Mandragora (Mandrake)
Toxic, used as a sedative, can relax muscles. It is a major component of ancient anesthetic formulas and Yunnan Baiyao. Different parts (flowers, seeds, leaves, roots) have various uses in folk medicine, treating different diseases. Chewing ten seeds can treat insomnia.

2鬼针草 (Ghost Needle Grass)
Can be eaten as a vegetable when young and is quite tasty. It is said to be effective in lowering transaminases and can disperse liver heat.

3苦菜 (Bitter Herb)
In Yunnan, people refer to green vegetables as bitter herbs, but the one in the picture is the true bitter herb. It is listed as a superior herb in ancient texts, beneficial for the stomach and gallbladder, and has anti-tumor properties, making it suitable for modern people.
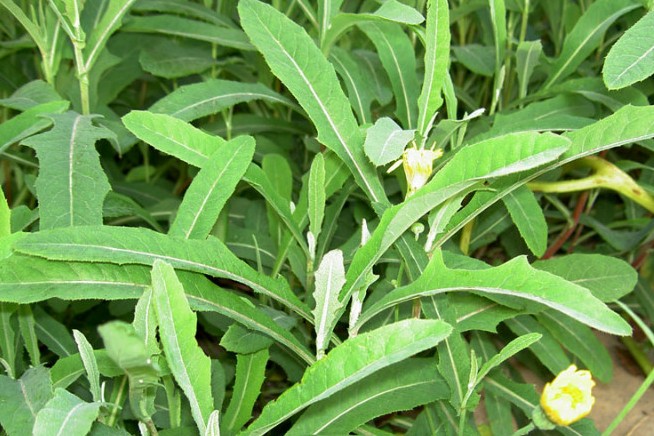

4葵菜 (Sunflower Greens)
There are wild and cultivated varieties. Listed as a superior herb in the “Shennong’s Herbal Classic”, it is a vegetable beneficial for health, though most regions are unaware of its edibility. The wild variety can benefit the five organs, with roots used to clear kidney pathways and leaves cooked with brown sugar to treat sores effectively.

5荨麻 (Nettle)
Some texts mention it as toxic, while others say it has mild toxicity. In the past, it was often used medicinally, but now it is more commonly consumed as a vegetable. Its stinging hairs can cause a prickling sensation upon contact. It can be made into soup or fried with eggs for a delicious dish. It treats children’s coughs and toothaches due to wind-heat. One patient reported that its roots have remarkable effects on treating urticaria.

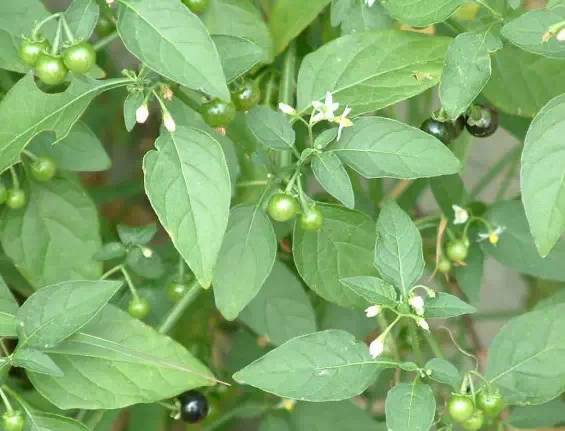
6龙葵 (Black Nightshade)
Clears heat and treats tumors, also a commonly used wild vegetable, with liver-protecting, stomach-strengthening, and vision-improving properties.

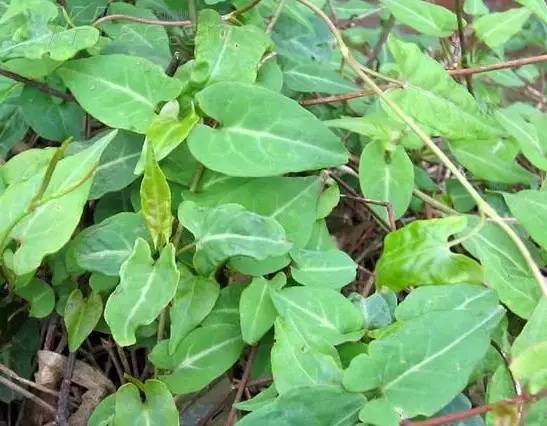
7黄袍 (Yellow Robe)
The fruit is delicious, appetizing, and softens the liver, making it good for children.

8何首乌 (Fo-Ti)
Used to tonify qi and blood, it has a mild flavor and can be consumed regularly. Raw form detoxifies and promotes bowel movements without harming yin. The vine has calming and blood-nourishing effects.

9乌袍 (Black Robe)
The fruit has similar effects as Yellow Robe. The leaves and tender tips, cooked with brown sugar, are effective for treating liver-related diarrhea without side effects.

10野薄荷 (Wild Mint)
Tastes and acts similarly to cultivated mint, disperses wind-heat, eliminates foul qi, and detoxifies from fish and shrimp.

