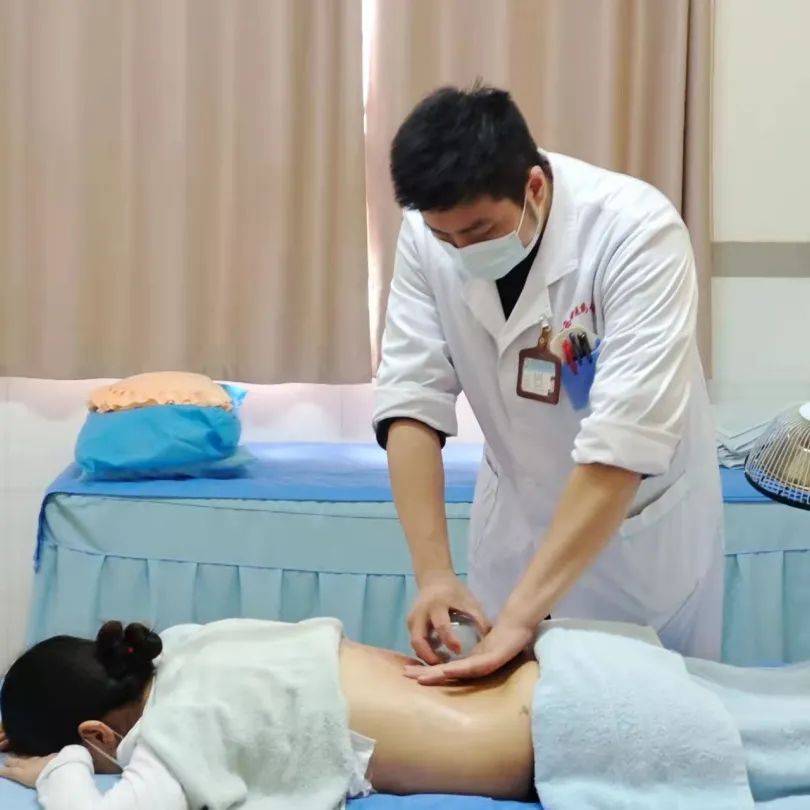

Zou Guan Therapy is one of the external treatment methods in Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), integrating the effects of warm moxibustion, cupping, gua sha, and herbal therapy. It has the functions of strengthening the body’s resistance, expelling pathogenic factors, promoting circulation, and dispelling wind and cold.
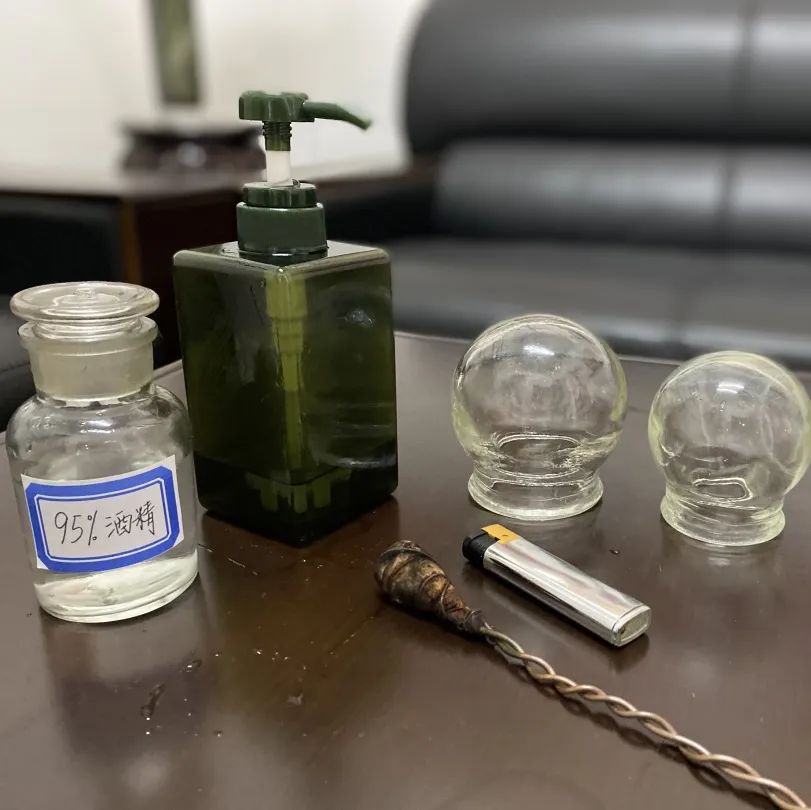


