What are the Seven Emotions?
In Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), it is believed that humans experience emotional fluctuations of joy, anger, worry, contemplation, sadness, fear, and shock, collectively referred to as the “Seven Emotions”.
When these seven emotions are excessively stimulated, they can lead to an imbalance of Yin and Yang, disrupt the flow of Qi and blood, and result in various diseases. It is essential to manage these emotions appropriately. For instance, extreme joy or sorrow, or excessive fear can disturb the balance of Yin and Yang and the flow of Qi and blood, causing mental disturbances that manifest physically as various ailments.
What are the Six Desires?
The concept of the Six Desires was first introduced in the “Lüshi Chunqiu”: “Those who are fully alive have their six desires met appropriately.”
Philosopher Gao You commented: “The Six Desires are life, death, hearing, sight, taste, and smell.” This indicates that the Six Desires broadly refer to human physiological needs or desires.
To survive, one fears death and seeks to live a rich and colorful life. Therefore, the mouth desires food, the tongue desires taste, the eyes desire sight, the ears desire sound, and the nose desires scent. These desires are innate and do not require teaching.
Later, these were summarized as “desires of sight, hearing, scent, taste, touch, and thought”.
The Relationship Between the Seven Emotions and the Five Organs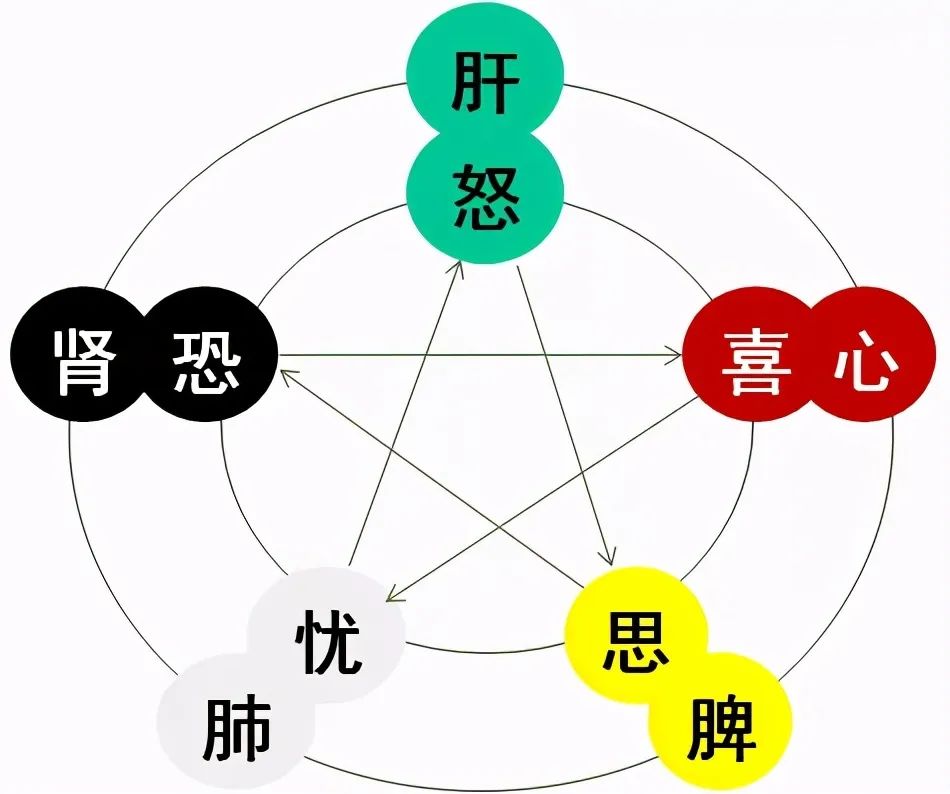
1. Anger Harms the Liver
Anger is a common emotion. When one is angry, Qi rises, harming the liver, leading to feelings of gloom, irritability, dizziness, and is also a significant cause of hypertension, coronary heart disease, and gastric ulcers.
2. Joy Harms the Heart
Joy can promote the flow of Qi and blood, relax muscles, and aid in recovering from fatigue. However, excessive joy can damage the heart Qi.
The story of Fan Jin in “Rulin Waishi”, who suddenly became a successful scholar in old age and suffered a mental breakdown due to mixed feelings of joy and sorrow, is a classic case of joy harming the heart.