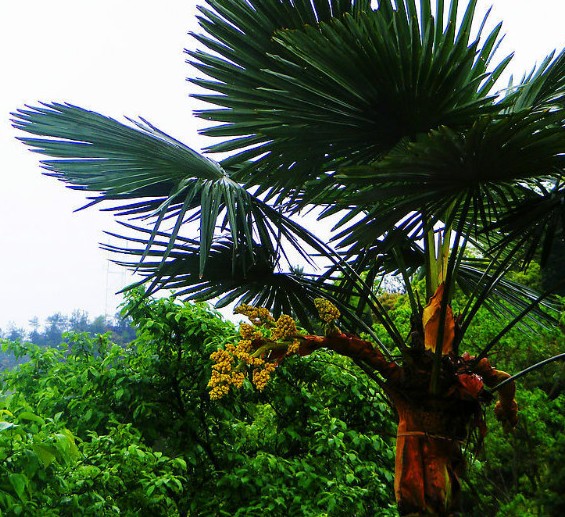
11棕榈 (Palm Grass)
Used for its fibers, flowers, and roots, it has astringent properties and can stop bleeding, particularly effective for gynecological discharge.

12灰灰菜 (Gray Herb)
Generally not used medicinally, it was used in ancient recipes to make winter ash, now rarely used, but can clear lung and abdominal stagnation.
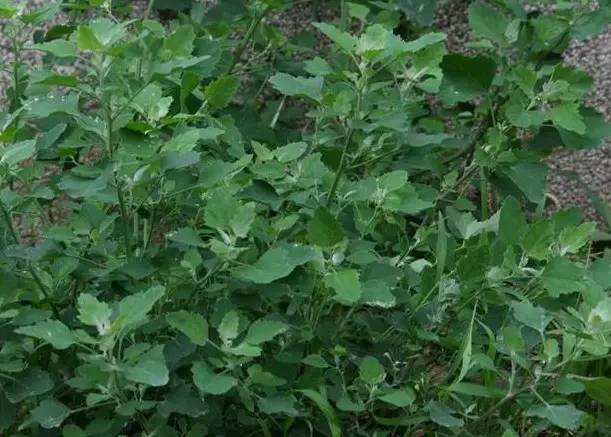

13夏枯草 (Summer withering grass)
Grows seasonally, harmonizes blood, draws yang into yin, and treats insomnia. Salty in taste, it can soften hardness and disperse accumulations. Non-toxic, the tender shoots can be used as a vegetable, but in Yunnan, many vegetables are available, and few people eat it.

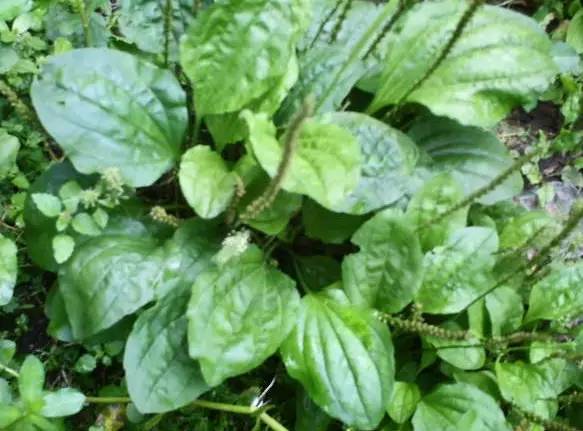
14车前草 (Plantago)
Used in pharmacies, both the seeds and the grass have similar effects, clearing bladder heat, benefiting kidney qi, and preventing stones. Additionally, it can draw lung heat out through urination, treating coughs. There are large-leaf and small-leaf varieties, with the small-leaf being superior.

15铁蒿 (Iron Wormwood)
Many types of wormwood exist, some for medicinal use, some for food, and some for both. Pharmacies often use Qinghao (Sweet Wormwood) and Huanghao (Yellow Wormwood). Iron Wormwood can clear empty heat and is similar to Qinghao, with a less bitter taste. During difficult times, common people also consume it to stave off hunger, and it has health benefits, but unfortunately, it is not researched or developed.

16金银花 (Honeysuckle)
All parts of the honeysuckle can be used medicinally and is one of the precious Chinese medicinal materials recognized by the State Council. Honeysuckle has functions of clearing heat and detoxifying, antibacterial and anti-inflammatory, and liver-protecting. Clinically applied in treating respiratory infections, headaches, and sore throats. 1. Antibacterial, honeysuckle inhibits Staphylococcus, Shigella, and Streptococcus pneumoniae. 2. Honeysuckle can neutralize cholesterol, reducing intestinal absorption of cholesterol. 3. Effective for influenza, pneumonia, coronary heart disease, and hyperlipidemia, it enhances immunity and delays aging.
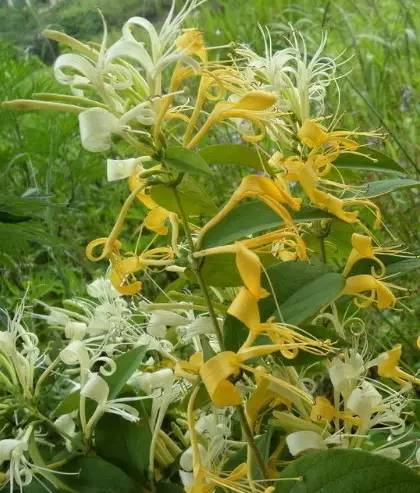

