Before reading, please click the blue text "Brief Health Discussion" above, then click "Follow" so you can receive articles for free. Remember to follow for free subscription!
Tongue diagnosis is a simple and effective method for assisting in diagnosis and differentiation by observing the color and shape changes of the tongue.
Tongue diagnosis is one of the key components of TCM observation diagnosis.
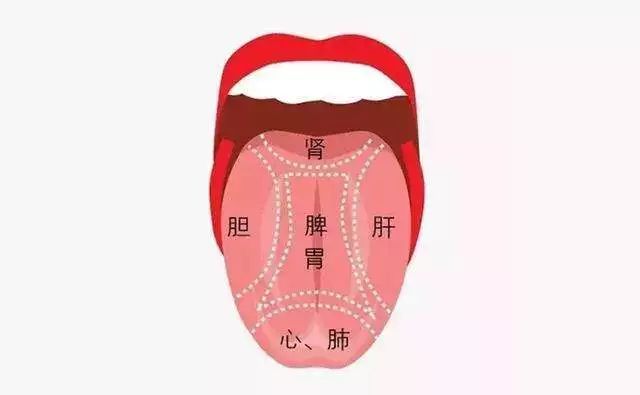
The tongue is the sprout of the heart, the external manifestation of the spleen, and the coating is produced by the stomach qi. The hand Shaoyin heart channel connects to the root of the tongue, the foot Shaoyin kidney channel runs alongside the root of the tongue, the foot Jueyin liver channel connects to the root of the tongue, and the foot Taiyin spleen channel connects to the root of the tongue, spreading beneath the tongue. Therefore, changes in the internal organs can be reflected in the tongue body and tongue coating. Tongue diagnosis mainly examines the shape, color, moisture, and dryness of the tongue body and coating to determine the nature of the disease, the severity of the condition, the abundance or deficiency of qi and blood, the balance of body fluids, and the deficiency or excess of the internal organs.
Is it blood deficiency, qi deficiency, phlegm dampness, or blood stasis? All can be roughly identified the moment you stick out your tongue.
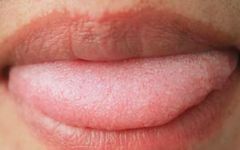
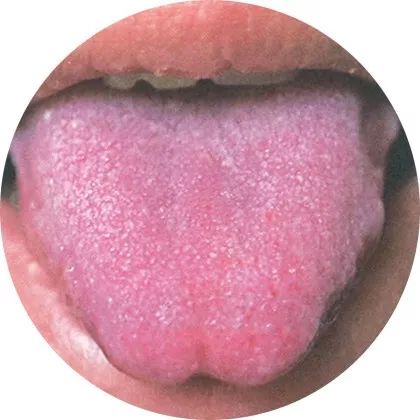
The most enviable tongue type is the “Peach Blossom Tongue”. Generally, people with a balanced constitution have the most beautiful tongue appearance, which is a light red color resembling a peach blossom, with a thin layer of white coating. This enviable tongue appearance is called “Peach Blossom Tongue”.
During tongue diagnosis, observe in the order of tip of the tongue – middle of the tongue – root of the tongue – sides of the tongue. First look at the tongue body, then the tongue coating, for about 30 seconds. If the diagnosis is unclear after one observation, allow the patient to rest for 3-5 minutes and then observe again.
Below is a commonly seen clinical tongue coating color chart. With these high-definition tongue diagnosis charts, you can know your health by looking at your tongue. Everyone should have a copy!
Tongue Shape and Surface
1Red spots on the tongue: Internal heat accumulation
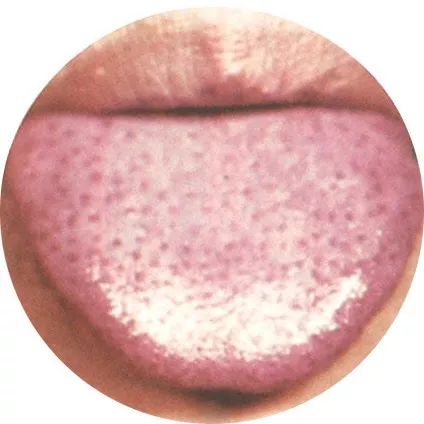
If there are red spots or prickles on the tongue, it indicates excessive internal heat.

