Tongue diagnosis is a technique that allows us to glimpse the secrets of the body. Is it blood deficiency, qi deficiency, phlegm-dampness, or blood stasis? All can be discerned at the moment you stick out your tongue.
When a wind-cold cold starts, the tongue coating becomes thick. At this time, drinking ginger tea to dispel cold and dampness is most effective. When the tongue coating turns yellow, ginger tea should no longer be consumed; in this case, heat-clearing methods are needed.
If the tip of the tongue is particularly red one day, it is advisable to drink some lotus seed tea early to prevent insomnia due to excessive heart fire at night.
After a few days of business travel, if the spleen and stomach feel uncomfortable, the tongue coating will definitely become thick and greasy. Cooking a pot of *Wuzhi Maotao* (Five-Finger Peach) damp-dispelling soup will prevent future issues.
See, tongue diagnosis is like a relatively easy-to-master magic trick; it is not as mysterious as it seems.
The most enviable tongue type is the “Peach Blossom Tongue”. Generally, people with a balanced constitution have the most beautiful tongue appearance, which is a light red color resembling peach blossoms, with a thin white coating. This enviable tongue type is referred to as “Peach Blossom Tongue”. If the tongue body is red, it indicates heat; if the tongue body is white, it usually indicates cold.
The “Peach Blossom Tongue” is typically found in individuals with a good constitution from birth and who pay attention to maintenance afterward. This tongue type is indeed rarer than beautiful women.
Before observing the tongue appearance, pay attention to the following points:
- Do not eat colored foods such as coffee or orange juice;
- Do not observe it right after waking up;
- Do not observe it within half an hour after meals;
- Do not observe it after taking antibiotics or chemical additives.
1. Qi Deficiency: Those with sufficient qi and those with qi deficiency look completely different.
Main manifestations of qi deficiency include: dull complexion, poor physical strength, easy fatigue, sensitivity to cold and wind, frequent colds, abdominal bloating after eating, and loose stools.
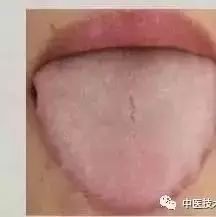
People with qi deficiency often have a swollen tongue.
Qi deficiency tongue appearance:
The edges of the tongue have tooth marks. People with qi deficiency often have tooth marks on both sides of the tongue—imprints from the teeth. This is because those with qi deficiency easily accumulate dampness that cannot be expelled, leading to swelling of internal organs and skin over time. If the tongue coating covers the entire tongue without revealing the tongue body, it indicates heavy internal dampness. If the tongue coating becomes thicker, it indicates increasing internal dampness. If the tongue is round and swollen with tooth marks, it often has two saliva lines when extended, indicating heavy internal dampness.
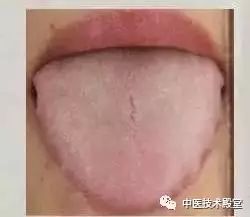
If the tongue has cracks in the middle, and the tooth marks on the sides are not obvious, but the cracks in the middle are very pronounced (everyone has cracks in the middle of the tongue, but in normal individuals, they are not obvious), and even branch out into various types of cracks, it indicates poor spleen and stomach function, insufficient spleen and stomach qi, and inability to lift the tongue coating, resulting in noticeable cracks.
-
If there is no tongue coating, or if the tongue coating is extremely thin, making the entire tongue appear pale, it indicates poor constitution, especially insufficient spleen and stomach qi. Individuals with this tongue appearance may be suffering from a serious illness, as the spleen and stomach have been affected, leading to the loss of tongue coating. Such individuals must first regulate their spleen and stomach; only with sufficient spleen and stomach qi can the body be saved. This tongue appearance may also result from improper diet damaging the spleen and stomach.
2. Phlegm-Dampness: Those with phlegm-dampness are most prone to the three highs (hypertension, hyperlipidemia, and hyperglycemia).
Main manifestations of phlegm-dampness include: overeating, frequent social engagements, late-night snacks, excessive fluid intake, and poor emotions.
Spleen deficiency can lead to increased dampness in the body, which can develop into a phlegm-damp constitution. This is because dampness that lingers in the body can condense into phlegm—body fluids gradually evaporate and condense, ultimately forming a viscous substance. Phlegm-damp obstruction is partly caused by lifestyle habits, such as unbalanced diet, excessive consumption of cold foods, and irregular eating. However, the root cause is often poor emotional health.
Observing the tongue:
-
If the tongue surface is sticky and not refreshing, with visible moisture and stickiness, and the groove in the middle of the tongue is very pronounced, such individuals generally have the “three highs”—high blood pressure, high blood lipids, and high blood sugar. If the tongue coating is slightly yellow, not overly greasy, but just beginning to show yellow stickiness, it indicates that this person is starting to have phlegm-damp conditions. If accompanied by redness in the cheeks, it indicates internal heat and requires heat-clearing.