17蒲公英 (Dandelion)
Taste and function: Sweet, slightly bitter, cold. Clears heat and detoxifies, reduces swelling and disperses lumps. Main indications: Upper respiratory infections, conjunctivitis, epidemic mumps, mastitis, gastritis, dysentery, hepatitis, cholecystitis, acute appendicitis, urinary tract infections, pelvic inflammatory disease, and boils. Application references: 1. For epidemic mumps and mastitis: fresh dandelion crushed and applied to the affected area. 2. For chronic osteomyelitis: 15 grams of dandelion, 1 tablespoon of fermented rice, mixed with water after meals. 3. For boils: dandelion, wild chrysanthemum, honeysuckle, and ground herb each 30 grams, decocted in water for consumption.
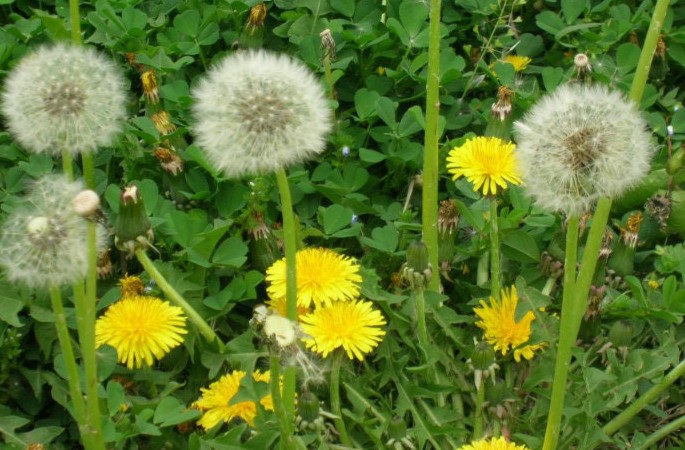

18鸭跖草 (Duckweed)
Main indications: 1. Urinary obstruction. Use 1-2 ounces of duckweed and 1-2 ounces of plantago, crush to extract juice, add a little honey, and take on an empty stomach. 2. Dysentery (red and white). Use duckweed to decoct soup for daily consumption. 3. Throat obstruction. Use duckweed juice to gargle. 4. Hemorrhoids and swelling. Use duckweed and Bichan flower together, crush and apply to the affected area. Other names: Bamboo joint vegetable, duckweed, ear ring grass, blue flower vegetable, green butterfly, triangle vegetable, three pod vegetable, bamboo grass, blue flower water bamboo grass, light bamboo leaves. Taste and properties: Sweet, bland, cold. Enters the lung, stomach, and small intestine meridians. Dosage: 15-30g; fresh product 60-90g. For external use, apply as needed. (1) Used for external heat, or heat disease with persistent fever, or throat swelling and pain, and for boils and ulcers. This product is sweet and cold, with heat-clearing and detoxifying effects. For external heat or persistent fever from heat disease, it can be used alone or combined with other heat-clearing herbs. For throat redness and swelling, it can be combined with dandelion, black plum, or earth cow knee, and big green leaves. For treating boils and ulcers, it can be combined with ground herb, dandelion, and wild chrysanthemum.
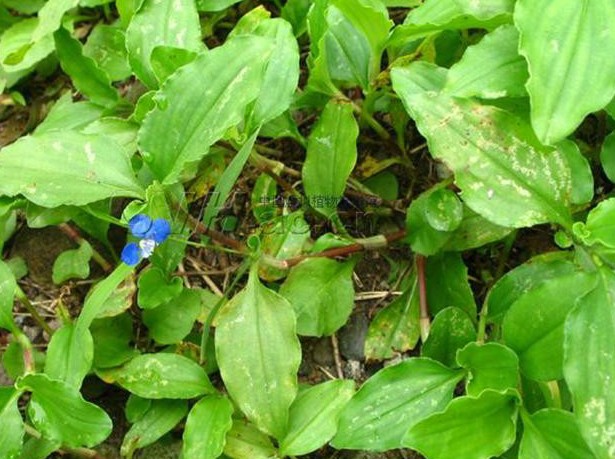

19垂盆草 (Hollow Leaf Grass)
Grows near water, has a sweet, bland, slightly sour, and cool taste. Can clear heat and detoxify, reduce swelling, and promote urination. Main indications: For burns, boils, snake bites, and cancerous tumors: fresh grass 1-4 ounces, wash, crush, and take juice. Dried product 5-10 grams, decocted for consumption. For external use, fresh grass as needed, wash, crush, and apply to the affected area.

20灯笼草 (Lantern Grass)
This one needs no introduction, as it is often foraged in childhood. It has a sour taste, clears heat and detoxifies, promotes urination, stops bleeding, and reduces swelling. Main indications: (1) Sore throat, lung abscess, mumps. (2) Urinary obstruction, hematuria. For the above conditions, use 3-5 grams, decocted for consumption. (3) Gum swelling and pain: fresh grass washed, crushed, soaked in vinegar, and gargled. (4) Pemphigus: fresh whole grass washed, juice applied to the affected area. Note: This herb has a uterine contraction effect, contraindicated for pregnant women.

21苍耳子 (Cocklebur)
Taste: Warm, pungent, bitter. Main indications: Dispels wind and dampness, opens nasal passages. Used for wind-cold headaches, nasal congestion, wind rash itching, and dampness obstruction. Note: The whole plant of cocklebur is also medicinal, treating acute and chronic gastroenteritis and bacterial dysentery.

