliest record of using negative pressure for disease treatment.
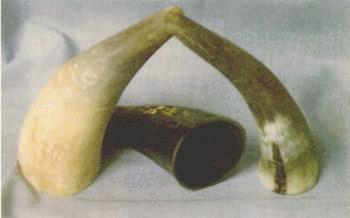
During the Eastern Jin dynasty, Ge Hong mentioned the use of the horn method for treating swelling in his work “Emergency Prescriptions Kept in the Sleeve” (《肘后备急方》). By the Sui and Tang dynasties, people began to replace animal horns with processed bamboo cups. By the Song, Jin, and Yuan dynasties, bamboo cups completely replaced animal horns, and the methods became more refined, leading to the name change from “Jiao Fa” to “Suction Tube Method”. In the Ming and Qing dynasties, cupping therapy was widely used in surgery, with records found in many surgical texts such as “Yizong Jinjian” (《医宗金鉴》) and “Surgical Great Accomplishment” (《外科大成》). After the founding of New China, cupping therapy underwent continuous improvement and diversification, with glass cups becoming the primary tool used today.

Effects of Cupping Therapy
Cupping therapy acts on the skin surface, adjusting the functions of the internal organs (脏腑, zàngfǔ), meridians (经络, jīngluò), and the flow of qi (气, qì) and blood (血, xuè) through holistic effects. It helps to strengthen the body and expel pathogens, balancing yin (阴, yīn) and yang (阳, yáng). Through self-regulation, cupping therapy promotes qi circulation, invigorates blood flow, relaxes muscles, alleviates swelling and pain, and dispels wind and dampness, providing beneficial stimulation to restore normal bodily functions.
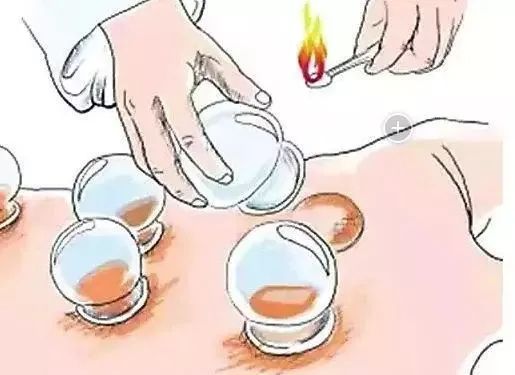
Indications for Cupping Therapy
Cupping therapy has a wide range of indications, whether for invigorating blood circulation and removing stasis, relieving dampness and itching, or warming and promoting yang qi. It holds a significant place in external treatment methods of TCM. It can treat:
1、Common colds, coughs, stomach pain, indigestion, and other internal medicine diseases;
2、Cervical spondylosis, stiff neck, lumbar disc herniation, lumbar muscle strain, shoulder periarthritis, rheumatic pain, and other orthopedic diseases;
3、Menstrual disorders, dysmenorrhea, mastitis, and other gynecological diseases;
4、Herpes zoster, eczema, and other dermatological diseases;
5、Toothache, temporomandibular joint disorder, sore throat, and other ENT diseases.
Application of Cupping Therapy
Depending on the location of the lesion and the nature of the disease, cupping therapy has different application methods.
1.Single Cupping Method
This involves using one cup alone. It is applied to conditions with a clear and limited range of lesions or fixed tender points.
2.Multiple Cupping Method
This involves using multiple cups simultaneously, also known as the排罐法 (pái guàn fǎ). It is suitable for conditions with a wide range of lesions or multiple selected points.