Red spots or prickles on the tip, middle, and sides of the tongue represent excessive heart fire, excessive gastrointestinal heat, and excessive liver and gallbladder fire, respectively.
2Cracked tongue: Deficiency of essence and blood
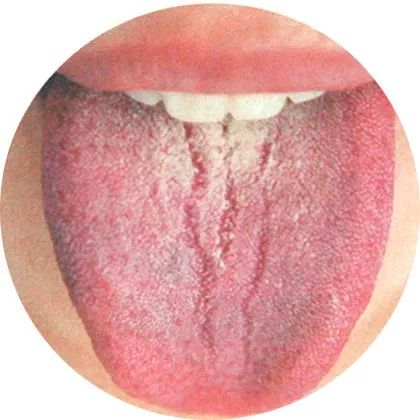
Cracks generally have no coating covering them,
indicating deficiency of essence and blood.

White and cracked coating indicates deficiency of essence and blood; a dark red and dry tongue with cracks indicates excessive heat damaging body fluids.
3Teeth marks on the tongue: Yang deficiency
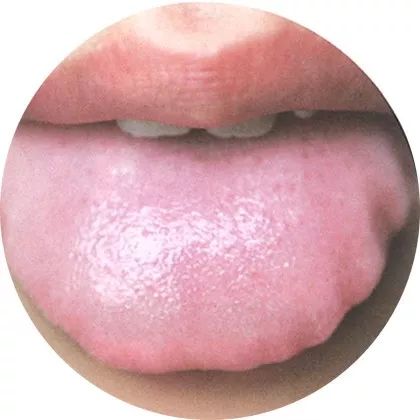
The tongue body is pale, and the coating is pale,
indicating deficiency of spleen and kidney yang, with internal dampness and phlegm.

This tongue appearance is very soft, indicating deficiency of yang qi in the body, leading to a decline in physical strength.
4Pale white tongue: Internal deficiency of sweat
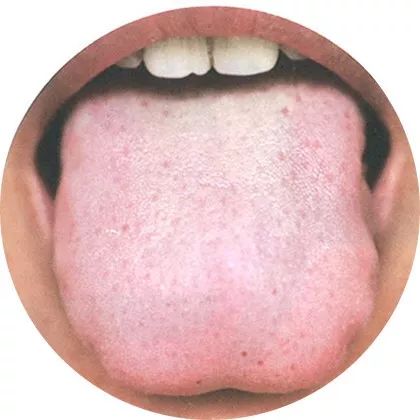
The tongue body is pale and plump, indicating deficiency of yang qi;
the tongue body is pale and thin, indicating deficiency of qi and blood.

Pale white tongue indicates a deficiency of the body, and a cold tongue appearance.
5Red tongue: Presence of pathogenic heat
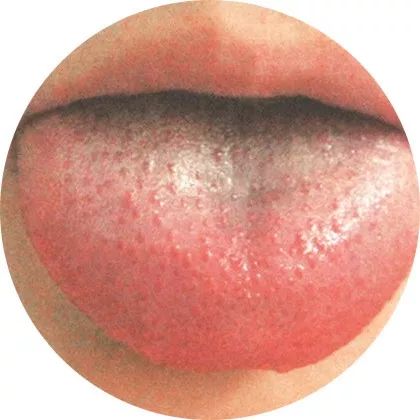
A red tip with prickles indicates heart fire rising; a tongue that is red with a yellow and dry coating indicates internal excess heat; a red tongue body with little or no coating indicates yin deficiency with internal heat.

