IntroductionThe pathways of the meridians may not carry a high score in exams, leading many to overlook them. However, when tested, they can become a source of lost points. Therefore, I will summarize the pathways of the twelve meridians here.
1. Hand Taiyin Lung Meridian (Shou Taiyin Fei Jing)
The Hand Taiyin Lung Meridian begins at the Middle Jiao (Zhongfu), connects downward to the Large Intestine, then returns along the stomach’s upper opening, passes through the diaphragm, and enters the Lung. From the lung system (trachea, throat area), it horizontally travels outward to the axilla, descends along the inner side of the upper arm, and runs between the Hand Shaoyin and Hand Jueyin meridians, reaching the elbow. It continues down the inner side of the forearm along the radial and ulnar borders, passing through the pulse point at the wrist (Cunkou), reaching the thenar eminence, and finally extending to the tip of the thumb (Shaoshang). Its branch diverges from the back of the wrist, traveling along the radial side of the index finger to its tip.
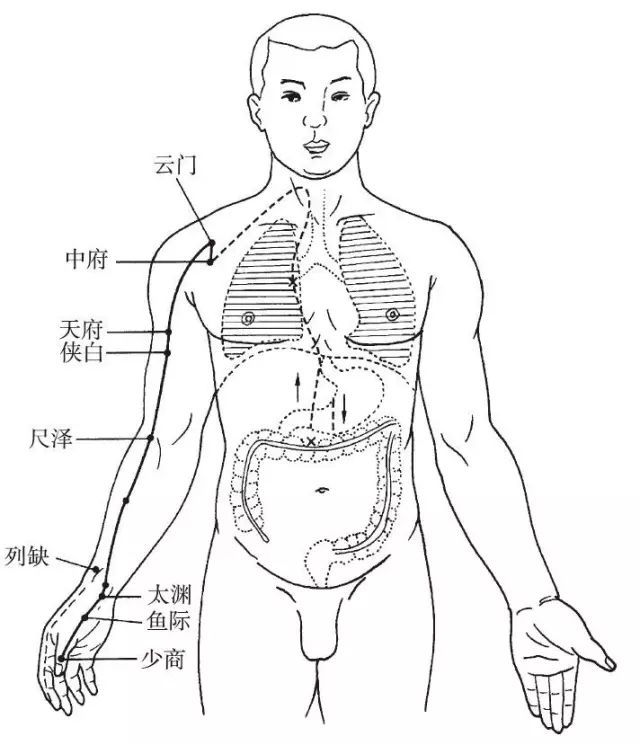
Figure 1 Hand Taiyin Lung Meridian (LU)
2. Hand Yangming Large Intestine Meridian (Shou Yangming Da Chang Jing)
The Hand Yangming Large Intestine Meridian begins at the tip of the index finger (Shangyang) (radial side), travels along the radial side of the index finger, passes between the 1st and 2nd metacarpals, ascends between the two tendons at the back of the wrist, along the outer side of the forearm, to the outer side of the elbow, then ascends along the outer side of the upper arm to the shoulder, passing in front of the acromion, and continues upward to the back, where it intersects with the Yang meridians at the Dazhui point. It then moves forward into the chest, connects with the Lung, descends through the diaphragm, and belongs to the Large Intestine. Its branch ascends from the chest to the neck, enters the lower teeth through the cheek, and returns to the upper lip, converging at the Philtrum (Shuigou), with the left meridian moving right and the right meridian moving left, terminating beside the opposite nostril (Yingxiang).