22马兰 (Malva)
Also a common wild vegetable. Other names: Malva head, stair front chrysanthemum, chicken intestine, red stem vegetable, etc. It belongs to the Malva genus of the mallow family. The whole plant is medicinal. It is cool in nature and pungent in taste. It enters the hand Taiyin lung and foot Jueyin liver meridians. It cools blood, clears heat, promotes dampness, and detoxifies. It treats hemoptysis, epistaxis, blood dysentery, traumatic bleeding, malaria, jaundice, edema, turbid urination, sore throat, throat obstruction, hemorrhoids, boils, and snake bites. Dosage: For internal use: decocted, 3-6 grams (fresh 1-2 ounces); or juice. For external use: crush and apply, grind into powder for mixing or decocted for washing.
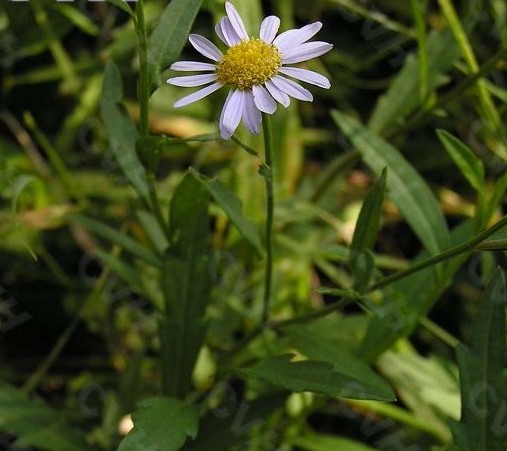

23荠菜 (Shepherd’s Purse)
A very common wild vegetable, it can be stir-fried, cold tossed, or used as dumpling filling.
Other names: Protective grass, fragrant field mustard, and so on. It belongs to the cruciferous family. The whole plant is medicinal. It is neutral in nature and sweet in taste. It enters the hand Shaoyin, Taiyin, and foot Jueyin meridians. It harmonizes the spleen, promotes urination, stops bleeding, and brightens the eyes. It treats dysentery, edema, gonorrhea, chyluria, hemoptysis, blood in stool, menorrhagia, and red painful eyes. Dosage: For internal use: decocted, 3-5 grams (fresh 1-2 ounces); or in pills or powder. For external use: grind into powder for mixing, crush and apply, or juice for application.

24小蓟 (Small Thistle)
One of the wild vegetables. Other names: prickly vegetable, cat thistle, prickly radish, knife vegetable, wild red flower, etc. It belongs to the thistle genus of the Asteraceae family. The whole plant or roots are medicinal. It is cool in nature and sweet in taste. It enters the liver and spleen meridians. It cools blood, dispels stasis, and stops bleeding. It treats hemoptysis, epistaxis, hematuria, blood dysentery, blood collapse, acute infectious hepatitis, traumatic bleeding, and boils. Dosage: For internal use: decocted, 1.5-3 grams (fresh 1-2 ounces); or juice or grind into powder. For external use: crush and apply or decocted for washing. Contraindications: Avoid in cases of spleen and stomach deficiency without stasis.
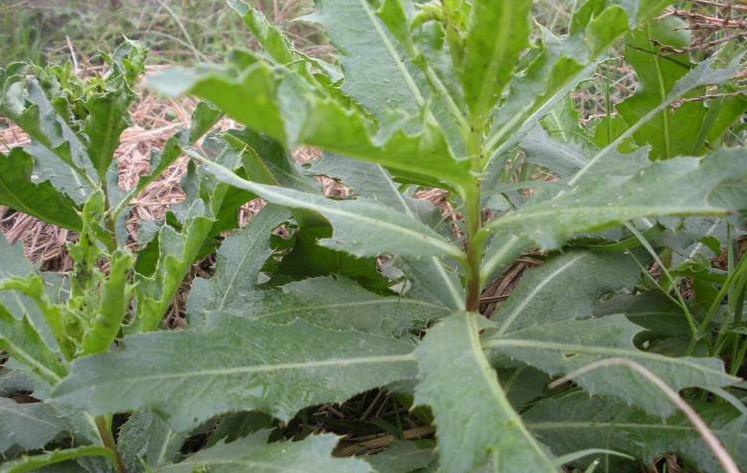

25水芹菜 (Water Celery)
One of the wild vegetables. It belongs to the Apiaceae family. The whole plant is medicinal. It is cool in nature and pungent in taste. It calms the liver, releases the exterior, and promotes rashes. It treats early-stage measles, hypertension, and insomnia. If foraged, be cautious of a toxic variety that is robust and generally grows scattered, while water celery grows in patches near water or wetland.