This indicates a heat syndrome, which may be due to excessive accumulation of heat in the body, while also observing if there are red spots on the tongue surface.
6Crimson tongue: Strong pathogenic heat
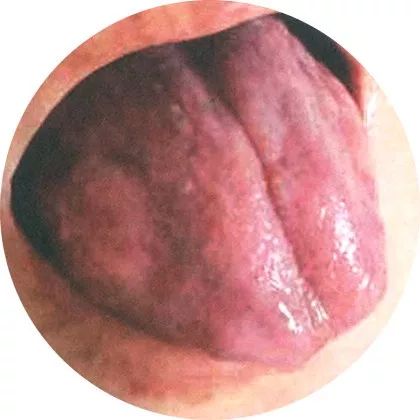
A red tongue body that is dry, with prickles or cracks, indicates intense internal heat; a red tongue without coating and smooth indicates exhaustion of stomach and kidney yin.

This tongue appearance indicates that the pathogenic heat has penetrated deeply into the blood and nutrients, usually indicating that body fluids have been depleted. The deeper the color, the more intense the heat and the more severe the condition.
7Purple tongue: Poor blood circulation
The tongue color is bluish-purple, indicating poor blood circulation.
A purple tongue with a reddish hue may indicate excessive accumulation of heat in the body.

Cold syndrome, heat syndrome, or blood stasis syndrome may all present with this tongue appearance, primarily caused by poor blood circulation.
Tongue Size
1Fat tongue: Internal cold deficiency
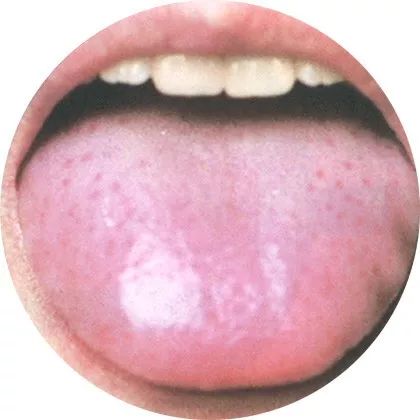
Pay attention to the color of the tongue,
the coating, and whether there are red spots, etc.

A yellowish coating on the tongue often indicates excessive heat in the heart and spleen; a swollen tongue with a dark purple color often indicates blood stasis blocking the channels.
2Fat pale tongue: Weak yang qi
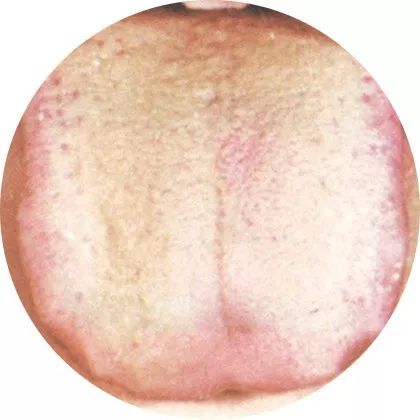
Due to weak yang qi, the warming and promoting functions are affected, and the distribution of body fluids is weakened, resulting in a plump and pale tongue.

Fat pale tongue is a manifestation of weak yang qi and retention of water and dampness.
3Thin red tongue: Nutritional deficiency
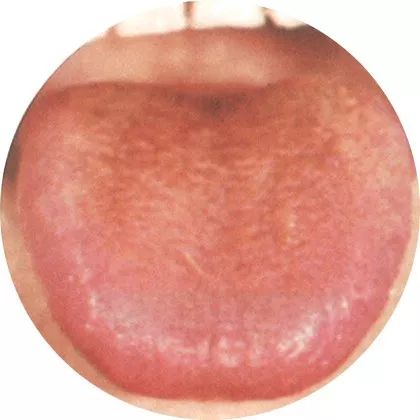
A red tongue indicates internal heat,
or inflammation, prolonged heat damaging body fluids,
leading to depletion of nutrients in the body.

A thin tongue indicates a lack of nutrition and moisture in the body.
4Thin pale tongue: Deficiency of both qi and blood
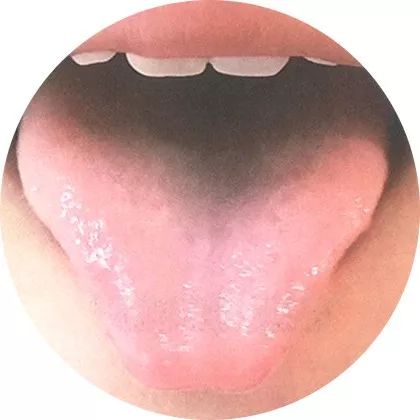
A thin pale tongue with obvious coating,
often accompanied by mild cold or digestive issues,
indicating a weak constitution.

