Author: Zhang Li, Chief Chinese Medicine Pharmacist, Guangzhou Red Cross Hospital Affiliated to Jinan University
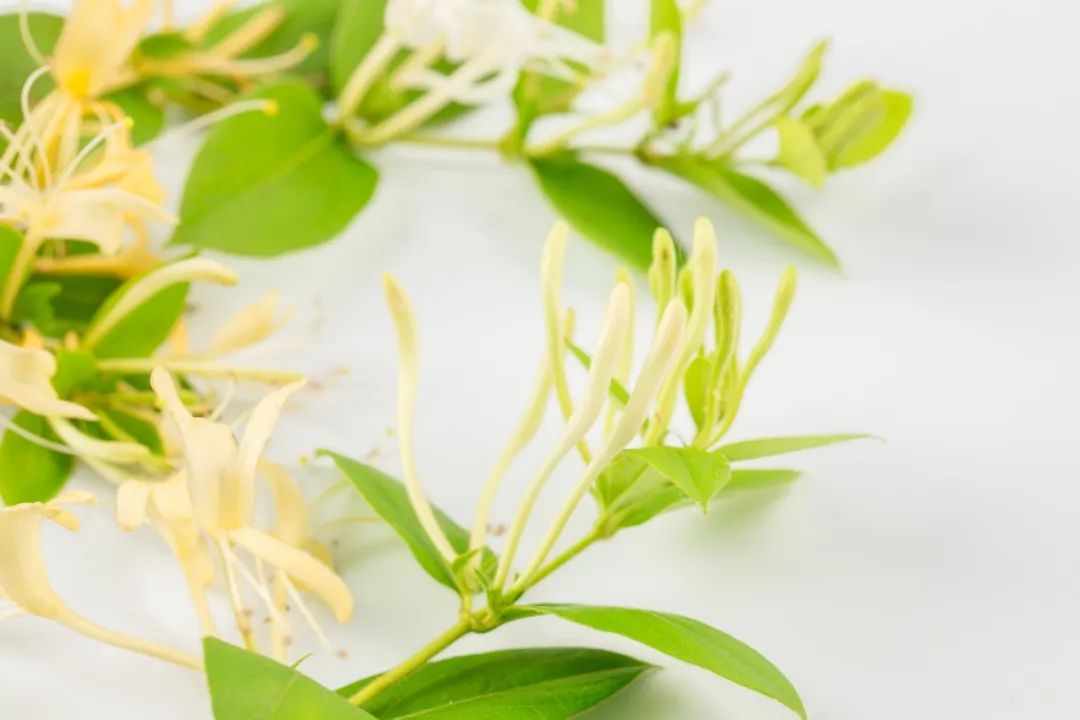

Are Jin Yin Hua and Shan Yin Hua the Same?
Before 2005, there was no distinction made between Jin Yin Hua (Honeysuckle Flower) and Shan Yin Hua (Mountain Honeysuckle). In southern China, Shan Yin Hua (Southern Jin Yin Hua) was generally considered to be the same as Jin Yin Hua. However, after 2005, the National Pharmacopoeia Commission clearly stated in the “Chinese Pharmacopoeia” that Southern Jin Yin Hua is not the true Jin Yin Hua. So, are Jin Yin Hua and Shan Yin Hua the same?
01
Source
Prior to the 2005 edition of the Chinese Pharmacopoeia, there was no clear specification regarding the source of Shan Yin Hua, and it was uniformly considered to be Jin Yin Hua. In the 2005 edition, Jin Yin Hua and Shan Yin Hua were separated. The main production areas of Shan Yin Hua and Jin Yin Hua are distributed in the north and south.
Jin Yin Hua: This product is the dried flower buds or newly opened flowers of the plant Lonicera japonica (Honeysuckle). It is harvested before flowering in early summer and then dried. Although Jin Yin Hua is distributed nationwide, it is mainly found in northern regions. According to “Chinese Medicinal Materials”, the primary production areas are Fengqiu in Henan and Pingyi in Shandong.