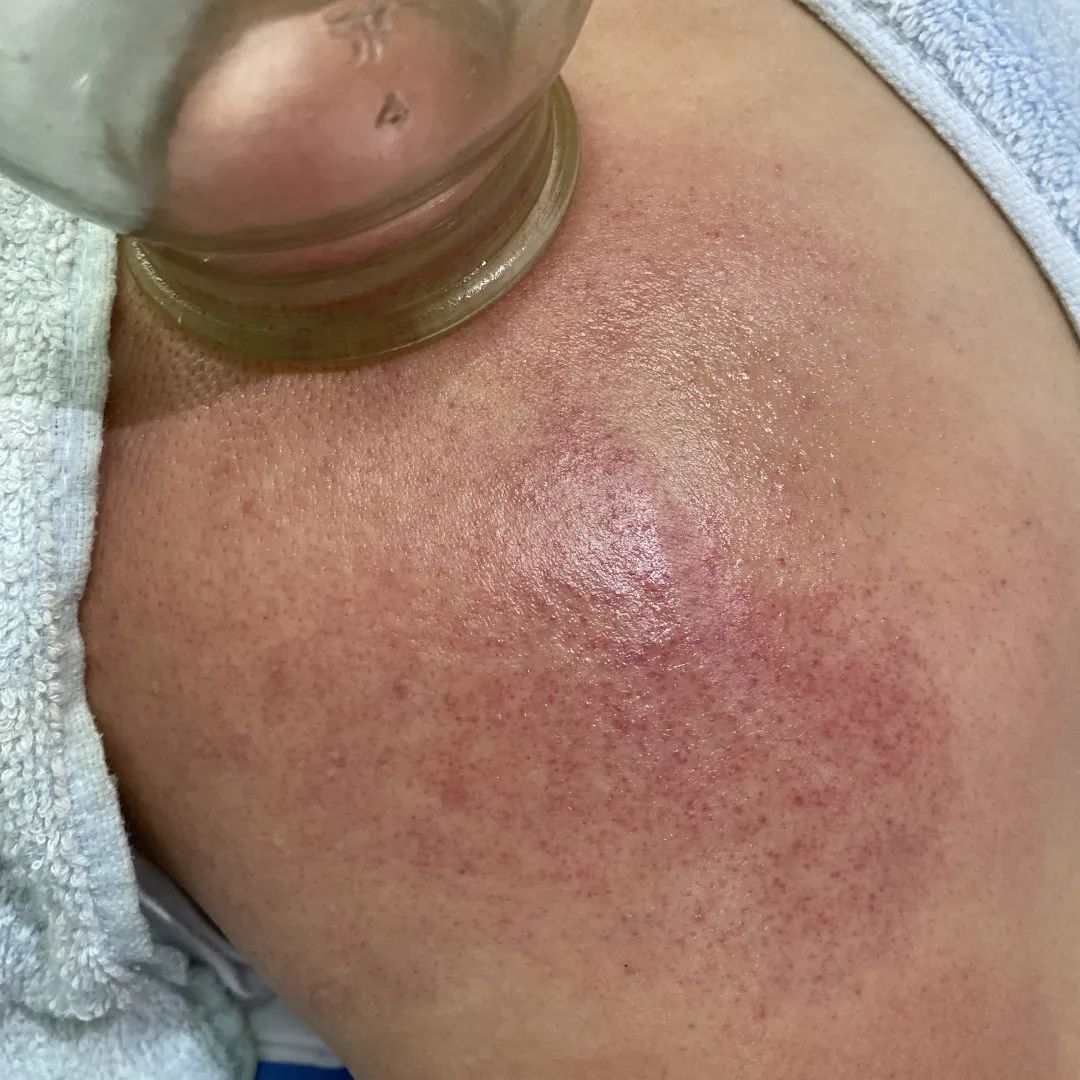
Zou Guan, also known as pushing cupping, involves first applying a lubricant such as petroleum jelly to the intended area. Then, using the flash fire method, the cup is suctioned onto the skin. The practitioner holds the cup and applies even pressure, moving it back and forth along a designated path until the skin in the cupping area becomes red and congested, at which point the cup is removed.
