
Click the blue text to follow us
What is Bloodletting Therapy?
Bloodletting therapy is a unique acupuncture treatment method in Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM). When used appropriately, it is not only harmless to the body but can also reduce the toxic side effects of certain Chinese and Western medications, making it one of today’s natural therapies. Its historical roots are very deep, being one of the most commonly used treatment methods since the era of the Huangdi Neijing (Yellow Emperor’s Inner Canon). This text considers bloodletting therapy as the first choice for treating diseases and alleviating suffering. It involves using a three-edged needle or a thick, sharp needle to puncture specific acupuncture points or superficial blood vessels on the patient, allowing a certain amount of blood to be released to achieve therapeutic goals.
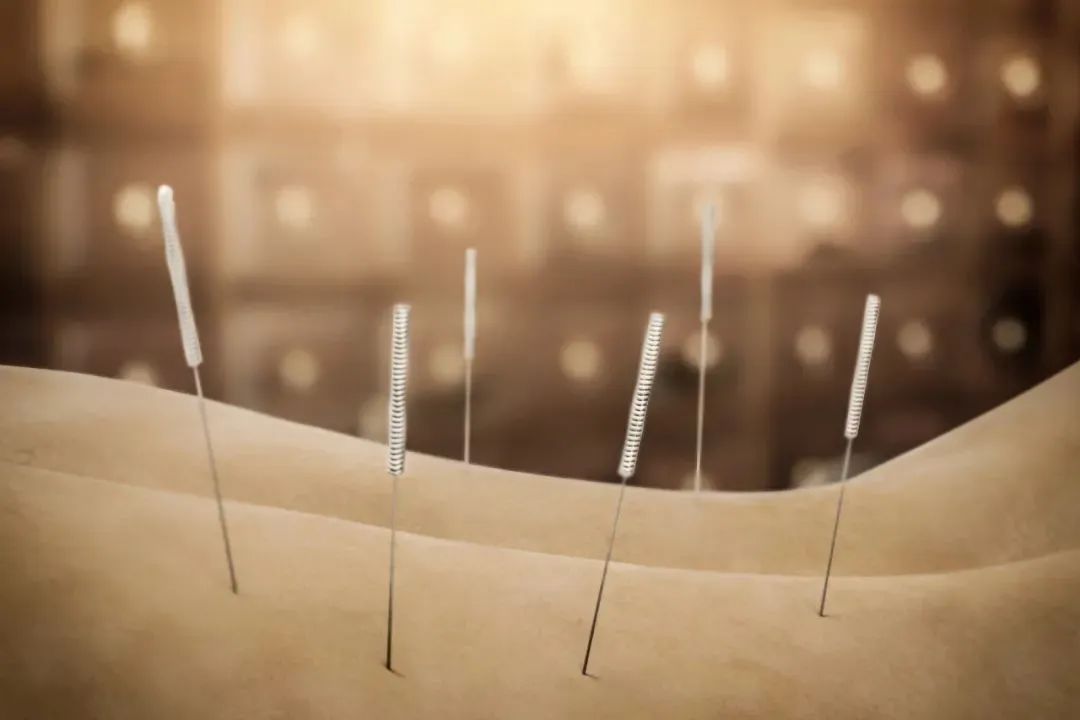
Bloodletting is an external treatment method that involves puncturing specific acupuncture points or superficial blood vessels based on the patient’s condition to release a small amount of blood or lymph fluid for therapeutic purposes. It is also known as cì luò (刺络) or cì xuè luò (刺血络).
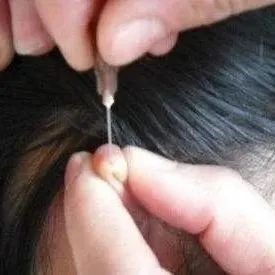
Research indicates that bloodletting therapy can promote metabolism, stimulate bone marrow hematopoiesis, accelerate metabolic processes, improve microcirculation and vascular function, and facilitate the elimination of harmful substances from the blood.
It is easy to perform and has rapid effects, often providing immediate relief from chronic ailments and stubborn diseases, achieving significant results that cannot be matched by medications or other acupuncture techniques.

Effects of Bloodletting Therapy
1. Antipyretic Effect
In TCM, fever is primarily categorized into two types: Yang excess fever and Yin deficiency fever. The antipyretic effect of bloodletting is applicable to the former.
Since excess Yang energy leads to an abundance of blood, bloodletting can reduce this excess, thereby diminishing the evil heat in the blood vessels and normalizing the body’s Qi and blood.
2. Analgesic Effect
TCM holds that “where there is flow, there is no pain; where there is pain, there is no flow.” This means that diseases with pain symptoms must have blockages in their meridians.
Bloodletting therapy can directly expel the stagnant pathogenic factors from the meridians, alleviating the blockage and allowing for immediate pain relief.
3. Detoxifying Effect
The detoxifying effect in TCM refers to the body’s inability to resist toxic evils due to pathological conditions, leading to symptoms such as “red thread sores” caused by excessive toxic fire.
Bloodletting not only expels the invading toxic evils with the blood but, more importantly, restores normal bodily functions through the principle of “regulating blood and Qi,” inhibiting the spread and regeneration of pathogenic evils.
4. Fire-Draining Effect
TCM believes that internal heat disturbances can lead to various diseases, often manifesting as irritability, limb pain and swelling, impatience, and even fever and confusion.
Bloodletting therapy can directly drain the fire-evil with the blood, making it suitable for various heat syndromes.
5. Swelling-Reducing Effect
Swelling and pain are often caused by Qi stagnation and blood stasis, leading to obstruction in the meridians.
Bloodletting can directly eliminate the stagnant Qi and blood along with pathogenic factors in the local meridians, promoting unobstructed meridian flow and achieving the goal of reducing swelling.
Bloodletting therapy can promote metabolism, stimulate bone marrow hematopoiesis, accelerate metabolic processes, improve microcirculation and vascular function, facilitate the elimination of harmful substances from the blood, and ensure beneficial substances are timely replenished into the blood circulation, helping the body re-establish homeostasis and restore normal physiological functions. By improving microcirculation, it can also prevent excessive inflammatory responses and promote recovery from inflammation.

Shiquan County Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital
Phone: 0915-6328120
Renai / Jingcheng / Inheritance / Innovation
Text and image editing: Health Management Center
Text and image review: Acupuncture Department