Shan Yin Hua: This product is the dried flower buds or newly opened flowers of the plants Lonicera maackii (Gray Woolly Honeysuckle), Lonicera xylosteum (Red-gland Honeysuckle), Lonicera japonica (Southern Honeysuckle), or Lonicera fulvotomentosa (Yellow-brown Woolly Honeysuckle). It is harvested before flowering in early summer and then dried. The main production areas for Lonicera maackii are Xiushan in Chongqing and Longhui in Hunan; the other three varieties of Shan Yin Hua are mainly distributed in southern regions such as Jiangxi, Guangdong, and Guizhou.
02
Distinguishing Characteristics
Jin Yin Hua and Shan Yin Hua also have obvious differences in appearance (Table 1). Jin Yin Hua is rod-shaped, thicker at the top and thinner at the bottom, while Shan Yin Hua is mostly elongated and slightly curved, with little difference in thickness at both ends.
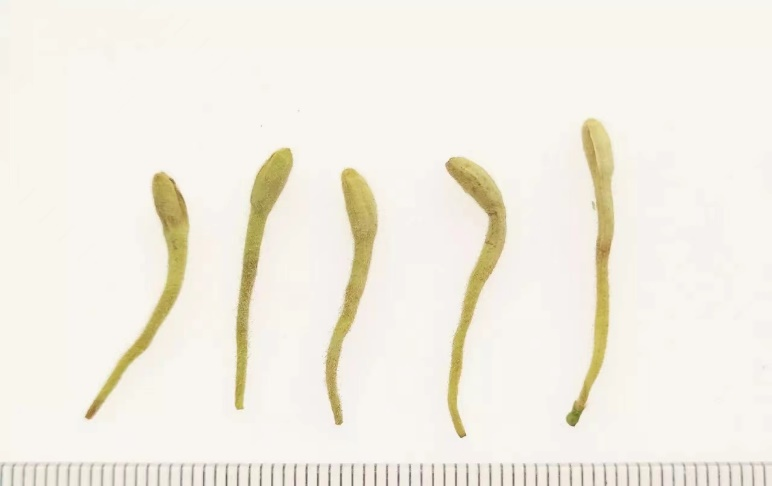

Jin Yin Hua (above)
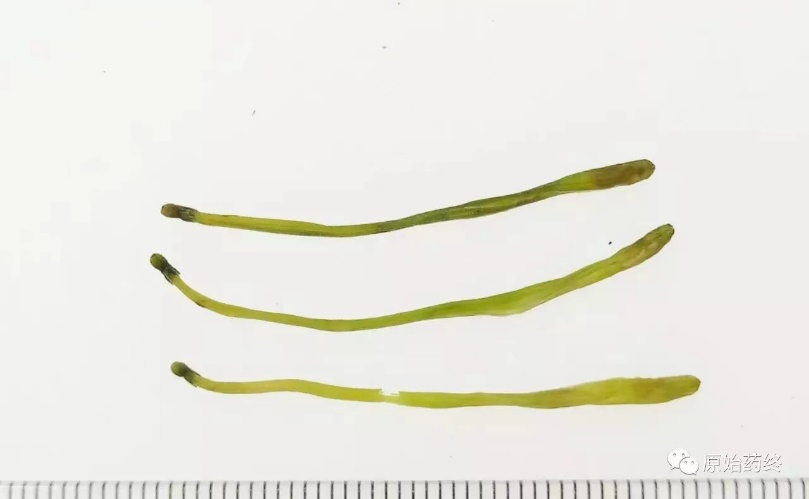

Shan Yin Hua (above)
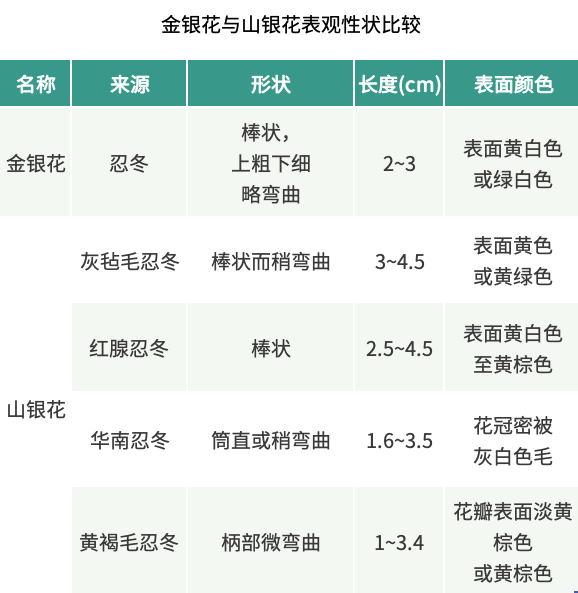
Table 1 (above)
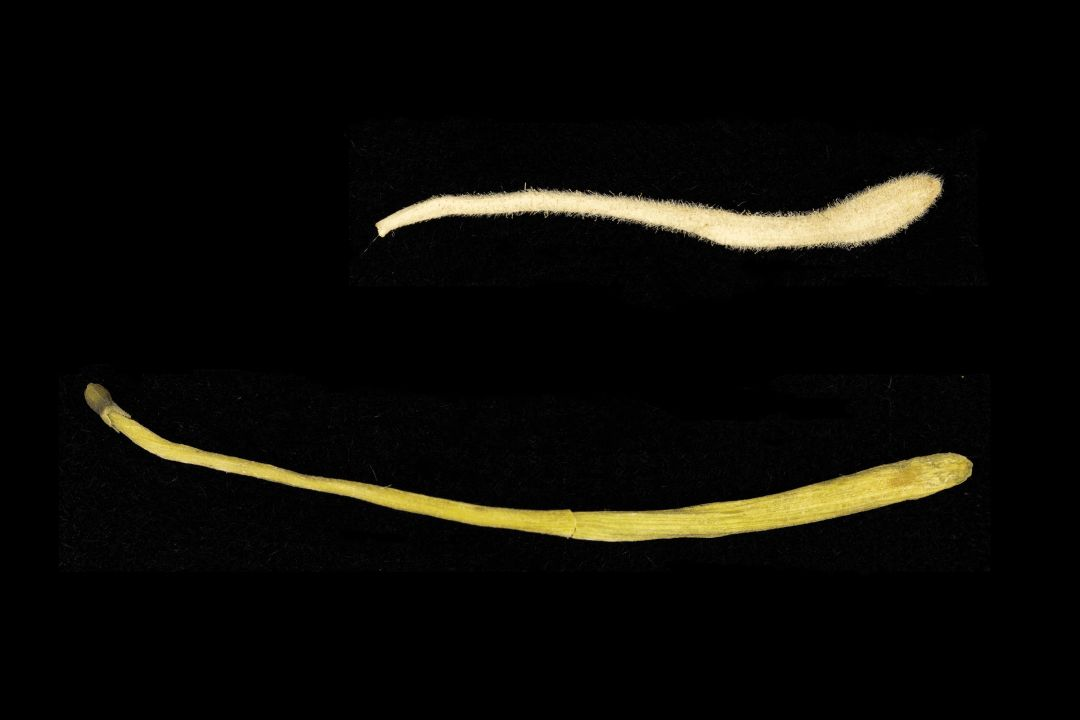

Image: Above: Jin Yin Hua, Below: Shan Yin Hua
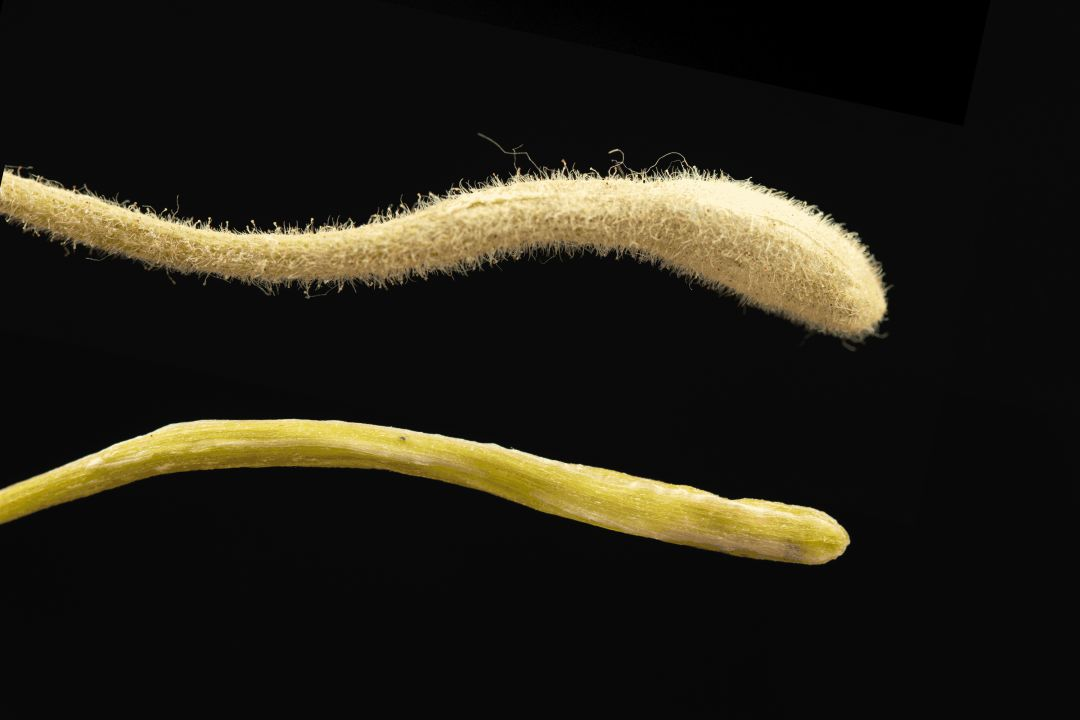

Image: Above: Jin Yin Hua, Below: Shan Yin Hua
03
Functions and Indications
Both Jin Yin Hua and Shan Yin Hua share the common effects of clearing heat and detoxifying, as well as dispersing wind-heat. Modern research indicates that both have antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, liver-protective, gallbladder-promoting, and blood sugar-lowering pharmacological effects. The antipyretic and anti-inflammatory effects are better with Jin Yin Hua, while Shan Yin Hua has stronger antiviral capabilities than Jin Yin Hua. Shan Yin Hua contains saponins that can cause allergic reactions, whereas the saponins in Jin Yin Hua do not cause allergic reactions. In all medicinal preparations of Jin Yin Hua and Shan Yin Hua, it is strictly stipulated that injections can only use Jin Yin Hua and not be replaced by Shan Yin Hua; in other forms, Shan Yin Hua can replace Jin Yin Hua.