This primarily reflects a pathological state of deficiency of both qi and blood, indicating malnutrition in the body.
5Old tongue: Confrontation of righteousness and evil
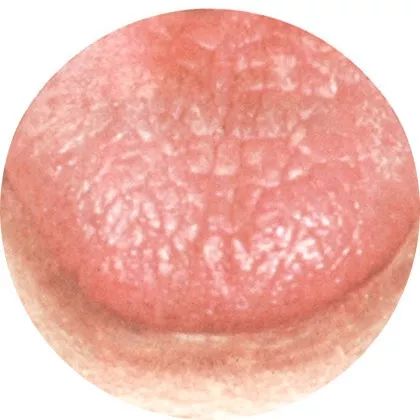
The tongue coating is yellowish-white, gray-black,
indicating a predominance of excess syndrome and heat syndrome.

Old tongue is commonly seen in the stage of confrontation between righteousness and evil, where the pathogenic qi is very fierce, but the body’s resistance is also strong.
6Tender tongue: Low metabolic function
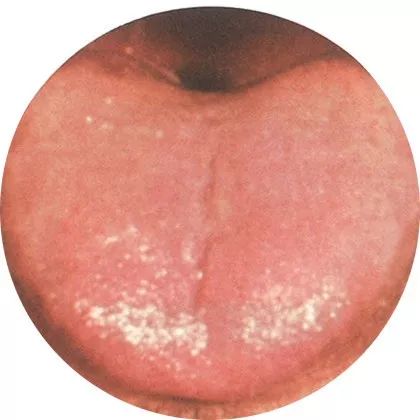
This often indicates deficiency syndrome, cold syndrome, and damp syndrome.

Weak internal organ function, low metabolic function, and weakened resistance or constitution are often seen in this tongue appearance.
Tongue Coating Thickness
1Thin coating: Mild condition
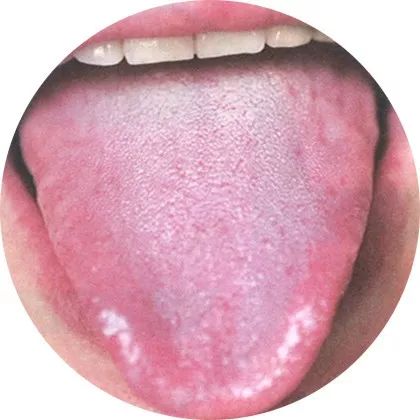
A thin white coating and a light red tongue are normal tongue appearances; a thin yellow coating mainly reflects the pathological characteristics of the initial stage of heat syndrome.

This indicates a normal tongue coating or the initial stage of a disease, or shows a mild condition.
2Thick coating: Gastrointestinal accumulation
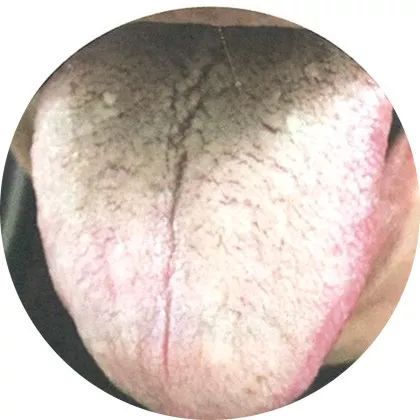
If the tongue body is red, the coating is yellow, thick, and dry, it indicates excessive heat in the qi level damaging yin; if it is a light red tongue with a thick, white, greasy coating, it indicates phlegm, dampness, and food stagnation.