-
A common appearance is a thick white greasy tongue coating, which is a thick layer of white tongue coating that cannot be wiped away or scraped off, and is covered with a layer of greasy mucus. This tongue appearance often indicates poor spleen and stomach function, digestive issues, and frequent problems such as diarrhea and stomach pain. Especially in high temperatures and heavy humidity, thick white greasy tongue coatings are particularly likely to occur.
-
A thick yellow tongue coating is also quite common. A thick yellow coating indicates internal damp-heat, and this tongue appearance is often seen in individuals who enjoy drinking alcohol. If the tongue coating is quite yellow, it may indicate severe internal heat, and it is advisable to drink more heat-clearing teas.
Individuals with a thick white greasy tongue coating can consume more winter melon and ginger. It is recommended to simmer winter melon, coix seed, yam, and ginger together for soup, and *Huo Xiang Zheng Qi* (Agastache Qi Rectifying) water can also be used. If the tongue coating is thick and yellow, dietary therapy is not very effective, and some Chinese patent medicines, such as *Huang Lian Shang Qing Wan* (Coptis Heat Clearing Pill) and *Dan Zhi Xiao Yao Wan* (Dan Zhi Free and Easy Wanderer Pill), can be used.
If the tongue coating is very greasy and thick, it indicates excessive internal nutrition that cannot be transformed into heat, leading to more serious imbalances. Individuals with this tongue appearance and phlegm-damp constitution must not supplement their bodies further.
Ancient phlegm-damp dispelling formula: *Wen Dan Tang* (Warm Gallbladder Decoction) formula: 30g Poria (Fu Ling), 6g dried tangerine peel (Chen Pi), 6g *Ban Xia* (Pinellia), 6g bamboo shavings (Zhu Ru), 6g bitter orange (Zhi Shi), 6g honey-fried licorice (Zhi Gan Cao).
Method: Add the above herbs to water, boil for 30 minutes, divide the decoction into two portions, and mix with warm water for foot baths, each time for 20 minutes. The water temperature should not be too hot, just enough to cover the feet.
The fundamental cause of phlegm-damp constitution is also spleen deficiency, as the spleen is unable to transform and transport water and dampness, leading to prolonged stagnation in the body. Therefore, individuals with phlegm-damp constitution can also frequently drink *Wuzhi Maotao* (Five-Finger Peach) qi-boosting and damp-dispelling soup.
3. Yang Deficiency: Insufficient yang qi leads to a timid life.
Main manifestations of yang deficiency include: sensitivity to wind and cold, especially in the abdomen and lower limbs, pale complexion, lack of color, frequent clear urination, large volumes of urine, decreased libido, and abdominal or stomach pain when exposed to cold.
Currently, there are many individuals with yang deficiency, which indicates insufficient warming function in the body. The kidneys can produce kidney yin and kidney yang. Kidney yang is responsible for warming the body, promoting development, reproduction, and vitality.
What causes kidney yang deficiency? Excessive consumption of kidney essence, such as staying up late, excessive sexual activity, serious illnesses (the body consumes kidney yang while fighting disease), and excessive use of cold medicines, etc.
Observing the tongue:
The tongue appearance of yang deficiency is similar to that of blood deficiency, but the difference is that the tongue coating of yang deficiency is white, the tongue body is pale, and the tongue does not appear red, looking relatively “aged”; while the tongue appearance of blood deficiency is pale white and appears tender.
Individuals with yang deficiency, when the deficiency is mild, have heavier internal dampness, so the tongue is more salivary, which in TCM is called “water-slippery tongue coating”; when the yang deficiency is more severe, the body fluids cannot rise, leading to dry mouth and tongue.
TCM remedies for regulating yang deficiency: For insufficient kidney yang, *Jin Gui Shen Qi Wan* (Golden Cabinet Kidney Qi Pill) can be taken; for elderly individuals with frequent nighttime urination, *Jin Gui Shen Qi Wan* can also be taken; if stomach pain occurs upon contact with cold substances, *Fu Zi Li Zhong Wan* (Aconite Middle-Strengthening Pill) can be taken.
4. Blood Deficiency: Those who nourish blood age slowly.
Main manifestations of blood deficiency include: dizziness when standing up after squatting for a short time, poor memory, insomnia, some people experience vivid dreams, heart fatigue, unwillingness to think, easy fatigue, and body temperature fluctuating with the external environment.
Currently, there are many individuals with blood deficiency, especially women.
In TCM, blood is produced after the spleen and stomach absorb nutrients from food. Modern individuals often have many issues with their spleen and stomach. How do these problems arise? “Overeating leads to discomfort!” When the spleen and stomach are damaged by excessive eating, their ability to absorb nutrients is compromised, leading to abnormal blood supply.
Many children’s anemia is related to eating too well and too much. Excessive fatigue and worry can deplete heart blood. Various forms of blood loss can also lead to blood deficiency, so the probability of blood loss throughout a person’s life is quite high.
