Many people have experienced this: when visiting a hospital, doctors often ask us to stick out our tongues. This is because tongue diagnosis (舌诊, shé zhěn) is an important method in TCM observation (望诊, wàng zhěn). The five internal organs have corresponding reflection areas on the tongue, and any pathological changes in the internal organs will be directly reflected on our tongue.Doctors observe the tongue based on two indicators: the color of the tongue and tongue coating, and the thickness and shape of the tongue. You might want to stick out your tongue in front of a mirror to check.Color of the Tongue
A normal tongue color is generally pleasing, typically pale red to light pink.
If the tongue is too pale or white, it indicates cold (寒, hán) or deficiency of qi and blood (气血不足, qì xuè bù zú);
If it is red or dark red, it indicates the presence of heat (热, rè);
If it appears dark purple, it indicates stasis of blood (瘀血, yū xuè).
Color of the Tongue Coating1White CoatingWhite coating generally indicates the presence of cold dampness (寒湿, hán shī) in the body, which is particularly common in modern individuals. Why? Because modern people often experience high work pressure and irregular eating and sleeping habits, leading to dampness in the spleen and stomach, which is reflected on the tongue.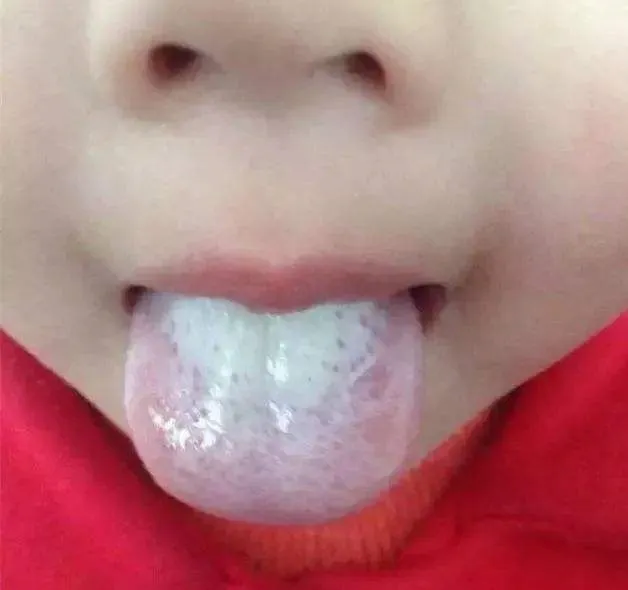 White coating can be seen in healthy individuals (sub-health status) as well as in mild illnesses, early stages of diseases, and recovery periods. Early-stage diseases or localized lesions that have not affected the whole body, such as adolescent goiter, trauma, tinea pedis, plum pit qi (梅核气, méi hé qì), early breast cancer, cervical cancer, etc.For instance, in the case of COVID-19, it is recognized as a damp epidemic (湿疫, shī yì), and most patients with COVID-19 exhibit a white and greasy tongue coating, indicating a strong relationship between the white coating and internal cold dampness.2Yellow CoatingYellow coating generally represents the presence of heat (热, rè) in the body. If the tongue coating is yellow and greasy, it indicates damp-heat (湿热, shī rè) in the body, and one should clear heat and eliminate dampness, regulating the spleen and stomach.