3. Contemplation Harms the Spleen
TCM states: “Contemplation leads to Qi stagnation”. Excessive thinking can disrupt the nervous system’s function, reduce digestive fluid secretion, and result in loss of appetite, dullness, emaciation, shortness of breath, fatigue, and depression.
4. Worry Harms the Lungs
Worry is closely related to the lungs. Extreme worry can harm the lungs, leading to dry cough, shortness of breath, hemoptysis, hoarseness, and changes in breathing rate.
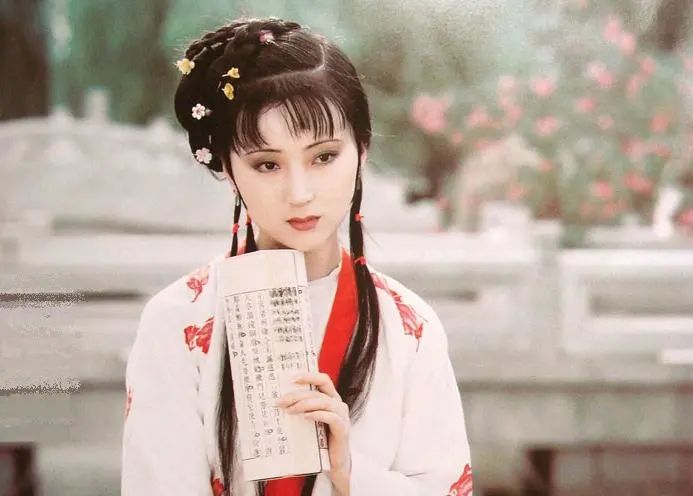
The character Lin Daiyu in “Dream of the Red Chamber”, who is sentimental and melancholic, is a good example of someone whose health is harmed by worry.

5. Fear Harms the Kidneys
Fear can disrupt the nervous system, causing tinnitus, deafness, dizziness, impotence, and can even lead to death. The saying that someone can be “scared to death” reflects this principle.
What is the Principle of the Seven Emotions Causing Disease?
The Seven Emotions can cause disease by harming the internal organs, primarily affecting the Qi mechanism of the organs, leading to abnormal ascension and descent of Qi, and chaotic circulation of Qi and blood. Different emotional stimuli have varying effects on the Qi mechanism.
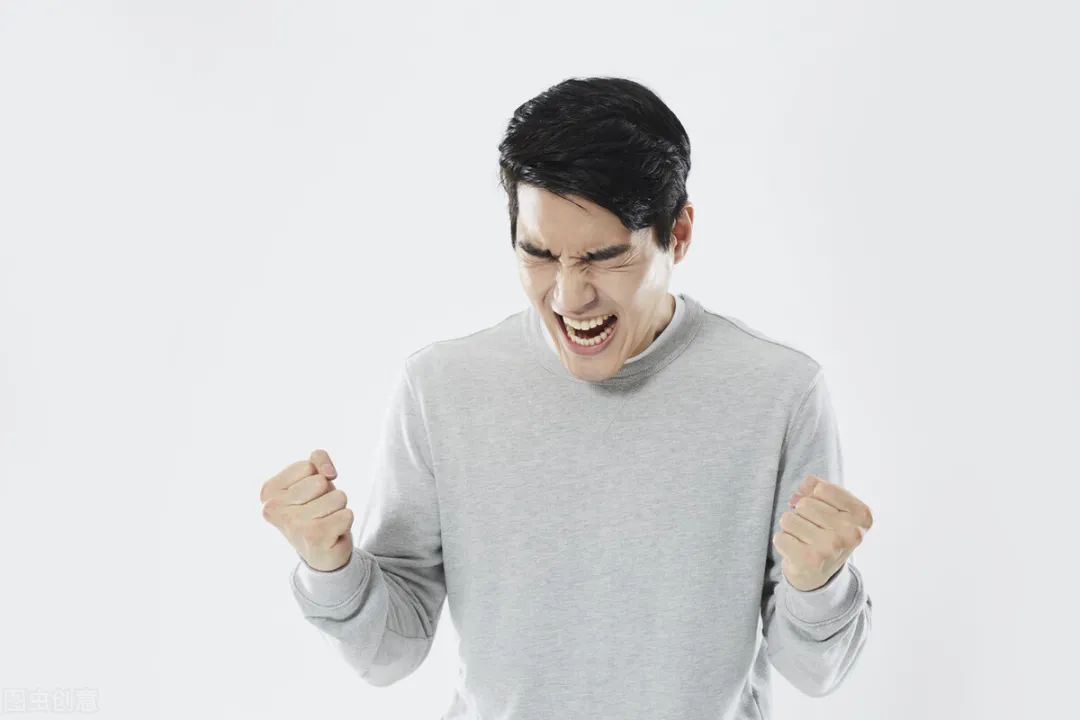

Anger causes Qi to rise, meaning excessive anger can cause liver Qi to rebel upwards, with blood following the rebellious Qi.
