Section 1: Solid Dosage Forms
Learning Objectives: 1. Classification, characteristics, and general quality requirements of solid dosage forms 2. Powders and granules 3. Tablets 4. Capsules 》 Classification, characteristics, and quality requirements 》 Clinical applications and precautions 》 Analysis of typical prescriptions
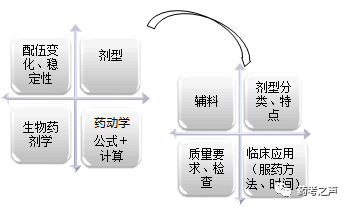
Pharmaceutics – What to Expect?
1. Overview of Solid Dosage Forms 1. Classification 》 By dosage form
》 By release rate
2. Characteristics of Solid Dosage Forms

① Good stability, mature technology, relatively low cost ② Similar operations in pre-treatment units ③ Drugs dissolve before being absorbed into the bloodstream ④ Easy dosage control ⑤ Convenient in five aspects (production, storage, transportation, carrying, and usage)
2. Powders Drug + excipients → grinding, mixing → drying powder 1. Classification ① By use: oral, topical ② By composition: single, compound ③ By dosage: divided doses (for packaged use), undivided doses (for external use)

2. Characteristics of Powders ① Small particle size, large specific surface area, easy to disperse, fast acting ② Large coverage for external use, also protective and astringent ③ Simple preparation, easy dosage control, suitable for children and the elderly ④ Convenient in five aspects ⑤ Sensitive to light, moisture, and heat

3. Quality Requirements for Powders ① Fine powder for oral use, finest powder for topical use ② Toxic, expensive, small dosage: Preparation Method ③ Multi-dose: with divided dose tools ④ Toxic + oral: single-dose packaging ⑤ Sealed and airtight (to prevent volatilization and moisture absorption)

Supplement: Mixing – to ensure uniformity Stirring, grinding, sieving Equal Increment Method (Preparation Method): Toxic, expensive, small dosage

4. Quality Inspection Items for Powders ① Particle size: Chemical drugs for topical use and powders for burns or severe wounds and pediatric Chinese medicine powders, must pass through a No. 7 sieve (120 mesh, 125μm) with a powder weight of not less than 95%. ② Loss on drying: 2.0% ③ Moisture: 9.0% (Chinese medicine) ④ Sterility: topical (for burns, severe wounds, or clinically necessary)
|
Finest powder |
All pass through a No. 6 sieve and contain at least 95% of powder that can pass through a No. 7 sieve |

5. Clinical Applications and Precautions for Powders 》 External use: finest powder (ulcers, injuries) Sprinkle, adjust dressing (with tea, yellow wine, sesame oil) 》 Internal use: fine powder (for the elderly and children) ① Not urgent, appropriate amount, drink less water ② Take with warm water, avoid food within half an hour, large amounts divided into doses ③ If inconvenient to take, mix with honey or encapsulate ④ Directly swallow to warm the stomach and relieve pain

6. Examples of Powders

Internal use + external use, divided doses
Class Practice

|
A: The incorrect statement about the characteristics of powders is A. Easy to disperse, fast acting, especially suitable for drugs sensitive to damp heat B. Convenient for children to take C. Simple preparation, easy dosage control D. Large coverage for external use E. Convenient for storage, transportation, and carrying |
|
Correct Answer: A |
|
A: The incorrect statement about the characteristics of powders is A. Small particle size, large specific surface area B. Easy to disperse, fast acting C. Especially suitable for moisture-sensitive drugs D. Convenient for packaging, storage, transportation, and carrying E. Convenient for infants and the elderly to take |
|
Correct Answer: C |