White coating can be seen in healthy individuals (sub-health status) as well as in mild illnesses, early stages of diseases, and recovery periods. Early-stage diseases or localized lesions that have not affected the whole body, such as adolescent goiter, trauma, tinea pedis, plum pit qi (梅核气, méi hé qì), early breast cancer, cervical cancer, etc.For instance, in the case of COVID-19, it is recognized as a damp epidemic (湿疫, shī yì), and most patients with COVID-19 exhibit a white and greasy tongue coating, indicating a strong relationship between the white coating and internal cold dampness.2Yellow CoatingYellow coating generally represents the presence of heat (热, rè) in the body. If the tongue coating is yellow and greasy, it indicates damp-heat (湿热, shī rè) in the body, and one should clear heat and eliminate dampness, regulating the spleen and stomach.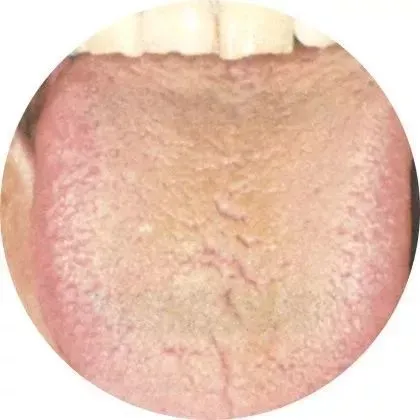 From a pathological perspective, yellow coating is often associated with inflammatory infections: various acute infectious diseases, such as meningococcal meningitis, Japanese encephalitis, leptospirosis, typhoid fever, diphtheria, and severe stages of bacterial dysentery, as well as severe pneumonia, severe hepatitis, intestinal infections, acute pyelonephritis, pelvic inflammatory disease, sepsis caused by staphylococcus and streptococcus, acute pancreatitis, appendicitis, intestinal obstruction, ruptured ectopic pregnancy, mid or late stages of acute perforated ulcer disease, peritonitis, acute cholecystitis, cholelithiasis, and urinary tract infections, can all present with yellow coating.In cases of cold and fever, if yellow coating is observed, it may be accompanied by dry mouth, sore throat, cough, and yellow phlegm, which in TCM is referred to as wind-heat type cold (风热型感冒, fēng rè xíng gǎn mào). Fever can lead to yellow coating appearing as soon as two days, indicating a close relationship between fever and yellow coating. Treatment should focus on cooling herbs and avoid stimulating spicy foods and tonics to prevent exacerbating the condition.3Gray-Black CoatingThis is primarily caused by the proliferation of filiform papillae on the tongue turning black. The color of black coating can vary from brown-black, gray-black, charred black to pitch black. If this coating appears, it indicates a prolonged illness with a complex and severe condition.
From a pathological perspective, yellow coating is often associated with inflammatory infections: various acute infectious diseases, such as meningococcal meningitis, Japanese encephalitis, leptospirosis, typhoid fever, diphtheria, and severe stages of bacterial dysentery, as well as severe pneumonia, severe hepatitis, intestinal infections, acute pyelonephritis, pelvic inflammatory disease, sepsis caused by staphylococcus and streptococcus, acute pancreatitis, appendicitis, intestinal obstruction, ruptured ectopic pregnancy, mid or late stages of acute perforated ulcer disease, peritonitis, acute cholecystitis, cholelithiasis, and urinary tract infections, can all present with yellow coating.In cases of cold and fever, if yellow coating is observed, it may be accompanied by dry mouth, sore throat, cough, and yellow phlegm, which in TCM is referred to as wind-heat type cold (风热型感冒, fēng rè xíng gǎn mào). Fever can lead to yellow coating appearing as soon as two days, indicating a close relationship between fever and yellow coating. Treatment should focus on cooling herbs and avoid stimulating spicy foods and tonics to prevent exacerbating the condition.3Gray-Black CoatingThis is primarily caused by the proliferation of filiform papillae on the tongue turning black. The color of black coating can vary from brown-black, gray-black, charred black to pitch black. If this coating appears, it indicates a prolonged illness with a complex and severe condition.