Joy causes Qi to relax, which includes both alleviating tension and dispersing heart Qi. Under normal circumstances, joy can ease tension, promote the smooth flow of Ying and Wei, and enhance mood.
Sadness causes Qi to dissipate, meaning excessive sadness can lead to lung Qi depression, a loss of will, and depletion of lung Qi.
Fear causes Qi to descend, meaning excessive fear can lead to kidney Qi instability, causing Qi to leak downwards.
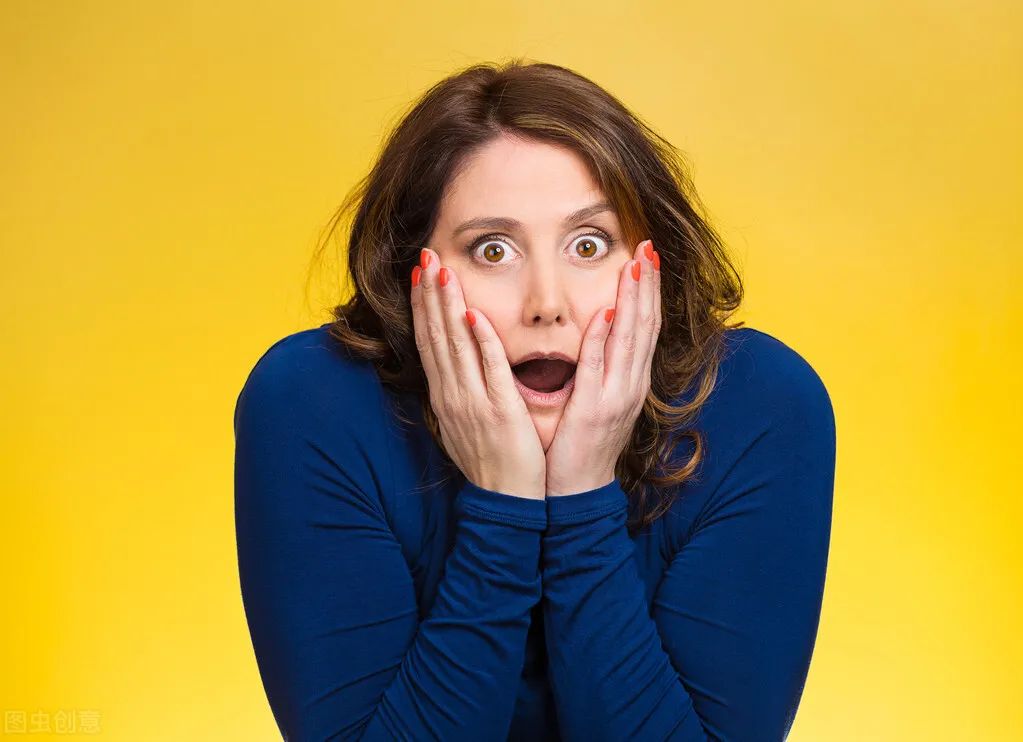

Shock causes Qi to become chaotic, meaning sudden shock can leave the heart unanchored, the spirit ungrounded, and the mind unsettled.
Contemplation causes Qi to stagnate, meaning excessive contemplation can harm the spirit and damage the spleen, leading to Qi stagnation.
The Seven Emotions represent TCM’s understanding of basic human emotions. Beyond the Seven Emotions, love and hate, pride and shame, dignity and contempt, etc., are also fundamental expressions of human emotions.