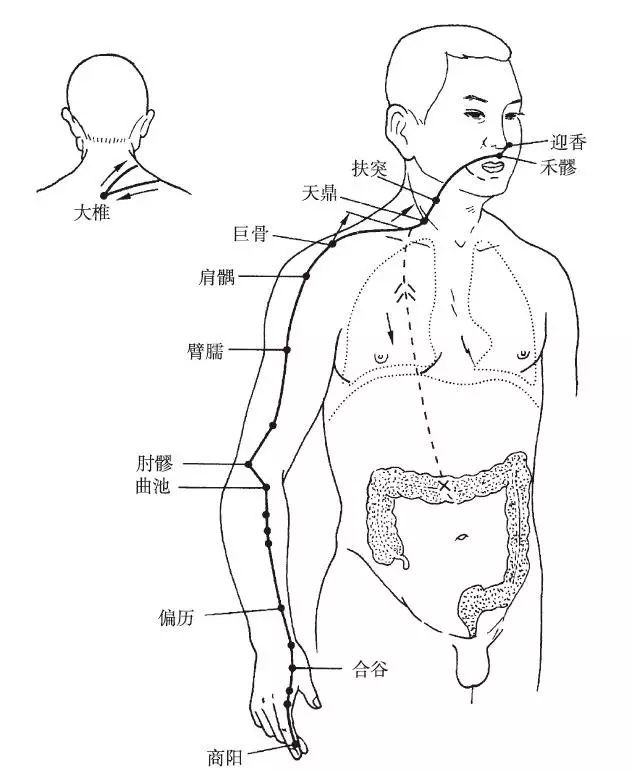
Figure 2 Hand Yangming Large Intestine Meridian (LI)
3. Foot Yangming Stomach Meridian (Zu Yangming Wei Jing)
The Foot Yangming Stomach Meridian begins at the side of the nose (Chengqi), ascends to the root of the nose, intersects with the Foot Taiyang Meridian, then descends along the outer side of the nose, enters the upper gum, returns to encircle the lips, and enters the lower lip, converging at the Chengjiang point. It then travels backward along the lower jaw’s edge to the Daying point, continues along the jaw’s angle to the Jiache point, ascends to the front of the ear, passes the Shangguan point of the Foot Shaoyang Meridian, and ascends to the forehead. Its branch descends from the Daying point to the Renying point, enters the throat, passes through the diaphragm, enters the Stomach, and connects with the Spleen. The straight pathway of the meridian descends from the Renying point along the inner side of the breast, travels beside the navel to the lower abdomen’s Qichong area; a branch diverges from the Stomach, descends to the Qichong area, and converges with the straight pathway. From there, it descends through the Bi Guan and Futu points to the center of the knee joint. It continues down the outer edge of the tibia, travels across the dorsum of the foot to the outer tip of the 2nd toe (Lidui); a branch diverges from 3 cun below the knee, descending to the outer tip of the middle toe; another branch diverges from the dorsum of the foot, traveling straight along the inner side of the big toe to its tip.
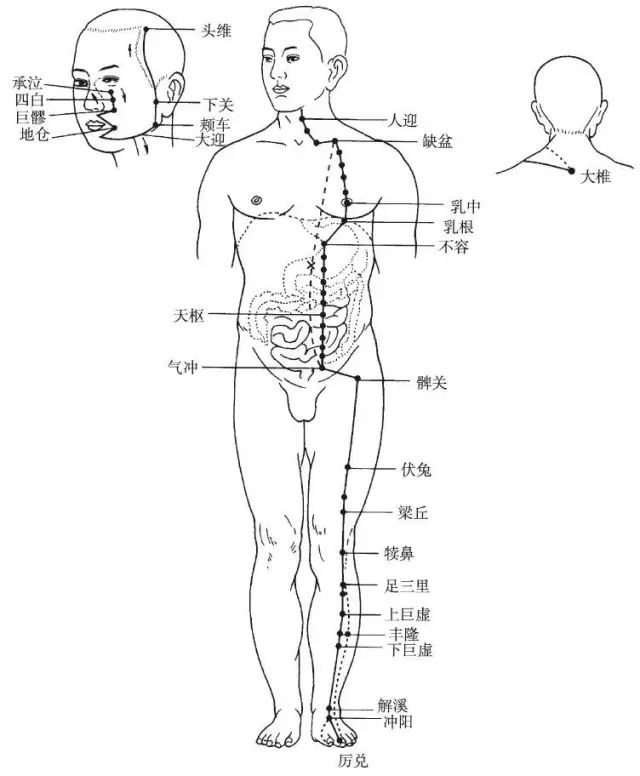
Figure 3 Foot Yangming Stomach Meridian (ST)
4. Foot Taiyin Spleen Meridian (Zu Taiyin Pi Jing)
The Foot Taiyin Spleen Meridian begins at the tip of the big toe (Yinbai), travels along the inner side of the big toe, passes behind the 1st metatarsophalangeal joint, ascends to the front of the inner ankle, continues along the inner side of the tibia, ascending to 8 cun above the inner ankle, where it intersects with the Foot Jueyin Meridian, then ascends along the inner side of the thigh to the abdomen, belonging to the Spleen and connecting with the Stomach. It then ascends through the diaphragm, flanking the pharynx, connects to the root of the tongue, and disperses under the tongue. Its branch diverges from the Stomach above the diaphragm, entering the heart (Dabao).
