Qi · Huang · Learning · SocietyMaking Traditional Chinese Medicine More Beautiful | More Interesting | More Relevant to Life
Pulse diagnosis is a method where the doctor uses their fingers to press on the patient’s arteries, observing the pulse’s characteristics to understand the patient’s condition and differentiate between syndromes.
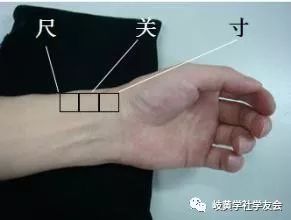
Diagnosing the Cun (寸) pulse

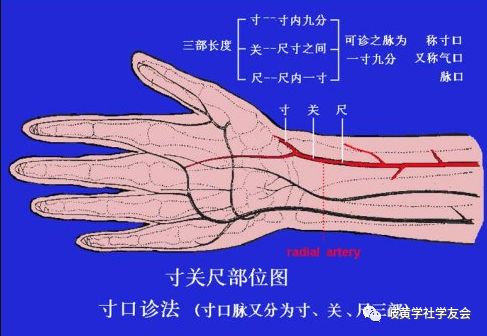
Location of the Cun, Guan, and Chi pulsesIllustration
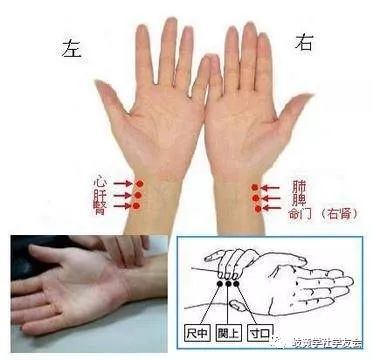
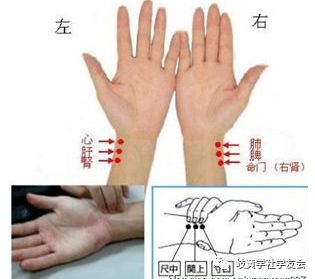
Left hand: Heart, Liver, Kidney; Right hand: Lung, Spleen, Life
Normal Pulse vs. Pathological Pulse
Characteristics of a Normal Pulse
Pulse position: neither floating nor sinking, sinking pulse is not interrupted
Pulse rate: 4-5 beats per breath, consistent rhythm
Pulse shape: present in all three positions, neither large nor small
Pulse quality: calm and gentle, smooth and strong
“Pulse present in all three positions, calm and strong”
Significance: Healthy organ function, abundant Qi and blood, balanced Yin and Yang, smooth Qi flow
Pathological Pulses
(1) Floating Pulse Characteristics: easily felt with light pressure, slightly reduced with heavy pressure (superficial)
Main condition: Exterior syndrome, Yang deficiency with exterior excess
(2) Sinking Pulse Characteristics: not felt with light pressure, only felt with heavy pressure (deep)
Main condition: Interior syndrome
(3) Slow Pulse Characteristics: pulse is slow, less than 4 beats per breath (slow), pulse rate <60 beats/min
Main condition: Cold syndrome / Interior excess heat syndrome
(4) Rapid Pulse Characteristics: pulse is rapid, 5-6 beats per breath (fast), pulse rate >90 beats/min
Main condition: Heat syndrome (excess heat, deficient heat, false heat)
(5) Knotted Pulse Characteristics: pulse is slow with irregular stops (slow and irregular)
Main condition: Excess Yin with Qi stagnation (blood stasis, phlegm obstruction, food blockage, cold congealing)
(6) Choppy Pulse Characteristics: pulse is rapid with irregular stops (rapid and irregular)
Main condition: Excess Yang with excess heat / Excess pathogenic obstruction
(7) Intermittent Pulse Characteristics: pulse is slow with regular stops (slow and regular)
Main condition: Intermittent pulse weakness—organ Qi deficiency (long-term)
Intermittent pulse strength—emotional disturbance (short-term)
(8) Surging Pulse Characteristics: pulse is wide, strong on arrival and weak on departure (strong arrival and weak departure)
Main condition: Yang, excess, heat syndrome
(9) Thin Pulse Characteristics: thin like a thread, distinct with pressure (thin)
Main condition: Thin pulse weakness—Qi and blood deficiency
Thin and slow pulse—Spleen deficiency with damp obstruction
(10) Slippery Pulse Characteristics: smooth and flowing, round and smooth with pressure (flowing)
Main condition: Slippery and deep pulse—phlegm and food accumulation
Slippery and rapid pulse—excess heat syndromes
In youth, a slippery and gentle pulse—normal pulse (Qi and blood abundant)
In women, a slippery and harmonious pulse—pregnancy (nourishing blood for fetus)
(11) Rough Pulse Characteristics: pulse is thin, slow, and not smooth, rhythm is uneven (not smooth and uneven)
Main condition: Rough pulse strength—Qi stagnation and blood stasis;
Rough pulse weakness—deficiency of essence and blood.