26天胡荽 (Coriander)
Other names: broken copper coin, chicken vegetable, pot coriander, etc. It belongs to the Apiaceae family. The whole plant is medicinal. It is cold in nature and bitter and pungent in taste. It clears heat, promotes urination, reduces swelling, and detoxifies. It treats jaundice, dysentery, gonorrhea, urinary obstruction, eye cloudiness, throat swelling, boils, and traumatic injuries. Dosage: For internal use: decocted, 3-5 grams; or juice. For external use: crush and apply, stuff in the nose, or juice for ear drops. Application references: 1. For hepatitis with jaundice: fresh coriander 5-8 grams (dried 3-5 grams), decocted for consumption, three times daily. 2. For acute jaundice hepatitis: fresh coriander 1-2 ounces, half each of sugar and wine, decocted for consumption, daily one dose. 3. For yellow jaundice and children’s wind-heat: crush fresh coriander, add a little salt, and drink with boiling water. 4. For dysentery: coriander, snake gourd, prickly pear root, and pomegranate peel, decocted for consumption. 5. For kidney stones: fresh coriander 1-2 ounces, decocted for consumption. 6. For urinary obstruction: fresh coriander 1 ounce, crushed and squeezed for juice, mixed with sugar for consumption. 7. For children’s malnutrition: fresh coriander 5-10 grams, steamed with chicken liver or pig liver for consumption. 8. For shingles: fresh coriander 1 handful, crushed and squeezed for juice, mixed with realgar powder for application. 9. For ear infections: fresh coriander juice for ear drops. 10. For whooping cough: fresh coriander 5-10 grams, crushed and mixed with honey and hot water for consumption.
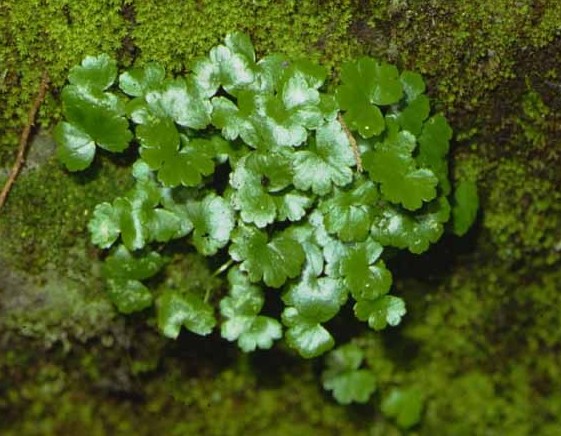

27酢浆草 (Sour Grass)
Other names: three-leaf sour grass, vinegar mother grass, and quail sour. It belongs to the Oxalidaceae family. The whole plant is medicinal. It is cold in nature and sour in taste. It enters the Yangming and Taiyang meridians. It clears heat and promotes dampness, cools blood, disperses stasis, reduces swelling, and detoxifies. It treats diarrhea, dysentery, jaundice, gonorrhea, red and white discharge, measles, hemoptysis, epistaxis, throat swelling, boils, scabies, hemorrhoids, prolapse, traumatic injuries, and burns. Dosage: For internal use: decocted, 2-4 grams (fresh 1-2 ounces), juice or grind into powder. For external use: decocted for washing, crush and apply, juice for application, or decocted for gargling. Application references: 1. For diarrhea: three grams of sour grass, steamed with brown sugar. 2. For dysentery: sour grass ground into powder, five grams, taken with boiling water. 3. For damp-heat jaundice: one to one and a half ounces of sour grass, decocted twice, divided for consumption. 4. For hematuria and heat dysuria: fresh grass juice mixed with honey for consumption. 5. For urinary obstruction: a handful of sour grass, ground for juice, mixed with wine for consumption. 6. For red and white discharge: dried sour grass ground into powder, taken with warm wine. 7. For measles: two to three grams of sour grass, decocted for consumption. 8. For malaria: three grams of sour grass, decocted for consumption. 9. For rotten gums: fresh grass mixed with a little salt, crushed for juice, used to wash the affected area, three to five times a day. 10. For throat swelling: fresh grass one to two ounces, a little salt, crushed, wrapped in gauze to hold in the mouth. Or decocted for gargling, also treats oral inflammation. 11. For mastitis: five grams of sour grass, decocted for consumption, residue applied externally.

28卷耳 (Roll Ear)
Chinese medicinal name:婆婆指甲菜, other names:瓜子草, 高脚鼠耳草. It belongs to the Caryophyllaceae family. The whole plant is medicinal. It is sweet in taste. It clears urinary heat symptoms. Dosage: For internal use: decocted, 5-6 grams. For external use: crush and apply. Application references: 1. For initial mastitis: fresh grass crushed and mixed with wine lees to make a cake, heated and applied to the wrist pulse point, left breast on right wrist, right breast on left wrist. 2. For children’s wind-cold cough, fever, nasal congestion: roll ear, coriander, 5-6 grams, and two to three grams of Hu Tui Zi leaves, decocted, sweetened with brown sugar, taken before meals twice daily. 3. For boils: fresh roll ear whole grass mixed with tung oil, crushed, and applied to the affected area.
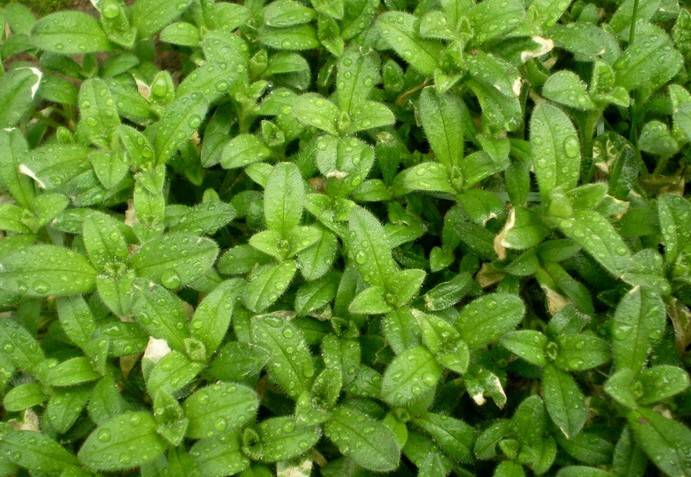