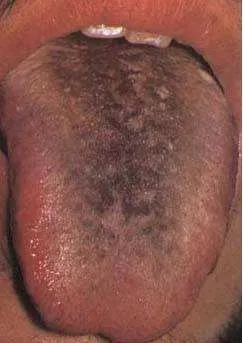 Among patients with black coating, half of the cases are caused by various inflammatory infections, including pneumonia and pyelonephritis. Dysfunction of the central nervous system can also lead to black coating. Certain critically ill patients, such as those with chronic organ failure, severe liver damage in late-stage cirrhosis, chronic renal failure with uremia, and various late-stage cancers, may also present with black coating, indicating a critical stage of illness.Of course, black coating does not necessarily indicate a severe illness; poor oral hygiene and infrequent brushing can promote the growth of fungi and lead to prolonged keratinization of the tongue papillae, resulting in black coating. Frequent smokers may also develop black coating due to the irritation of the tongue papillae by smoke or chemicals in tobacco. Regular consumption of Chinese herbs can also lead to black coating due to drug sedimentation and staining, which will improve after stopping the medication.Color of the TongueUnderstanding the symbolism of the tongue and tongue coating colors allows us to infer the prognosis of our health. However, in addition to color, we can also assess health status through the shape and size of the tongue.A normal tongue has a moderate thickness and size. If the following conditions occur, attention is needed.1Teeth-Marked TongueA tongue that is too large indicates spleen deficiency (脾虚, pí xū); if there are teeth marks, it indicates a more severe version of spleen deficiency—spleen dampness (脾湿, pí shī); individuals with this condition are often weak, speak little, feel fatigued, and have cold hands and feet.If you notice a teeth-marked tongue, try to avoid eating raw fruits and cold drinks, as they can exacerbate dampness. It is recommended to use moxibustion (艾灸, ài jiǔ) for regulation or drink a decoction of Fu Ling (茯苓, fú líng) and Bai Zhu (白术, bái zhǔ).2Thin Tongue
Among patients with black coating, half of the cases are caused by various inflammatory infections, including pneumonia and pyelonephritis. Dysfunction of the central nervous system can also lead to black coating. Certain critically ill patients, such as those with chronic organ failure, severe liver damage in late-stage cirrhosis, chronic renal failure with uremia, and various late-stage cancers, may also present with black coating, indicating a critical stage of illness.Of course, black coating does not necessarily indicate a severe illness; poor oral hygiene and infrequent brushing can promote the growth of fungi and lead to prolonged keratinization of the tongue papillae, resulting in black coating. Frequent smokers may also develop black coating due to the irritation of the tongue papillae by smoke or chemicals in tobacco. Regular consumption of Chinese herbs can also lead to black coating due to drug sedimentation and staining, which will improve after stopping the medication.Color of the TongueUnderstanding the symbolism of the tongue and tongue coating colors allows us to infer the prognosis of our health. However, in addition to color, we can also assess health status through the shape and size of the tongue.A normal tongue has a moderate thickness and size. If the following conditions occur, attention is needed.1Teeth-Marked TongueA tongue that is