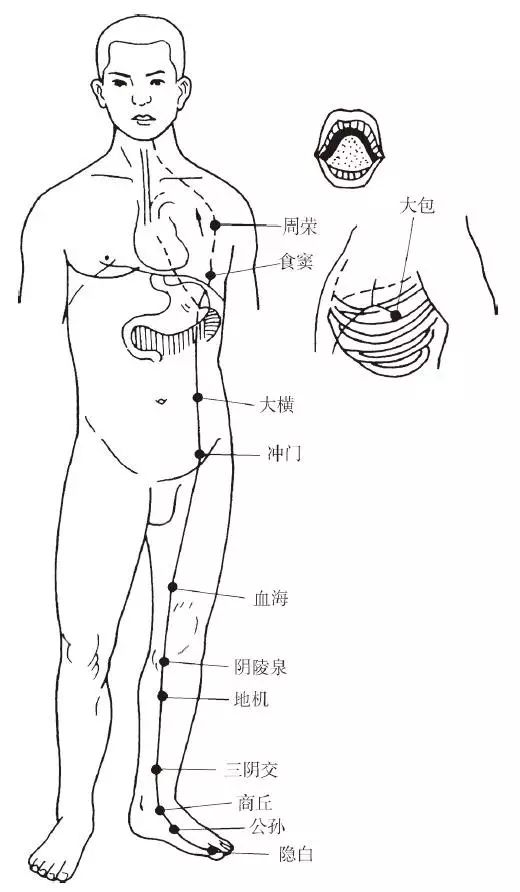
Figure 4 Foot Taiyin Spleen Meridian (SP)
5. Hand Shaoyin Heart Meridian (Shou Shaoyin Xin Jing)
The Hand Shaoyin Heart Meridian begins at the center of the heart (Jiquan), exits belonging to the heart system (the heart and other connected organs); it descends through the diaphragm, connecting with the Small Intestine. Its branch ascends from the heart system, flanking the esophagus, connecting to the eye system (the tissue connecting the eyeball to the brain). The straight pathway of the meridian ascends from the heart system to the Lung, then descends outward to the axilla, travels along the inner side of the upper arm, running behind the Hand Taiyin and Hand Jueyin meridians, reaching the elbow; it continues down the inner side of the forearm to the pea bone area of the palm, entering the palm, and terminating at the radial side of the little finger (Shaochong).
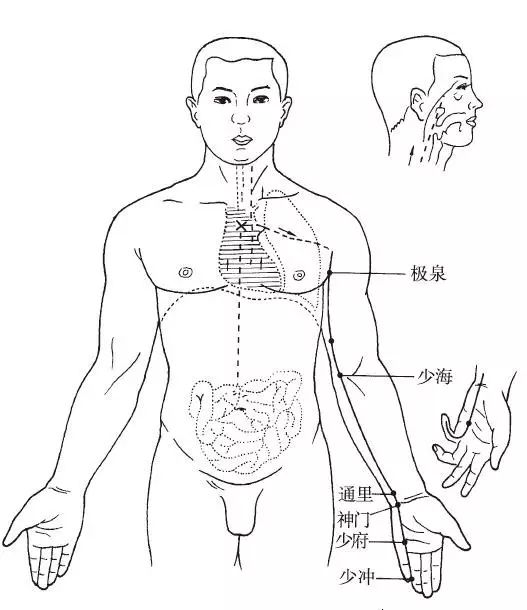
Figure 5 Hand Shaoyin Heart Meridian (HT)
6. Hand Taiyang Small Intestine Meridian (Shou Taiyang Xiao Chang Jing)
The Hand Taiyang Small Intestine Meridian begins at the ulnar side of the little finger (Shaoze), travels along the outer side of the hand to the wrist, exits at the ulnar styloid, ascends along the outer side of the forearm, passing between the ulnar olecranon and the inner condyle of the humerus, along the outer side of the upper arm, reaching the shoulder joint, encircling the scapula, intersecting at the Dazhui, and descending into the chest, connecting with the heart, passing through the esophagus, and reaching the stomach, belonging to the Small Intestine. Its branch diverges from the chest, travels along the neck, ascends to the outer canthus of the eye, and enters the ear. Another branch diverges from the cheek, ascends beneath the eye socket, reaching beside the nose, and converges at the inner canthus of the eye, obliquely connecting to the zygomatic area (Tinggong).