29漆姑草 (Lacquer Grass)
Other names:珍珠草, 地松. It belongs to the Caryophyllaceae family. The whole plant is medicinal. It is cool in nature and bitter and pungent in taste. It treats lacquer sores, bald sores, boils, scrofula, dental caries, children’s milk accumulation, and traumatic internal injuries. Dosage: For internal use: decocted, 3-5 grams, or ground into powder. For external use: crush and apply or juice for application. Application references: 1. For lacquer sores: fresh grass crushed, mixed with loofah leaf juice, and vegetable oil for application. 2. For dental caries: crushed and stuffed into the tooth gap. 3. For traumatic internal injuries: lacquer grass 5 grams, decocted for consumption. 4. For snake bites: lacquer grass and realgar crushed and applied. 5. For scrofula tuberculosis: lacquer grass 5-10 grams, decocted for consumption, and fresh grass applied externally.
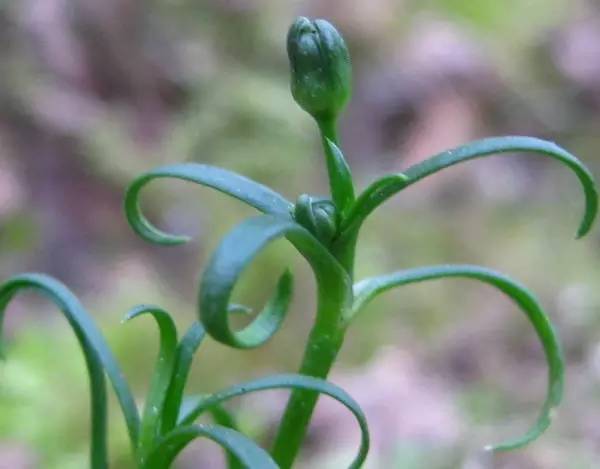

通泉草 (Tongquan Grass)
Chinese medicinal name:绿兰花, other names:虎仔草, 石淋草, 脓泡药. It belongs to the Scrophulariaceae family. It is cool in nature, slightly sweet, and non-toxic. The whole plant is medicinal. It reduces inflammation and detoxifies. It treats boils, abscesses, and burns. Application references: 1. For abscesses: dried Tongquan grass, ground into fine powder, mixed with cold water for application, changed once a day. 2. For boils: dried Tongquan grass and hibiscus leaves crushed together, taken with rice washing water. 3. For burns: fresh grass crushed for juice, applied with clean cotton.

波斯婆婆纳 (Persian Watercress)
Chinese medicinal name:肾子草, other names:灯笼草, 波斯水苦荬. It belongs to the Scrophulariaceae family. It is neutral in nature, pungent, bitter, and salty. The whole plant is medicinal. It detoxifies, treats kidney deficiency, and alleviates rheumatism. Application references: 1. For kidney deficiency: one ounce of lantern grass, cooked with meat for consumption. 2. For scabies: lantern grass decocted for washing. 3. For rheumatic pain: one ounce of lantern grass, boiled with wine for warm consumption. 4. For chronic malaria: one ounce of lantern grass, one penny of stinky mountain, decocted for consumption. 5. For children’s scrotal swelling: three ounces of lantern grass, decocted for steaming and washing the affected area.

32泽漆 (Zeqi)
Taste: slightly cold, bitter; toxic. Main indications: Promotes urination and reduces swelling, transforms phlegm and disperses lumps, kills insects and relieves itching. Used for ascites, edema, tuberculosis, cervical lymphadenitis, excessive phlegm and cough, and skin diseases. Dosage: Decoction, 5-10 grams. For external use, apply as needed. Caution for those with spleen and stomach deficiency.

33狗尾巴草 (Dog Tail Grass)
Other names: green dog tail grass, grain weed, dog tail grass, bright grass, Arhat grass, and fox tail. Main indications: Clears heat, eliminates dampness, and reduces swelling. Treats boils, sores, and red eyes. Dosage: For internal use: decocted, 2-4 grams (fresh 1-2 ounces). For external use: decocted for washing or crush and apply (sweet taste). Properties and indications: Mild, neutral, functions to dispel wind and brighten the eyes, clear heat and promote urination. Used for wind-heat colds, conjunctivitis, red painful eyes, jaundice hepatitis, and urinary obstruction; externally treats cervical lymphadenitis.

35一串红 (One String Red)
The medicinal part is the whole plant, which can be harvested throughout its growth period, used fresh or dried for later use. Taste and properties: Sweet, neutral. Clears heat, cools blood, and reduces swelling. Main indications: For initial boils: fresh one string red as needed, crushed and applied externally.

