Tongue diagnosis is a very important part of the four diagnostic methods in Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM). TCM believes that the tongue coating is formed by the qi of the spleen and stomach rising, the stomach fluids ascending, and condensing on the surface of the tongue.
What exactly is tongue coating? What warning signs do abnormal tongue coatings indicate for diseases? Today, we will discuss this topic.
 Expert Guidance: Sheng Xiaoyang Vice Chairman of the Maternal and Child Nutrition Branch of the Chinese Nutrition SocietyMember of the Children’s Health Committee of the Chinese Medical Doctor AssociationDirector of the Shanghai Association for Maternal and Child Health (Shanghai Maternal and Child Health Association)Director of the Shanghai Trace Element Research SocietyStanding Committee Member of the Medical Popularization Committee of the Shanghai Women Doctors Association
Expert Guidance: Sheng Xiaoyang Vice Chairman of the Maternal and Child Nutrition Branch of the Chinese Nutrition SocietyMember of the Children’s Health Committee of the Chinese Medical Doctor AssociationDirector of the Shanghai Association for Maternal and Child Health (Shanghai Maternal and Child Health Association)Director of the Shanghai Trace Element Research SocietyStanding Committee Member of the Medical Popularization Committee of the Shanghai Women Doctors Association
1. What is Tongue Coating?

Through modern technology research on tongue coating, we recognize that tongue coating is a mixture containing various components. The filiform papillae of the tongue are the basic condition for the formation of tongue coating. The surface of the filiform papillae is covered with keratinized squamous epithelial cells. When the keratinized epithelial cells shed slowly and mix with food residues, saliva, bacteria, etc., they adhere to the surface of the tongue papillae, forming tongue coating.
The degree of proliferation and differentiation of the filiform papillae determines the thickness of the tongue coating. The epithelial cells on the surface continuously keratinize and shed, maintaining a dynamic balance. When this balance is disrupted due to various factors, abnormal tongue coating will appear.
2. Common Tongue Coating Abnormalities in Children