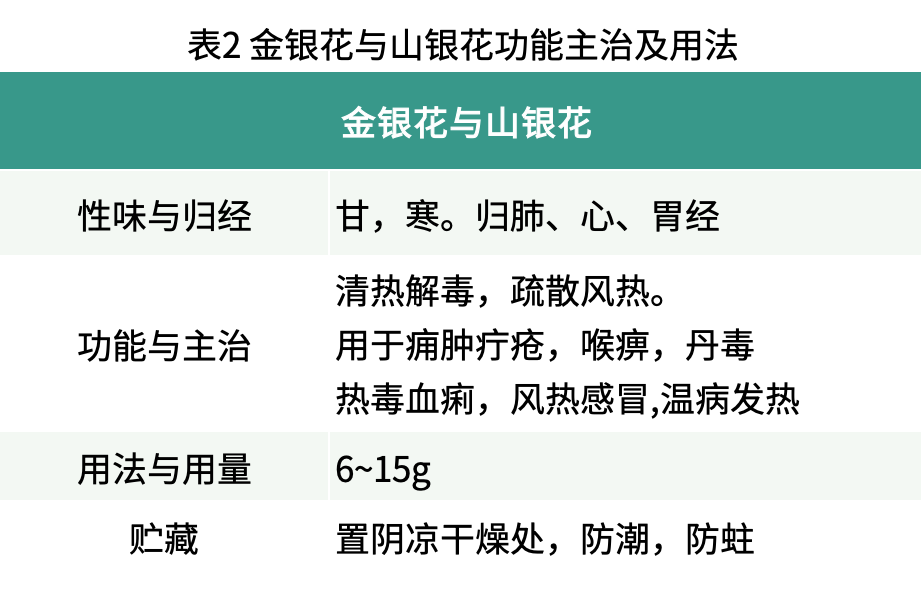
Table 2 (above)
04
Content Differences
The main chemical components of Jin Yin Hua and Shan Yin Hua are basically the same, divided into flavonoids and organic acids, with differences only in the content and types of certain chemical components. Comparing the contents of chlorogenic acid and luteoloside, Shan Yin Hua has a higher content of chlorogenic acid, while Jin Yin Hua has a higher content of luteoloside.
The “Chinese Pharmacopoeia” stipulates that Jin Yin Hua: the dried product must contain no less than 1.5% chlorogenic acid and no less than 3.8% total phenolic acids. The content of luteoloside must not be less than 0.050%. Shan Yin Hua: the dried product must contain no less than 2.0% chlorogenic acid and no less than 5.0% total saponins of Lonicera maackii and Lonicera japonica.
05
Authenticity
After the late Qing Dynasty, Jin Yin Hua began to be cultivated, with Henan as the main production area, particularly in Mixian (now Xinmi), known for its high-quality products, referred to as “Mi Yin Hua”. Since the 1970s, Fengqiu has gradually developed into the core authentic production area of Jin Yin Hua, inheriting the excellent quality of the authentic medicinal material Mi Yin Hua.
-END-
Some images in this article are sourced from the internet for public welfare dissemination. We thank the authors of the images, and if there is any infringement, please contact us for removal.

This article is an original work by “PSM Yao Dun Public Welfare”. For reprints, please leave a message.
Review Expert: Wang Yuqing, Deputy Chief Chinese Medicine Pharmacist, Guangzhou Red Cross Hospital Affiliated to Jinan University

References
[1] Hu Lujian, Luo Jiangnan, Guo Huiling, et al. Comparative Study on the Differences Between Jin Yin Hua and Shan Yin Hua [J]. Journal of Jiangxi University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2019, 031(005):120-124. [2] Zhang Jing, Xu Baohai, Pan Xu. Research on the Key Points of Identification Between Jin Yin Hua and Shan Yin Hua [J]. Beijing Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2019, 38(1):4. [3] Feng Yalan, Dong Qing, Yu Jiamiao, et al. The “Dispute” Between Jin Yin Hua and Shan Yin Hua [J]. Shaanxi Agricultural Science, 2018, 64(7):6. [4] Feng Feng, Duan Xiaoyi, Xu Meixia, et al. Research on the Quality Grade Standards of Jin Yin Hua [J]. Journal of Food Safety and Quality Detection, 2020, 11(18):7. [5] Hu Zhongjun, Ke Wen. How to View the “Dispute Between the Two Flowers” [J]. Science and Technology Management Research, 2015, 35(13):5.


SearchArticles Related to Jin Yin Hua