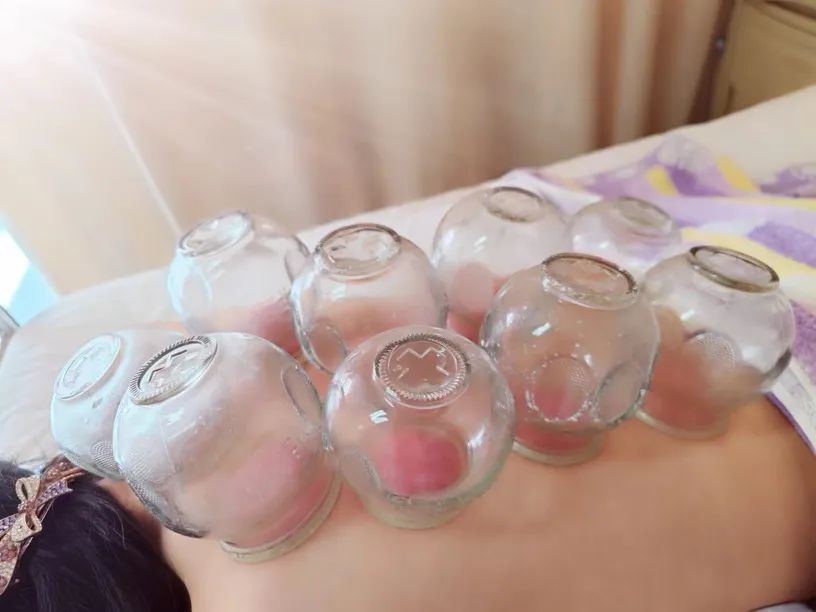

Commonly, several cups are applied to multiple points or acupuncture points, with several to dozens of cups used. For example, multiple cups may be arranged in a line along a specific meridian or muscle bundle on the skin surface.
3.Retention Cupping Method
Also known as the sitting cupping method, this involves leaving the cup in place for 5-15 minutes after suction, allowing the superficial skin and muscles to be drawn into the cup. Mild cases result in skin redness, while severe cases may lead to subcutaneous bruising. This method is often used for treating wind-cold-damp bi syndrome and pain in the neck, shoulders, waist, and legs.
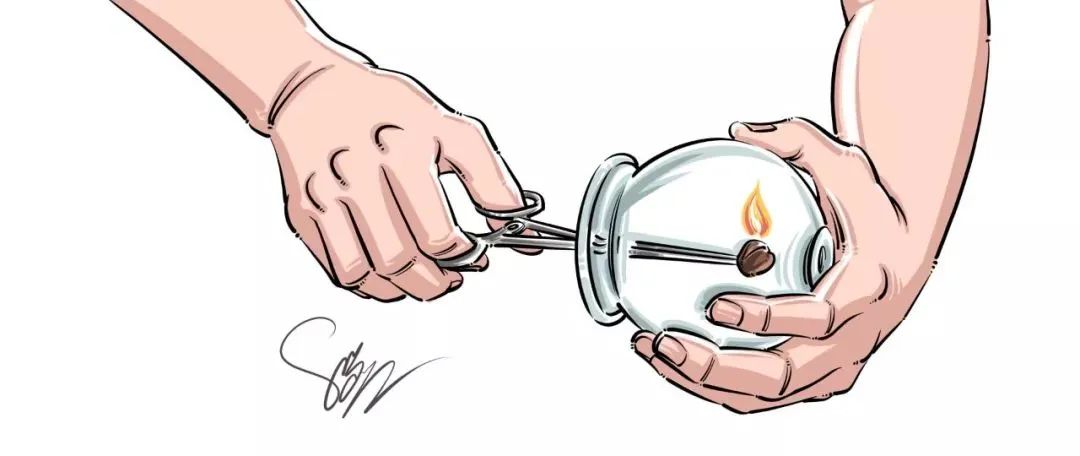
4.Flash Cupping Method
This involves using the flash fire method to apply the glass cup to the treatment area, then immediately removing it, repeating the suction and removal multiple times until the skin turns red or the bottom of the cup becomes warm. This method is mainly used for facial paralysis.

5.Sliding Cupping Method
Also known as the pushing cupping method. The operation involves applying a lubricant such as petroleum jelly to the cupping area, while also applying oil to the rim of the glass cup. After suctioning with the flash fire method, the cup is held at the bottom, slightly lifted in the direction of movement, and pulled along the muscle, bone, or meridian path, repeating until the skin in the sliding area turns purple-red. This method is mainly used for larger areas with thick muscles, such as the lower back, and is often used for colds and coughs.
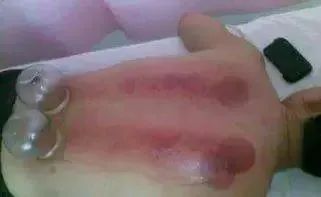
6.Needle Cupping Method
This refers to a treatment method that combines acupuncture (针刺, zhēncì) with cupping therapy.