This indicates a transition from a mild to a severe condition, or the presence of gastrointestinal accumulation.
3Dry coating: Vomiting and diarrhea damaging body fluids
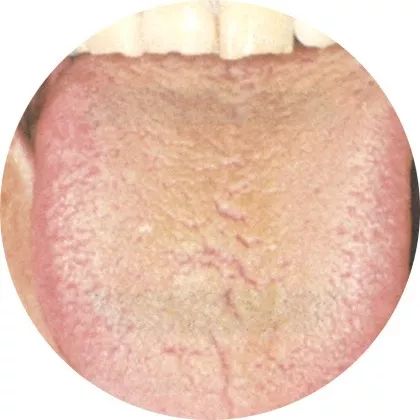
If the tongue coating is just dry and white, it indicates poor circulation of body fluids; if the tongue coating is dry and yellow, it indicates excessive stomach heat; if the tongue coating is dry and black, it indicates extreme heat damaging yin.

This generally indicates high fever, vomiting, and diarrhea damaging body fluids. It is also important to check the color of the tongue itself.
4Rough coating: Body fluid deficiency
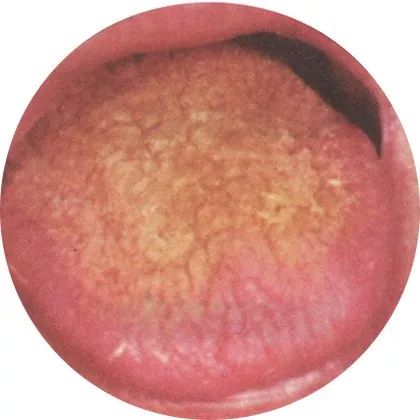
If the internal dryness becomes severe, one should be concerned about chronic diseases such as hyperlipidemia and diabetes; those with asthma may feel difficulty in breathing.

This rough coating indicates a severe deficiency of body fluids.
5Slippery coating: Mental fatigue
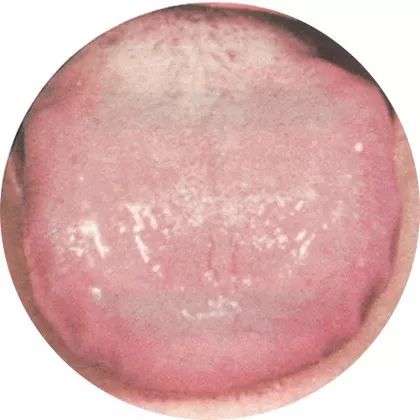
If the body is easily fatigued, mentally drained, and lacking energy, it indicates a state of various functional declines and reduced immunity.

This indicates deficiency syndrome and cold syndrome. It is also important to pay attention to the size of the tongue and the teeth marks on the edges.
6Greasy coating: Dampness and turbidity accumulation
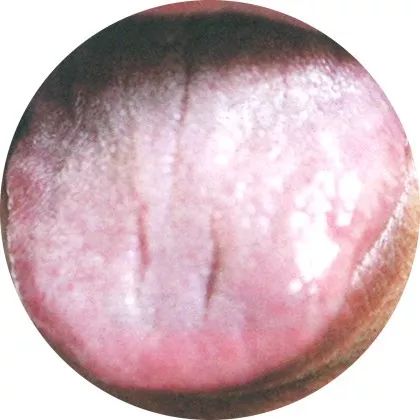
The tongue coating is white and adheres to the surface of the tongue, indicating internal cold and dampness; if the tongue coating is yellow, it indicates internal dampness or phlegm turbidity accumulating and transforming into heat.

This indicates dampness and turbidity accumulation, with yang qi being restrained, primarily indicating phlegm dampness and food accumulation.
7Putrid coating: Excessive internal heat
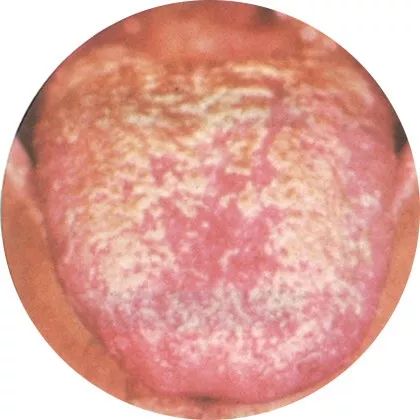
Be cautious of discomfort and infections caused by overeating.
Putrid coating is mostly associated with heat syndrome, primarily indicating food accumulation and phlegm dampness.
Color of the Tongue Coating
1White coating: Dampness and turbidity phlegm
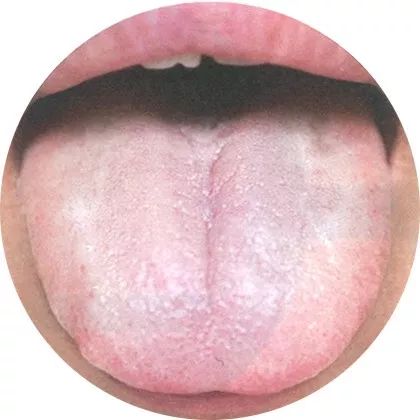
A thin white coating indicates a normal tongue coating or the initial stage of a superficial syndrome. A thin white and slippery coating indicates internal cold syndrome or damp syndrome; a thin white and greasy coating indicates dampness and turbidity, phlegm.