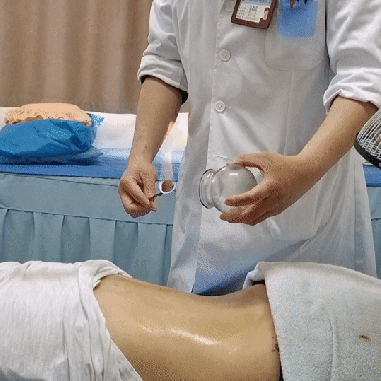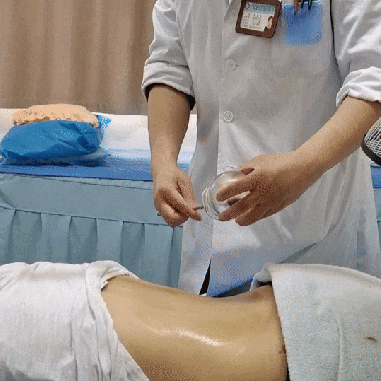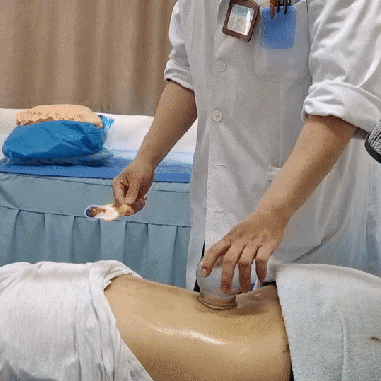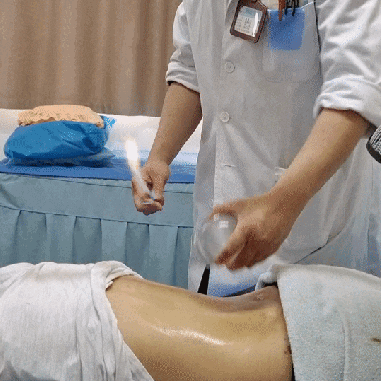
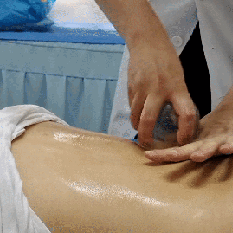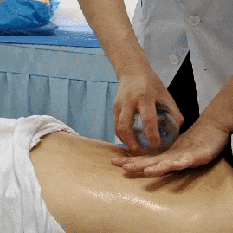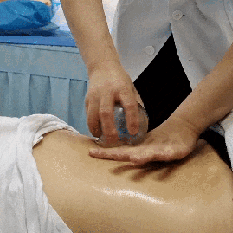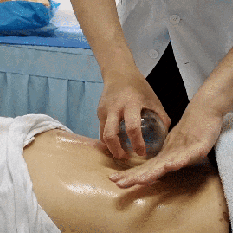
Case Study
Patient: Luo, female, 37 years old.
Chief complaint: Dizziness, soreness, and pain in the neck, shoulders, and lower back for 1 week.
History of present illness: The patient experienced dizziness due to accidental exposure to cold 1 week ago, presenting as a heavy sensation in the back of the head, which affected her work. She also reported pain in the neck, shoulders, and lower back, with noticeable stiffness and soreness, but no other significant discomfort. The tongue was pale with a white greasy coating, and the pulse was floating and tight.
Diagnosis: The symptoms were attributed to an external invasion of wind, cold, and dampness causing bi syndrome. After manual therapy to relieve muscle knots, the patient’s pain significantly decreased, but she still experienced some pulling, soreness, and a heavy sensation in the head. Following a TCM painless Zou Guan treatment, the soreness completely resolved, and her mind was clear with a rosy complexion.
Color Reflection
1. Dark purple-black cupping marks with spots: Generally indicate blood stasis due to cold obstruction;
2. Bright red cupping marks: Generally indicate deficiency of both Qi and Yin or excess heat due to Yin deficiency;
3. Dark red cupping marks: Generally indicate internal heat or high blood lipids;
4. No color change in cupping marks, cool to the touch: Generally indicate deficiency cold syndrome;
5. Cupping marks with skin texture or slight itching: Generally indicate wind or dampness on the surface;
6. Cupping marks that are moist red or light purple with blisters or watery appearance: Generally indicate significant internal cold dampness.