Observing the tongue:
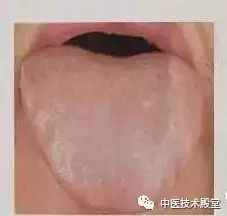
If the edges of the tongue are very pale, it indicates mild blood deficiency. If the tongue coating is not thick, and the color of the tongue body is very pale, even somewhat transparent, it is a typical sign of blood deficiency.
5. Yin Deficiency: The main characteristic is anxiety and excessive internal heat.
Main manifestations of yin deficiency include: irritability, rapid pulse, hot palms and soles, poor sleep, night sweats, dry stools, yellow urine, and soreness in the lower back and knees.
Children with yin deficiency often exhibit: very red lips, eye bags, susceptibility to colds, and swollen throats, being active with poor patience.
Individuals with yin deficiency have increasing internal heat. Staying up late, excessive consumption of spicy foods, and poor emotional health can all lead to yin deficiency.
Observing the tongue:
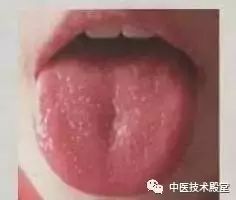
If a person does not have an external pathogen but has a thin or absent tongue coating, and the tongue body is red, it can be concluded that this person has a yin deficiency constitution. If the tongue coating is very thin or absent (atrophied), it is also a sign of yin deficiency. Many people have geographic tongue, where patches of coating are missing, exposing the red tongue body; this tongue appearance is mostly caused by yin deficiency.
Elderly individuals are more prone to yin deficiency because, with age, body fluids are consumed more, and by old age, they are already scarce, leading to a yin deficiency constitution. From the tongue appearance, elderly individuals often have very red tongues with many deep cracks, and they experience discomfort when consuming spicy foods, all of which are manifestations of yin deficiency.
Most individuals transition from a yin deficiency constitution to a blood deficiency constitution; yin deficiency and blood deficiency are interrelated and mutually affect each other. Severe yin deficiency can lead to blood deficiency. Many individuals with blood deficiency originally have pale tongues, but for unknown reasons, their tongues gradually turn red, indicating a transition from blood deficiency to yin deficiency.
6. Qi Stagnation: Calming the spirit is essential for strength.
Main manifestations of qi stagnation include: bitter and dry mouth, dry throat, dizziness, poor appetite, aversion to food, alternating chills and fever, nausea, acid reflux, upward qi, chest tightness, palpitations, abnormal heartbeats, and localized pain in the ribs, insomnia, and vivid dreams.
Qi stagnation refers to liver qi stagnation, which is the biggest issue for modern individuals. If emotions are not alleviated in a timely manner, it can lead to diabetes, tumors, and other issues over time.
Observing the tongue:
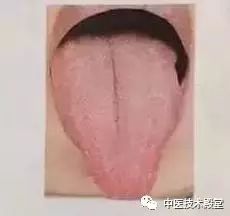
The most obvious characteristic of liver qi stagnation is that the tongue appears pointed and red, especially at the tip and edges. This is a manifestation of qi stagnation. If the tongue has a thick white coating that covers the entire tongue but the tip remains pointed, this is also a typical sign of liver qi stagnation.
If the tongue is pointed, with red edges and a red tip, and has a white coating, it indicates that this person has previously experienced liver qi stagnation, which continues to negatively affect their body; or that this person is currently experiencing liver qi stagnation.
If a newborn has a pointed tongue, parents should be alert to the possibility of qi stagnation in the child.
7. Blood Stasis: Aging is the process of increasing blood stasis in the body.
Main manifestations of blood stasis include: poor memory, bruising in various parts of the body, frequent dry throat, dry and rough skin, visible blood vessels on the skin, and frequent pain in certain areas of the body.
In addition to trauma, surgery, anger, qi deficiency, and cold exposure leading to blood stasis, “heat” can also cause blood stasis, as “heat” evaporates the liquid in the blood, making it viscous, leading to blood stasis in the body.
Observing the tongue:

-
If there are stasis points on the tip of the tongue, it indicates that blood stasis is about to form but has not yet formed. If there are many black or blue stasis spots on the tip and sides of the tongue, it indicates severe blood stasis. If the veins under the tongue are dark and thick, it indicates severe blood stasis in the body. If the tongue body is blue or purplish, it suggests the presence of blood stasis.
-
If the tip of the tongue is deviated, except for cases where the deviation is physiological, if the tongue tip was previously normal and has recently deviated, it indicates a need to pay attention to blood stasis. Generally, the direction in which the tongue tip deviates indicates where blood flow is blocked in the head. Note that cerebrovascular blockage is common in the elderly, so if the tongue direction changes, it is advisable to take the elderly for a check-up, as their bodies are very sensitive, and cerebrovascular blockage can occur suddenly.
The deviation of the tongue tip, stasis spots, and distended veins under the tongue generally do not appear together. However, if any one of these conditions appears, it indicates the presence of blood stasis in the body. If multiple conditions appear together, it indicates a serious condition.
If a woman has signs of blood stasis on her tongue, and heavy hair on her lips, it may indicate endocrine issues, requiring thorough examination, as there may be problems such as uterine fibroids or ovarian cysts.