Based on the moisture level and thickness of the tongue coating, it can be divided into thin white coating, white slippery coating, white dry coating, and white powdery coating.
2Yellow coating: Cold transforming into heat
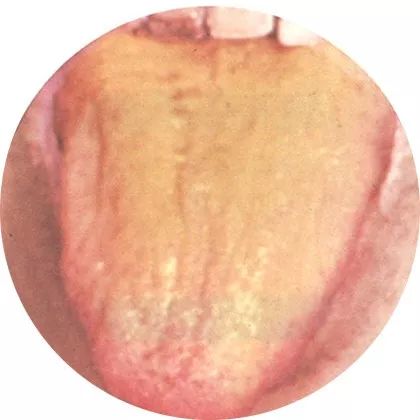
A thin yellow coating indicates mild heat; a yellow coating indicates severe heat; a scorched yellow coating indicates extreme heat; a yellow greasy coating indicates damp-heat syndrome.

Yellow coating indicates disease, primarily indicating spleen and stomach disease, internal syndrome, and heat syndrome.
3Gray coating: Dampness and turbidity obstruction
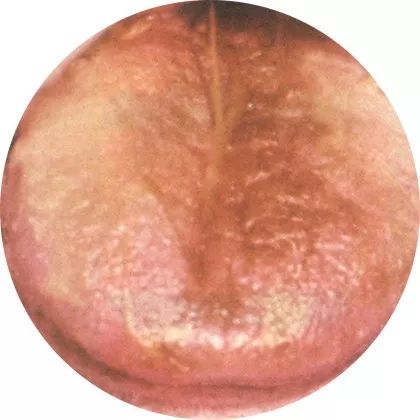
Once the tongue coating turns gray, it indicates that the disease has taken root in the body, and the condition has become serious.

A gray-white tongue coating indicates internal cold dampness or turbidity obstruction; a gray-yellow and dry coating indicates internal heat damaging body fluids.
4Black coating: Intensified pathogenic heat
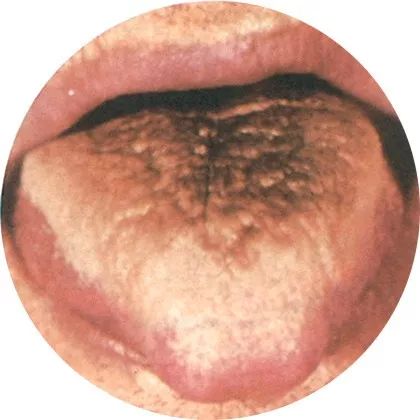
A dry black coating indicates the influence of chronic diseases and inflammation;
A greasy black coating indicates excessive accumulation of
pathogenic heat and dampness.

