“Damp-heat is the source of all diseases,” a statement that many do not understand. However, anyone well-versed in Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) health preservation can grasp the underlying principle. Dampness and heat are two external pathogenic factors that can cause illness in all seasons. Dampness is heavy, turbid, and sticky, making it difficult to eliminate, and it can manifest in various parts of the body, affecting the organs, meridians, muscles, skin, and lower yin regions.
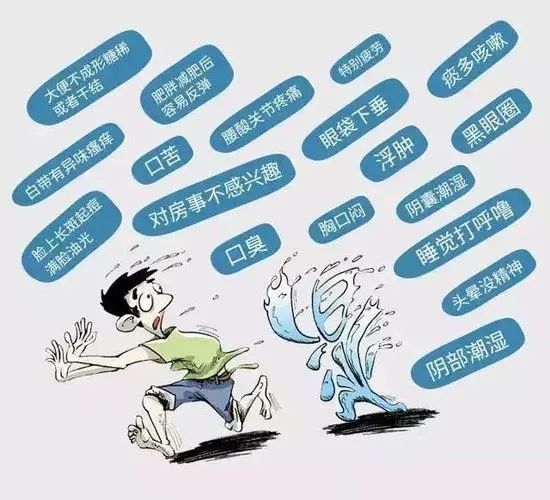
Dampness and heat can stagnate in the organs and meridians, easily obstructing the flow of qi and damaging yang energy. The nature of dampness is to linger, making it difficult to move, and it often remains in one place, leading to chronic conditions that are hard to resolve. Especially when dampness and heat conjoin, it further complicates the elimination of dampness. As noted by Zhu Danxi of the Yuan Dynasty, “Among the six qi, damp-heat is the cause of illness in eight or nine out of ten cases.” Its treatment has always been challenging, often resulting in prolonged illness.Furthermore, damp-heat originates from the spleen and stomach, which are considered the “foundation of postnatal life.” The spleen and stomach are also the “source of damp-heat” and the “center of transmission.” The five zang and six fu organs are interconnected, and the twelve meridians and eight extraordinary vessels are linked, so once damp-heat affects the spleen and stomach, it can lead to systemic diseases. If damp-heat persists, it will transmit to other organs and meridians, even affecting the limbs and causing various diseases. Therefore, by preventing and treating damp-heat, we can effectively prevent many illnesses.Based on clinical experience, we can see that many diseases stem from damp-heat.

Most skin diseases are caused by damp-heat.
When damp-heat lingers in the spleen and stomach, it first affects the qi, blood, and body fluids of the five zang and six fu organs, exceeding the body’s required temperature, leading to various pathological phenomena that harm the skin, such as eczema, acne, melasma, psoriasis, and vitiligo. These conditions must be treated by addressing damp-heat to find effective remedies.
Most liver and gallbladder diseases are due to damp-heat in the liver.
Common symptoms of gallbladder disease include jaundice, with hepatitis and cholecystitis being frequently encountered conditions. The underlying cause of these diseases is related to damp-heat. When damp-heat persists in the spleen and stomach, it inevitably affects the liver and gallbladder, leading to dysfunction. Therefore, various acute and chronic hepatitis, liver cirrhosis, ascites, acute and chronic cholecystitis, gallstones, and acute and chronic pancreatitis are mostly associated with damp-heat. Treatment should primarily focus on eliminating damp-heat.
Diseases of the urinary and reproductive systems are also caused by damp-heat.
Many people have heard of the term “damp-heat descending,” which is an important phenomenon of damp-heat transmission. Damp-heat originates from the middle jiao, first harming the upper jiao, and eventually affecting the lower jiao. Therefore, whenever there is damp-heat in the body, it will inevitably harm the lower jiao, which includes the kidneys, bladder, large and small intestines, and reproductive organs. When damp-heat descends to the lower jiao, it predisposes individuals to illness, making urinary and reproductive system diseases often caused by damp-heat, and treatment should focus on addressing damp-heat.It is also important to note that many gynecological diseases severely affect the physical and mental health of modern women. The root cause of gynecological diseases characterized by dampness, odor, fishy, and putrid smells is the presence of damp-heat in the body. Understanding this, clinical prevention and treatment should focus on eliminating damp-heat under the guidance of a physician to avoid ignorance leading to harm.
Many modern diseases are also caused by damp-heat.
Hypertension, hyperlipidemia, diabetes, obesity, and fatty liver disease, when examined pathologically, are all caused by damp-heat. This is because damp-heat significantly affects qi, blood, and body fluids, and the root of these diseases lies in excessive internal energy, leading to the generation of damp-heat, which causes abnormalities in blood lipids, blood sugar, and blood viscosity. If we take preventive measures at the onset of damp-heat, many tragedies can be avoided. Additionally, conditions such as damp-heat cough and damp-heat heart disease (viral myocarditis) are caused by damp-heat invading the upper jiao, affecting the heart and lungs.In summary, damp-heat has created and continues to create troubles and suffering for modern people. We must pay attention to it, understand it, prevent it, and treat it to maintain our health. So how do we prevent it? We need to find methods from the root of the disease.
Additionally, conditions such as damp-heat cough and damp-heat heart disease (viral myocarditis) are caused by damp-heat invading the upper jiao, affecting the heart and lungs.In summary, damp-heat has created and continues to create troubles and suffering for modern people. We must pay attention to it, understand it, prevent it, and treat it to maintain our health. So how do we prevent it? We need to find methods from the root of the disease.
End
Previous Recommendations
What is “Oryzanol”? Why is it said to be the king of regulating human nerve function?
A single herb that can “penetrate” to open meridians, disperse lung qi, and benefit joints and lower back.
What vegetables and fruits are on the list of the top ten foods high in estrogen content?
The seven major uses of Wumei Wan (Black Plum Pill).