(12) String-like Pulse Characteristics: straight and long, like pressing a guitar string (hard)
Main condition: Liver and gallbladder disease / Various pain syndromes / Phlegm and fluid disease / Healthy elderly
① Cold stagnation in the liver pulse—tight string pulse; ② Liver fire rising—rapid string pulse
③ Phlegm and fluid accumulation—slippery string pulse; ④ Liver Qi invading the spleen—gentle string pulse
⑤ Liver and kidney Yin deficiency—thin string pulse; ⑥ Stomach Qi decline—sharp string pulse
(13) Weak Pulse Characteristics: weak when lifted, soft when pressed (weak)
Main condition: Deficiency syndrome (often Qi and blood deficiency)
① Soft and weak pulse—Qi deficiency; ② Thin and weak pulse—blood deficiency
③ Slow and weak pulse—Yang deficiency; ④ Rapid and weak pulse—Yin deficiency
(14) Full Pulse Characteristics: strong when lifted, full with pressure (strong)
Main condition: Excess syndrome
Full and floating pulse—excess heat syndrome, exterior excess syndrome; full and sinking pulse—excess cold syndrome, interior excess syndrome
Long-term illness with body weakness, yet still showing full pulse—isolated Yang escaping (poor prognosis)
Normal person with full pulse, also gentle—Qi and blood abundant (strong constitution)
Normal person with six pulses full and slightly strong—Six Yang pulse (normal pulse)
TCM Pulse Diagnosis Mnemonics
Some pulses are both floating and sinking; floating includes five pulses (Ru, Ge, Hong, Wei, San) that need careful examination, sinking includes four pulses (Fu, Xi, Lao, Ruo) that require heavy pressure to feel, floating and sinking include four pulses (Xu, Shi, Kuo, Chang) (Note: the character ‘焉’ here means ‘among’).
Floating Pulse: Lightly felt, heavy pressure yields nothing, floating like wood on water, strong with wind-heat, weak indicates blood deficiency.
Sinking Pulse: Felt only with heavy pressure, like a stone sinking in water, strong indicates cold pain, weak indicates deficiency cold.
Slow Pulse: Slow pulse, three beats per breath, extremely slow pulse to remember, indicates organ disease or much cold, carefully study between deficiency and excess.
Rapid Pulse: Rapid pulse, six beats per breath, rapid pulse to remember, distinguish between floating and sinking, deficiency and excess, different treatments for monarch and minister fire.
Weak Pulse: Weak pulse, all without strength, floating large and soft without root, weak body heat indicates middle heat, Qi deficiency indicates body weakness.
Full Pulse: Full pulse, large and long, three positions full indicates strongest strength, new illness shows strong evil Qi, long illness shows the disease is ominous.
Slippery Pulse: Slippery pulse, quite puzzling, like beads rolling on a plate, food accumulation and phlegm heat fullness in the chest, women’s pulse should indicate pregnancy.
Rough Pulse: Rough pulse, like bamboo scraping, thin, slow, and stagnant, indicates blood deficiency and dryness, women not pregnant or no menstruation.
Surging Pulse: Surging pulse, like waves, though strong on arrival, calm on departure, indicates strong evil Qi, fullness in the stomach is difficult to treat.
Thin Pulse: Thin pulse, like a thread, extremely thin when pressed, worry and overwork lead to Qi and blood deficiency, dampness and stagnation are also common.
Hidden Pulse: Hidden pulse, carefully sought, pressing down feels like touching bones, Qi stagnation, cold congealing, and food accumulation lead to obstruction, wanting to vomit but unable to.
Arterial Pulse: Arterial pulse, beats at the joints, no head or tail, round like a bean, indicates pain and fright, less Yin leads to pregnancy.
Leather Pulse: Leather pulse, floating and tense, like pressing on a drum skin, women half pregnant and experiencing bleeding, men with deficiency or nocturnal emissions.
Firm Pulse: Firm pulse, sinking and strong, firm and large, indicates internal accumulation of cold and pain, running piglet syndrome leads to calamity.
Rapid Pulse: Rapid pulse, with stops, like a horse running and occasionally stumbling, intense heat leads to loss of fluids, wheezing and rash indicate urgency.
Knotted Pulse: Knotted pulse, with stops, knotted pulse shape to remember, hernia and stagnation of cold Qi, emotional distress can also cause it.
Intermittent Pulse: Intermittent pulse, not immediate return, takes a long time to come back, long illness shows difficulty in treatment, pregnant women give birth, those with epilepsy find peace.
Rapid Pulse: Rapid pulse, comes quickly, anxious and urgent, pulse comes at seven or eight beats per breath, excess Yang without control leads to true Yin exhaustion, wheezing and hoarseness indicate danger.
Spring pulse is slightly string-like, summer pulse is slightly surging, long summer pulse is slightly slow, autumn pulse is slightly floating, winter pulse is slightly sinking.

Special Reminder: A beautiful day begins! I hope the articles from the Qi Huang Learning Society bring you a good mood for the day. If you like the article, don’t forget toclick the “Looking” button at the bottom right of the article or share it in your friend circle!. Due to network limitations, follow me for more! May you become your own divine doctor.