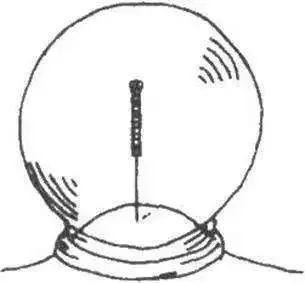
(1)Retention Needle Cupping Method, abbreviated as Needle Cupping (针罐, zhēn guàn).
This involves leaving the needle in place while applying the cup to the area centered around the needle for about 5-10 minutes. Once the skin is red and congested or bruised, the cup is removed, and the needle is withdrawn. This method enhances the combined effects of acupuncture and cupping. However, it is not suitable for the chest and back areas, as the negative pressure in the cup may deepen the needle insertion, potentially causing pneumothorax.
(2)Bloodletting Cupping Method, also known as Pricking and Cupping Method (刺络拔罐法, cì luò bá guàn fǎ). After disinfecting the skin at the treatment site, a plum blossom needle or three-edged needle is used to prick or puncture the skin to induce bleeding, followed by applying the fire cup to the punctured area to enhance the bloodletting treatment effect. The amount of blood drawn depends on the condition, ranging from a few drops to 3-5 ml. Generally, the cup is left in place for 10-15 minutes after bloodletting.
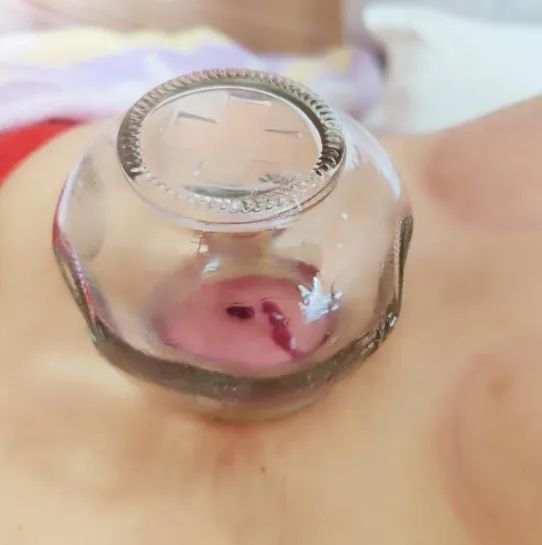
Precautions for Cupping Therapy
Although there are many methods of cupping, the basic requirements are consistent. Cupping should be performed in a clean, well-ventilated indoor environment, avoiding direct fan blows in summer and ensuring warmth in winter. Both the practitioner’s hands and the cupping area on the patient should be clean, and the cupping tools must be properly disinfected. Cupping therapy should not be performed after overeating, extreme hunger, excessive sweating, severe thirst, intoxication, or fatigue. It is also advised not to bathe within 3 hours after cupping.
Why are there cup marks after cupping?
After cupping, cup marks are usually left on the skin, indicating the internal conditions of cold, heat, deficiency, or excess. If the cup marks are bright red, it generally indicates a yang condition or heat condition; if the marks are light red, it often indicates a yin condition or cold condition; if blisters or water droplets appear, it usually indicates dampness; if there are no bruises or the redness disappears quickly after cupping, it suggests that the pathogenic factors are mild or nearly resolved.