too large indicates spleen deficiency (脾虚, pí xū); if there are teeth marks, it indicates a more severe version of spleen deficiency—spleen dampness (脾湿, pí shī); individuals with this condition are often weak, speak little, feel fatigued, and have cold hands and feet.If you notice a teeth-marked tongue, try to avoid eating raw fruits and cold drinks, as they can exacerbate dampness. It is recommended to use moxibustion (艾灸, ài jiǔ) for regulation or drink a decoction of Fu Ling (茯苓, fú líng) and Bai Zhu (白术, bái zhǔ).2Thin Tongue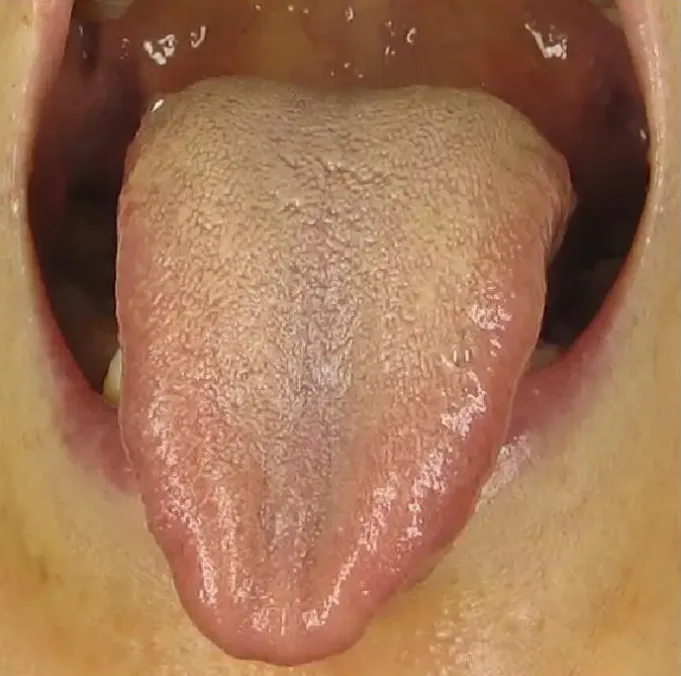 A tongue that is too thin indicates qi stagnation (气郁, qì yù); if it is both thin and narrow, it indicates deficiency of qi and blood (气血不足, qì xuè bù zú);3Stasis-Dotted Tongue
A tongue that is too thin indicates qi stagnation (气郁, qì yù); if it is both thin and narrow, it indicates deficiency of qi and blood (气血不足, qì xuè bù zú);3Stasis-Dotted Tongue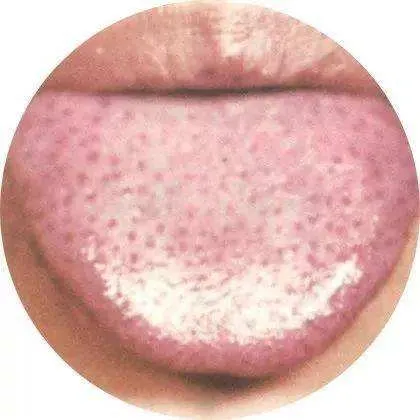 If there are spots or stasis on the tongue, it indicates stasis of blood (瘀血, yū xuè); TCM believes this is caused by liver qi stagnation (肝气不舒, gān qì bù shū), leading to internal blood stasis. At this time, one can take some herbs that soothe the liver and regulate qi, but the fundamental solution is to manage our emotions well, smile more, and the body will naturally improve.4Cracked Tongue
If there are spots or stasis on the tongue, it indicates stasis of blood (瘀血, yū xuè); TCM believes this is caused by liver qi stagnation (肝气不舒, gān qì bù shū), leading to internal blood stasis. At this time, one can take some herbs that soothe the liver and regulate qi, but the fundamental solution is to manage our emotions well, smile more, and the body will naturally improve.4Cracked Tongue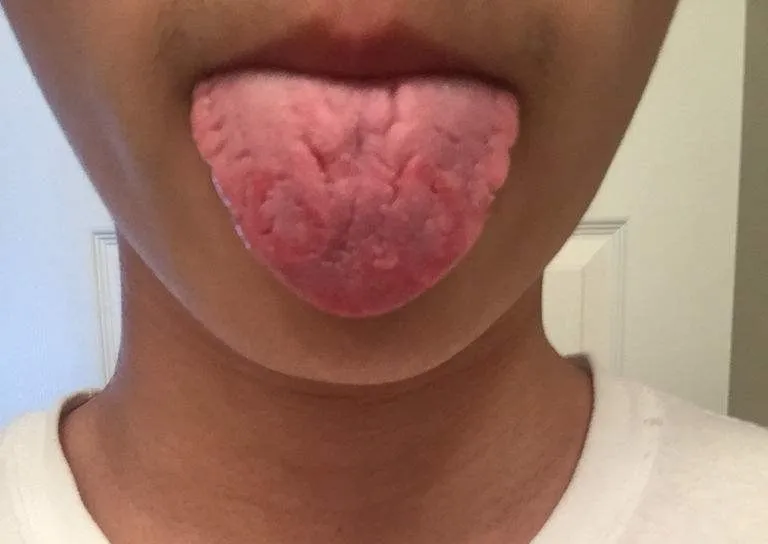 Generally, most people have slight cracks in the middle of the tongue, but if the cracks are prominent, it indicates deficiency of qi in the spleen and stomach (脾胃气不足, pí wèi qì bù zú), and one should focus on improving the spleen and stomach.5Blue Veins Under the Tongue
Generally, most people have slight cracks in the middle of the tongue, but if the cracks are prominent, it indicates deficiency of qi in the spleen and stomach (脾胃气不足, pí wèi qì bù zú), and one should focus on improving the spleen and stomach.5Blue Veins Under the Tongue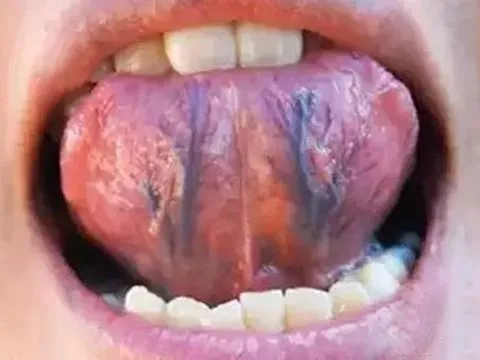 There are two veins under the tongue that flow quietly; under normal circumstances, these veins are faintly visible or not visible at all. However, when there is stagnation in the body and poor circulation of qi and blood, the veins under the tongue will become prominent, indicating a risk of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases.6Deviated Tongue
There are two veins under the tongue that flow quietly; under normal circumstances, these veins are faintly visible or not visible at all. However, when there is stagnation in the body and poor circulation of qi and blood, the veins under the tongue will become prominent, indicating a risk of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases.6Deviated Tongue If the tongue appears deviated or the root of the tongue feels numb, along with numbness in the index and middle fingers, this is often a precursor to a stroke (中风, zhòng fēng). In such cases, please seek medical attention immediately.
If the tongue appears deviated or the root of the tongue feels numb, along with numbness in the index and middle fingers, this is often a precursor to a stroke (中风, zhòng fēng). In such cases, please seek medical attention immediately.