36鸭舌草 (Duck Tongue Grass)
Duck Tongue Grass has a bitter taste and is cool in nature; it has heat-clearing and detoxifying effects. It treats dysentery, enteritis, acute tonsillitis, erysipelas, and boils. Preparation guidance: 1. For hemoptysis: one to two ounces of duck tongue grass, cooked with lean pork for consumption. 2. For red and white dysentery: appropriate amount of duck tongue grass, dried. Brew as tea daily for three to four days. 3. For boils: duck tongue grass mixed with tung oil for application. 4. For tooth extraction: two grams of water jade hairpin, two grams of jade hairpin flower root, one gram of Xinshi, and one fish (about one pound). Grind the first three herbs into fine powder, remove fish intestines, pack the herbs, and hang in a cool, ventilated place for about 50 days, when frost-like substances will grow on the fish scales, which is the medicinal powder used. When needed, slightly peel the gums, apply this medicine (about the amount of one scale), and the tooth can be extracted shortly after. This medicine should not be swallowed to avoid poisoning. 5. For snake and insect bites: fresh duck tongue grass, crushed and applied.Contraindications: Avoid in cases of deficiency-cold diarrhea.
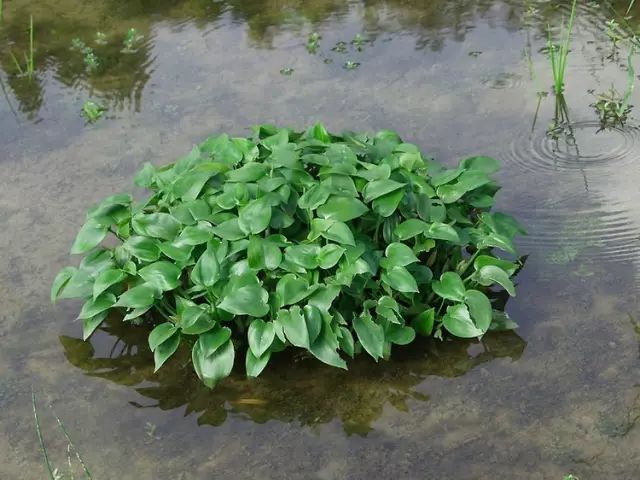

37凤眼兰 (Fengyan Orchid)
Other names: water hyacinth, water floating lotus. The whole plant is used medicinally. Collected in spring and summer, washed, used fresh or dried. Taste and properties: Mild, cool. Main indications: Clears heat and relieves summer heat, promotes urination and reduces swelling. Used for heat stroke, thirst, kidney inflammation, and urinary obstruction. Dosage: 0.5-1 ounce.
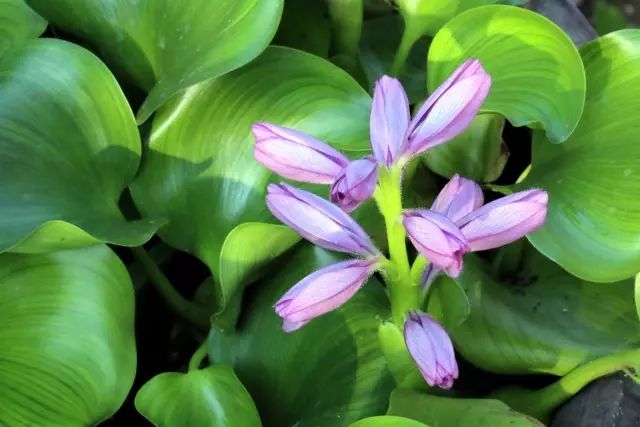

38兰花参 (Orchid Ginseng)
Tonifies deficiency, releases the exterior. Treats deficiency damage, hemoptysis, epistaxis, spontaneous sweating, night sweats, women’s leukorrhea, wind-cold cough, stomach pain, diarrhea, and knife wounds.

39柴胡 (Bupleurum)
Taste and properties: Slightly cold, bitter, pungent, enters the liver, lung, and spleen meridians. Main indications: Releases the exterior and clears heat, soothes the liver and relieves depression, and raises yang qi. Treats fever from colds, alternating chills and fever, malaria, liver qi stagnation, chest and rib distension, prolapse of the rectum, uterine prolapse, and irregular menstruation. Dosage: Decoction, 3-10 grams. For exterior-releasing and heat-clearing, the dosage should be slightly higher and preferably use the raw form.

42桑白皮 (Mulberry White Bark)
Taste and properties: Sweet and cold, enters the lung meridian. Main indications: Clears lung heat and relieves cough, promotes urination and reduces swelling. Used for lung heat cough, facial swelling, and urinary obstruction.

41玉竹 (Yuzhu)
Nourishes yin, moistens dryness, relieves restlessness, and quenches thirst. Treats heat disease with yin injury, cough with thirst, deficiency fever, easy hunger, and frequent urination.

40麦冬 (Ophiopogon)
Taste and properties: Sweet, slightly bitter, slightly cold. Enters the heart, lung, and stomach meridians. Main indications: Nourishes yin and generates fluids, moistens the lungs and clears the heart. Used for dry cough due to lung dryness, yin deficiency cough, throat obstruction and pain, fluid deficiency thirst, internal heat thirst, restlessness, and constipation.