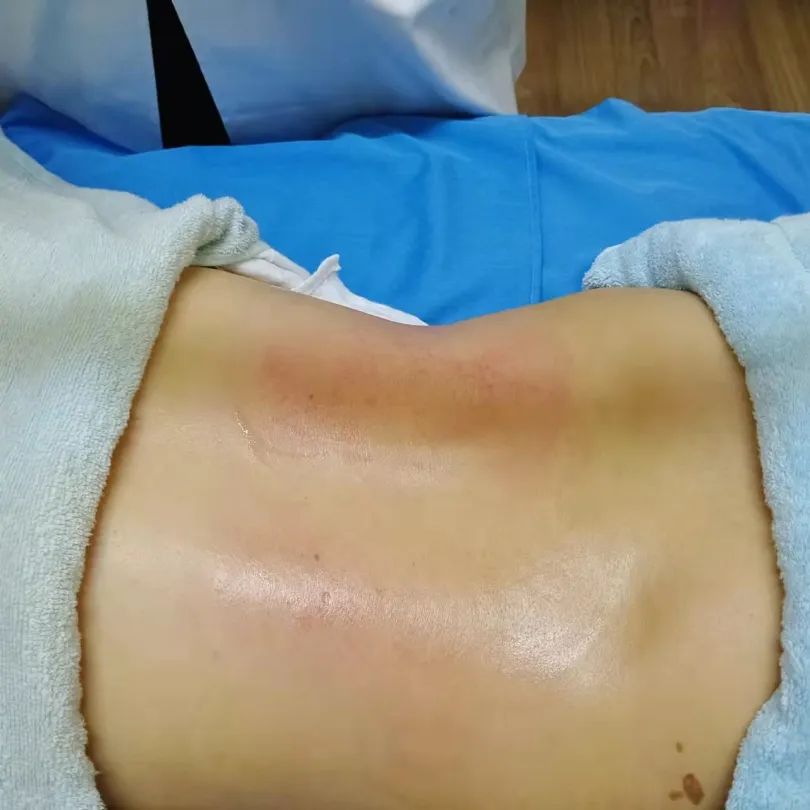
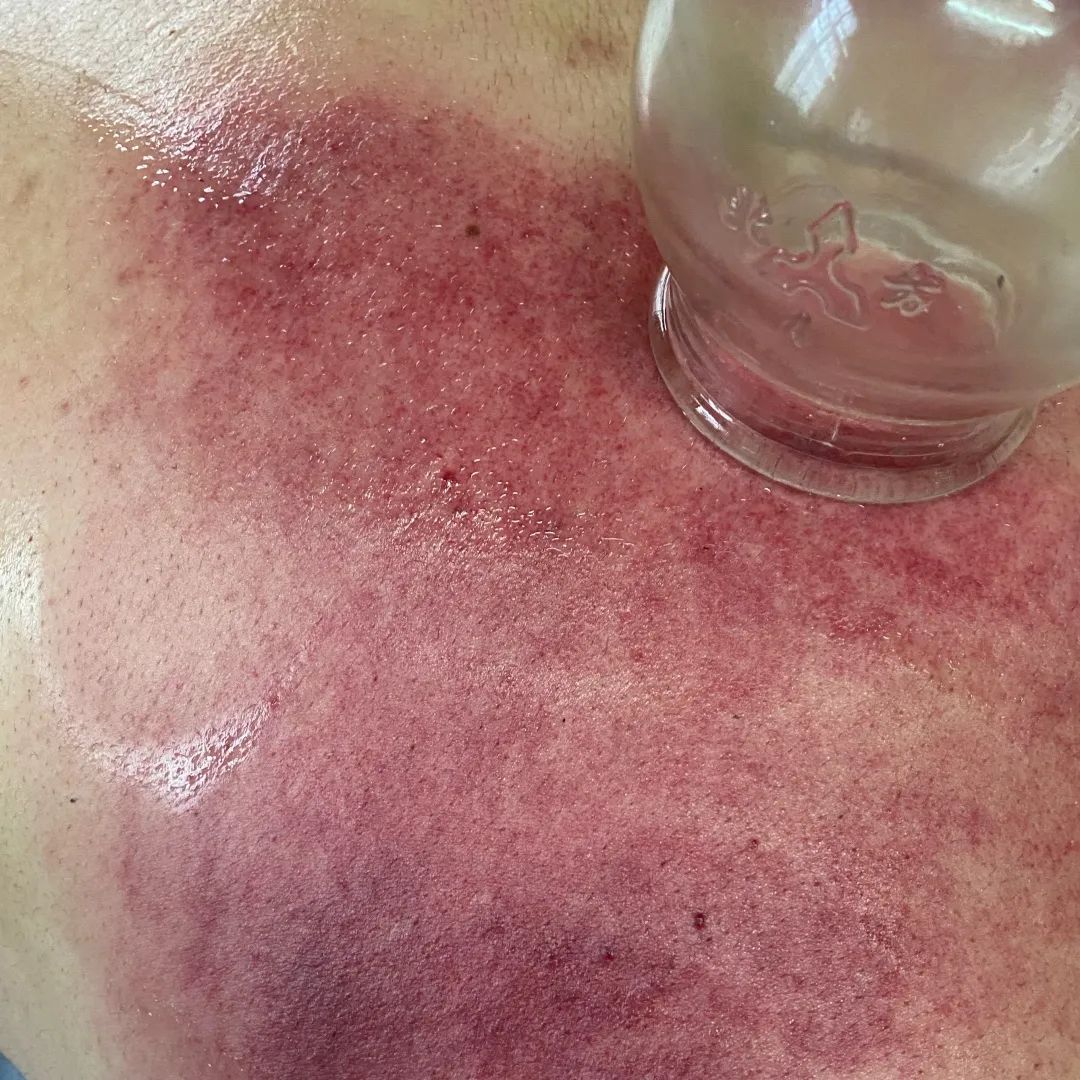
Indications
Joint pain
Wind-cold-damp bi syndrome
Neck, shoulder, lower back, and leg pain
Acute and chronic soft tissue injuries
Common cold
External headache and others
Contraindications
1. Pregnant women and during menstruation;
2. Individuals with bleeding disorders or tendencies;
3. Skin allergies, ulcers, or edema.
Precautions
1. Avoid bathing immediately after Zou Guan treatment to prevent catching a cold;
2. If there is localized itching, do not scratch to avoid infection;
3. Avoid raw, cold, spicy, and irritating foods during treatment;
4. Follow medical advice.
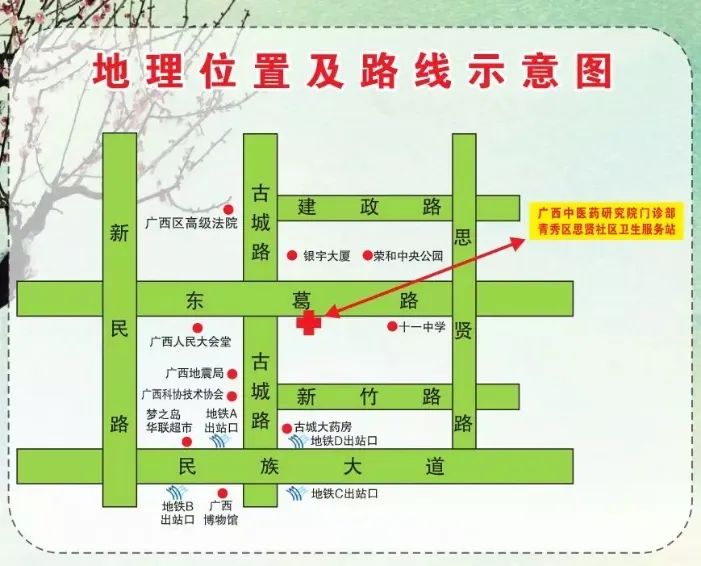
Consultation Location
20-1 Dongge Road, Outpatient Department of Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine
4th Floor, Acupuncture and Tuina Department
Working Hours
Monday to Friday 8:30 AM – 12:00 PM
3:00 PM – 6:00 PM
Saturday on rotation, please consult each physician for detailed times.
Contact numbers: Dr. Chen 13878809036
Dr. Huang 15807812843
Dr. Zeng 15676725968
Inheritance and Innovation
END
Harmony and Openness
Reviewed by: Chen Hong
Edited by: Chen Yizuo, Huang Yifang, Zeng Shirui
Previous classic reviews (click title to view immediately)
◆
Eliminate hidden dangers, prevent accidents, ensure safety – Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine conducts “March 3” and “Qingming Festival” pre-festival safety production inspections
◆
The fifth party branch of Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine held the 2021 annual organizational life meeting
◆
Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine held the second plenary meeting of the fourth staff representative assembly and the fourth member representative assembly of the labor union