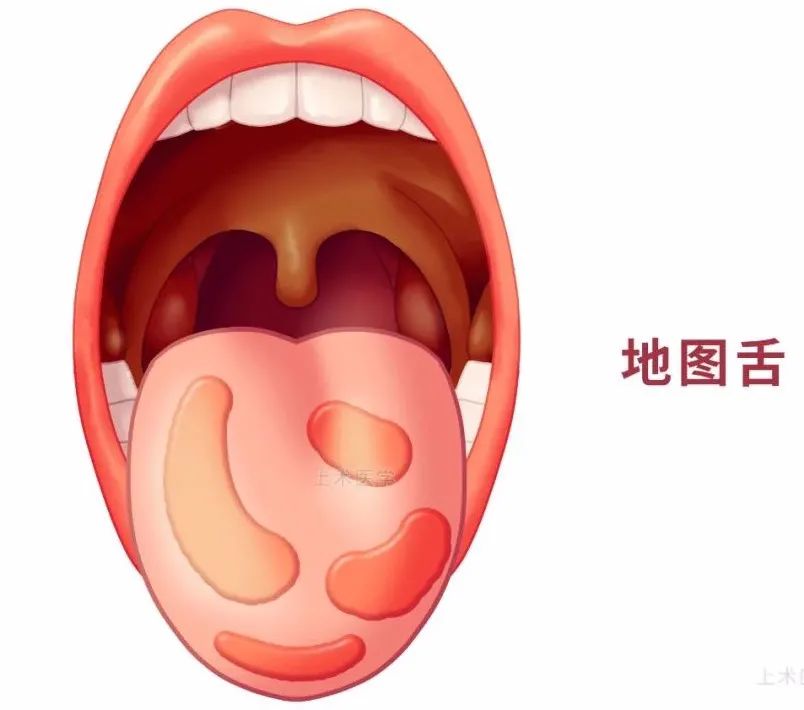
1) Geographic Tongue
Geographic tongue is a non-infectious inflammation of the tongue characterized by localized shedding and disappearance of filiform papillae on the tongue surface, with proliferative edges, resulting in a wandering map-like change, which is a chronic superficial mucosal disease of the tongue.
Many factors can lead to its occurrence: ① Immune factors, such as a family history of allergies or food allergies in children; ② Trace elements, such as zinc deficiency, B vitamin deficiency, etc.; ③ Psychological factors, such as frequent family disputes, academic pressure, family changes, etc.; ④ Disease factors, such as infectious gastrointestinal diseases, HIV infection, and the use of certain medications.
2) Mirror Tongue
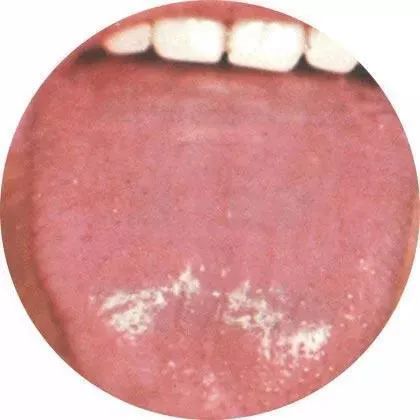
Mirror tongue refers to the phenomenon where the tongue coating is shed, and the tongue surface is smooth like a mirror, often representing oral manifestations of systemic diseases. The appearance of mirror tongue in children may indicate iron deficiency anemia, pernicious anemia, B vitamin deficiency, nutritional absorption disorders, etc. Extensive use of antibiotics may also lead to its occurrence.
3) Strawberry Tongue
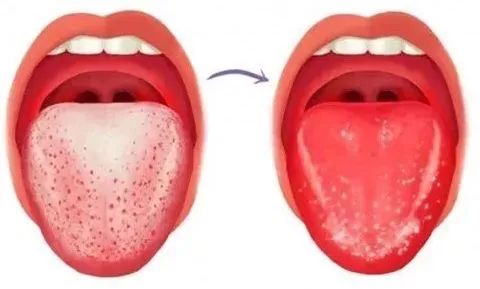
Strawberry tongue is characterized by congested and enlarged filiform papillae, with thin epithelium, bright red color, shallow grooves, and uneven surface, resembling a strawberry. It is sensitive to stimulation and often painful. Strawberry tongue is commonly seen in scarlet fever, Kawasaki disease, or in children with prolonged fever.
4) Beef Tongue
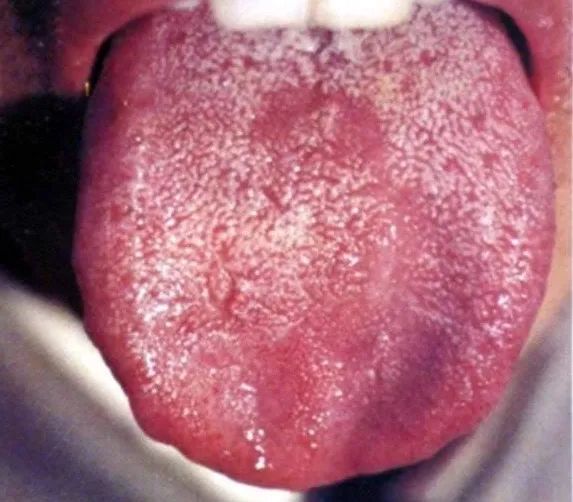
Beef tongue presents as a dark red tongue mucosa, with atrophy and dryness of the tongue papillae, often having fine grooves dividing the tongue surface into small sections, resembling a cross-section of beef. Beef tongue can be seen in cases of B vitamin deficiency or deficiencies of certain essential amino acids.
5) Thick Tongue Coating
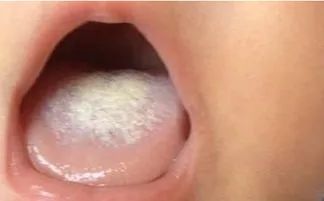
Thick tongue coating is often related to diet, such as frequently consuming cold, greasy, or junk food, leading to indigestion. Correcting dietary structure, increasing fruit and vegetable intake, drinking more water, and promoting bowel movements may help.
The tongue is a part of the oral mucosa that is prone to pathological changes and can sensitively reflect some changes in the body. Observing the tongue can be helpful in understanding the health status of a child, but it should also be combined with the child’s clinical manifestations for comprehensive assessment.
Popular Articles from Xingxiang Maternal and Child Health
DHA+PS, Unlocking the Mystery of Developing a Super Brain for Babies!Do children still need to supplement Vitamin D as they grow? The role of Vitamin D in respiratory infections In the hot summer, Vitamin D supplementation should not stop How much Vitamin D do children and adolescents need? Research on the role of Vitamin D in the prevention and treatment of COVID-19 The vitamin D status during pregnancy and its impact on the development of the baby’s nervous system

Hot Selling Section




Pharmaceutical Section