黄花菜 (Daylily)
Daylily is a perennial herbaceous plant with tender flower buds, rich in nutrients, containing abundant pollen, sugars, proteins, vitamin C, calcium, fats, carotene, amino acids, and other essential nutrients. Its carotene content is even several times higher than that of tomatoes. Daylily is sweet and cool in nature, with effects of stopping bleeding, reducing inflammation, clearing heat, promoting dampness, aiding digestion, brightening the eyes, and calming the mind. It is effective for hemoptysis, blood in stool, urinary obstruction, insomnia, and insufficient milk production, and can be used as a tonic after illness or childbirth. Taste: Sweet, neutral. Effects: Nourishes blood, calms the liver, promotes urination, and reduces swelling. Treats dizziness, tinnitus, palpitations, back pain, hemoptysis, epistaxis, blood in the large intestine, edema, gonorrhea, sore throat, and breast abscess. For breast abscess and swelling: Use daylily root for application. For children’s malnutrition: Use 15 grams of daylily leaves, decocted for consumption. Modern scholars have further discovered the medicinal value of daylily, such as Japanese scholars calling it “brain-healthy vegetable”; the Chinese “Journal of Nutrition” has evaluated daylily as having a significant effect in lowering serum cholesterol in animals. It is known that elevated cholesterol is a major factor leading to diseases in middle-aged and elderly individuals and body decline. There are not many delicious, nutritious vegetables that can combat aging, and daylily possesses these characteristics. Regular consumption of daylily can also moisturize the skin, enhance its elasticity and resilience, making it tender, plump, smooth, and soft, reducing wrinkles and fading spots, adding beauty. Daylily also has antibacterial and immune functions, with mild anti-inflammatory and detoxifying effects, and has a certain role in preventing infections. Daylily is a food that is close to damp heat, so those with ulcers, injuries, or gastrointestinal discomfort should eat less, and those with phlegm, especially asthmatics, should avoid it.

栀子 (Gardenia)
Meridians: Heart meridian; liver meridian; lung meridian; stomach meridian; triple warmer meridian. Classification: Rubiaceae family. Function classification: Heat-clearing and fire-purging herb. Effects: Purges fire and relieves irritability; clears heat and promotes dampness; cools blood and detoxifies; dried gardenia: cools blood and stops bleeding. Main indications: Heat disease with irritability; liver fire causing red eyes; headaches; damp-heat jaundice; dysuria; blood dysentery; oral and tongue ulcers; boils and swellings; sprains and swelling. Taste: Bitter, cold, non-toxic. Dosage: For internal use: decocted, 5-10 grams; or in pills or powder. For external use: appropriate amount, ground into powder or mixed for application.

藿香 (Patchouli)
Taste: Pungent; slightly warm. Meridians: Enters the lung, spleen, and stomach meridians. Main indications: Dispels summer heat and releases the exterior; transforms dampness and harmonizes the stomach. Treats summer colds; cold and hot headaches; chest and abdominal fullness; vomiting and diarrhea; pregnancy-related vomiting; nasal congestion; hand and foot ringworm.

溪黄草 (Xihuangcao)
Taste: Bitter, cold. Main indications: Clears heat and promotes dampness, reduces jaundice and dispels dampness. It is a very good herb for treating hepatitis. Taste and properties: Sweet and bitter, cool. Dosage: For internal use: decocted, 25-50 grams (fresh 100-150 grams). Main indications: Clears heat and promotes dampness, cools blood and disperses stasis. Treats acute hepatitis, acute cholecystitis, dysentery, enteritis, urinary obstruction, and traumatic swelling. Jaundice hepatitis: Symptoms include yellowing of the skin and sclera, chills and fever, fatigue, poor appetite, liver area pain, liver and spleen enlargement, yellow urine, red tongue with thin yellow coating, and wiry slippery pulse. Acute cholecystitis: Symptoms include chills and fever, right upper abdominal pain radiating to the right shoulder and back, dry mouth and bitterness, nausea and vomiting, or accompanied by constipation or diarrhea, jaundice, etc.

⊙This article is for the popularization of TCM knowledge and is not intended as a prescription. Please consult a doctor for use if needed.
⊙ Submission email: [email protected] (Original submissions are welcome)

PleaseClick the title below: “Traditional Chinese Medicine Health” to follow (for inquiries)
Stomach health, qi and blood deficiency, hypertension, white hair, foot baths, hair loss, coix seed, anemia (blood tonification), pharyngitis, stomach health, bathing, oral ulcers, bad breath, cold uterus, coix porridge effects, regulating spleen and stomach, colds, coughs, insomnia, cold intolerance, cold hands and feet, back pain, throat swelling, dampness removal, kidney tonification, height and weight table, vegetable pairing taboos, sleeping naked, finger massage, acne, cervical spondylosis, cardiovascular diseases, spot removal, blood tonification, leg slimming, safe period, breast self-examination, body cold, dysmenorrhea, weight loss, sexual health issues, endocrine issues, gynecological issues, health tests, constitution tests, standard three measurements test (bust, waist, hip), body mass index self-test, standard weight.
Diagnosis: Hand diagnosis, tongue diagnosis, observation diagnosis.
Acupoints:Shen Shu point, Jing Ming point, human eye acupoint map, eye acupoints, Zu San Li point, Yun Men point, Jie Xi point, Tian Zhu point.
 Like is a form of encouragement
Like is a form of encouragement