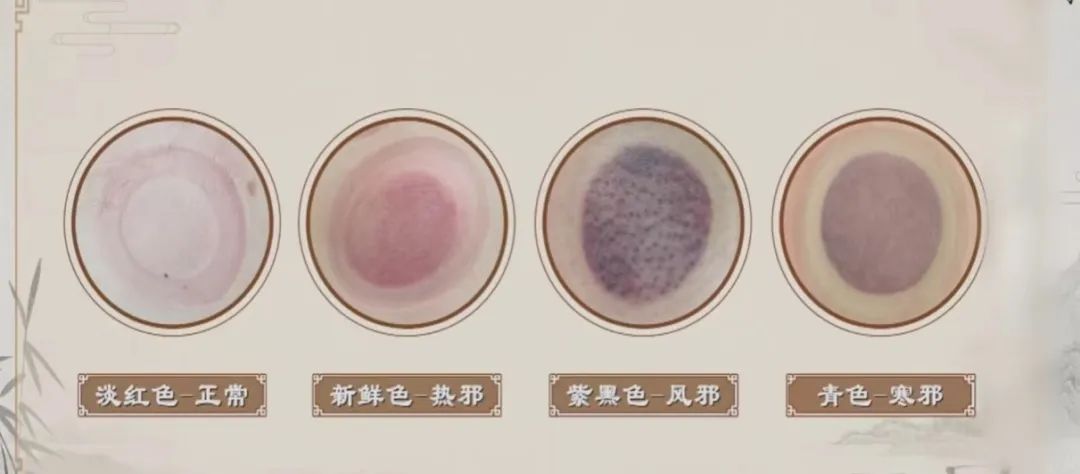
Next, we will briefly introduce the diagnosis based on cup marks:
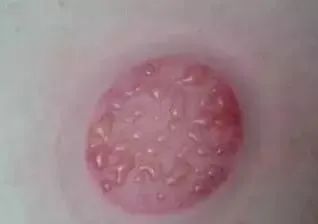
1.When cup marks show water vapor, blisters, or edema, it indicates that the patient has excess dampness, cold, or has been affected by cold and dampness;
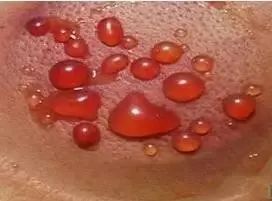
2.When cup marks present as blood-red or black-red blisters, it indicates a pathological reaction of long-term illness with dampness and blood stasis;
3.When cup marks are purple-red or purple-black, without any heat or redness, it indicates that the patient has cold with blood stasis, with varying severity;

4.When cup marks are purple-red or purple-black, or if there is a rash that is slightly painful to touch, accompanied by body heat, it indicates the presence of heat toxin in the patient;
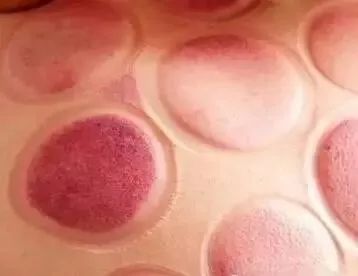
5.When cup marks are slightly itchy or show skin patterns, it indicates the presence of wind syndrome in the patient;

6.When cup marks show no color change and feel cool to the touch, it indicates a deficiency-cold syndrome in the patient.
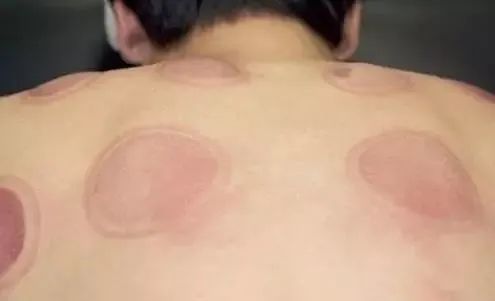
What to do if blisters appear after cupping?
The appearance of blisters after cupping is essentially due to the skin being “filled with water”. Pathological products such as phlegm, fluids, and dampness are drawn into the skin under negative pressure, forming blisters. The treatment methods are as follows:
1.Small blisters do not require treatment; just prevent infection and allow them to heal naturally;
2.Large blisters should be punctured with a sterilized needle, treated with anti-inflammatory medication, and kept clean; they will heal in time;
3.If the blisters are too large or numerous, it is advisable to seek medical attention.
Who should avoid cupping?
1.Individuals with skin allergies or skin injuries;
2.Pregnant women and women during menstruation;
3.After heavy meals;
Which areas should not be cupped?
Areas with skin allergies, ulcers, edema, and regions over the heart, major blood vessels, lower abdomen, navel, chest area, delicate skin, damaged areas, varicose veins, scarred areas, nipples, and bony protrusions should not be cupped.
What are the benefits of cupping therapy?
1.Enhances the body’s immune system.
2.Improves skin temperature, accelerates metabolism, and speeds up recovery from diseases.
3.Alters blood oxygen levels and regulates immune function.
4.Facilitates the elimination of metabolic waste and promotes blood circulation.
5.Unblocks meridians, relieves fatigue, and reduces stress.
People’s Hospital of Malong District, Qujing City

Contributed by: Zhang Liling Reviewed by: Wang Wenbing Edited by: Zhang Weifeng
 If you like our articles, please give us a thumbs up.
If you like our articles, please give us a thumbs up.