A black coating indicates a severe condition or a trend towards chronicity.
1. Typical tongue appearance of qi deficiency constitution
1Pale fat tongue with stasis spots
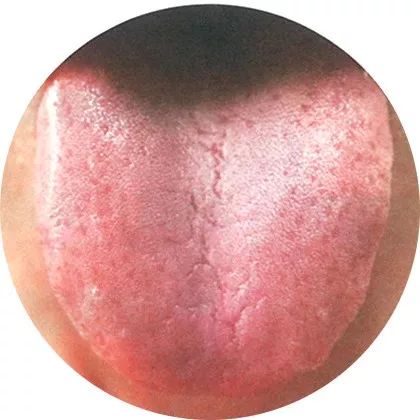
Tongue quality: Dull and plump
Tongue coating: Thin
Tongue surface: Obvious stasis spots on the front half of the tongue

This tongue appearance is often seen in patients with fatigue, easy fatigue, cold intolerance, and abdominal distension due to weak transformation.
2Dull tongue, thin greasy coating
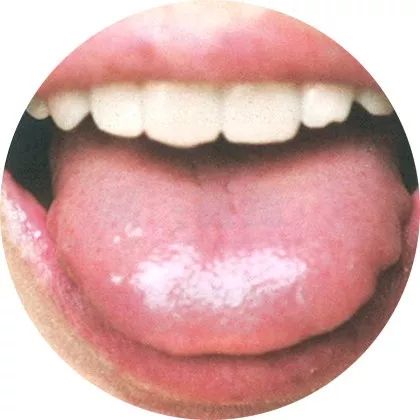
Tongue color: Dark red
Tongue coating: Thin greasy coating
Tongue surface: Moist

This tongue appearance is often due to deficiency of righteous qi, with poor transformation in the middle. Patients may experience general fatigue, memory loss, poor appetite, and abnormal bowel movements.
3Fat tender tongue, like a mirror
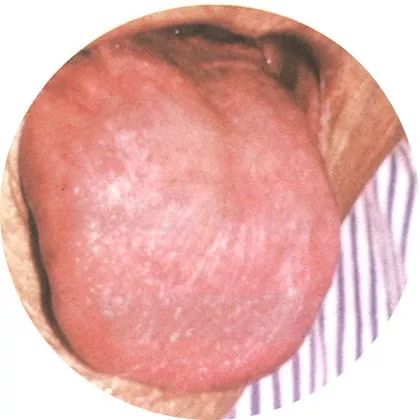
Tongue color: Slightly red
Tongue quality: Tender
Tongue body: Plump

This tongue appearance is typical of both qi and yin deficiency, and such patients may experience fatigue, shortness of breath, mental fatigue, and poor digestion.
4Pale dark tongue with stasis spots
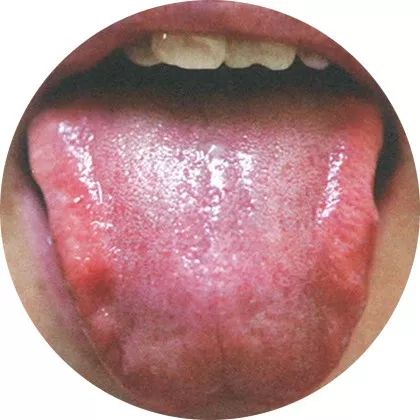
Tongue quality: Dull
Tongue coating: Few and thin white
Tongue body: Red tip with slight stasis spots

This tongue appearance is called a dull tongue, and clinically, this appearance is often due to complex conditions, leading to long-term deficiency of both qi and blood.
5Old tongue: Confrontation of righteousness and evil

Tongue coating color: Yellowish-white, gray-black,
indicating a predominance of excess syndrome and heat syndrome.

Old tongue is commonly seen in the stage of confrontation between righteousness and evil, where the pathogenic qi is very fierce, but the body’s resistance is also strong.
6Tongue diagnosis, face diagnosis, pulse diagnosis
Children’s differentiation and treatment / Children’s massage
Moxibustion / Gua Sha / Sanfu Moxibustion
Hand acupuncture / abdominal acupuncture / I Ching / dietary therapy
Organ adjustment / Sanjiao adjustment
Five movements and six qi / twelve meridians / fasting
Five animal play / ear diagnosis / postpartum care
Yijinjing / gynecology treatment / eight steel differentiation
Shanghan Lun / Zhu You Shu / repairing the root chakra
Linggui Eight Methods / Huangdi Neijing / acupuncture
Traditional Chinese medicine five elements / TCM growth assistance / TCM diagnosis
Health preservation center marketing retention speech
Member group + 900 TCM general courseware
Long press to recognize the QR code below to add WeChat for learning