Figure 6 Hand Taiyang Small Intestine Meridian (SI)
7. Foot Taiyang Bladder Meridian (Zu Taiyang Pang Guang Jing)
The Foot Taiyang Bladder Meridian begins at the inner corner of the eye (Jingming), ascends over the forehead, and intersects with the Du Meridian at the top of the head. Its branch diverges from the top of the head to the upper corner of the ear. The straight pathway of the meridian enters the skull to connect with the brain, then emerges along the occipital area, descending along the inner side of the scapula beside the spine to the lumbar region, entering the paravertebral muscles, connecting with the Kidney, and belonging to the Bladder. A branch diverges from the waist, descending beside the spine, passing through the buttocks, and entering the popliteal fossa; another branch descends from the inner sides of the left and right scapulae, passing through the paravertebral muscles, traversing the hip joint, descending along the outer side of the thigh, converging in the popliteal fossa, and continuing down through the gastrocnemius muscle, exiting behind the outer ankle, along the 5th metatarsal tuberosity, to the outer tip of the little toe (Zhiyin).
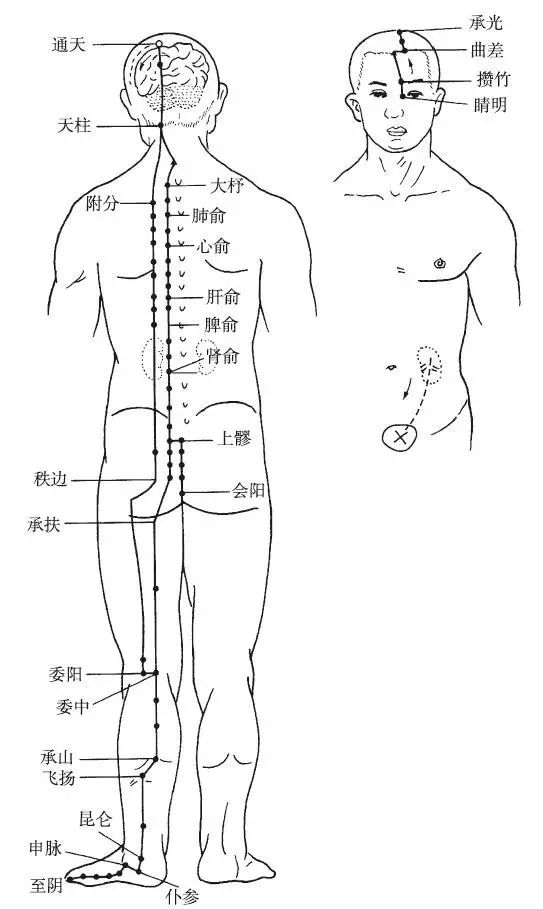
Figure 7 Foot Taiyang Bladder Meridian (BL)
8. Foot Shaoyin Kidney Meridian (Zu Shaoyin Shen Jing)
The Foot Shaoyin Kidney Meridian begins at the bottom of the little toe (Yongquan), travels diagonally across the sole of the foot, passing beneath the tuberosity of the navicular bone, behind the inner ankle, descending into the heel, ascending along the inner side of the calf, passing through the inner side of the popliteal fossa, ascending along the inner side of the thigh, penetrating the spine, belonging to the Kidney, and connecting with the Bladder (there is an acupoint pathway that also ascends from the horizontal bone point, along the anterior midline of the abdomen 0.5 cun beside the center, and 2 cun beside the center of the chest, terminating at the lower edge of the clavicle at the Yufu point) (Huangyu). Its straight branch ascends from the Kidney through the Liver and diaphragm, entering the Lung, traveling along the throat, and flanking the root of the tongue; another branch diverges from the Lung, connecting with the heart, flowing into the chest.
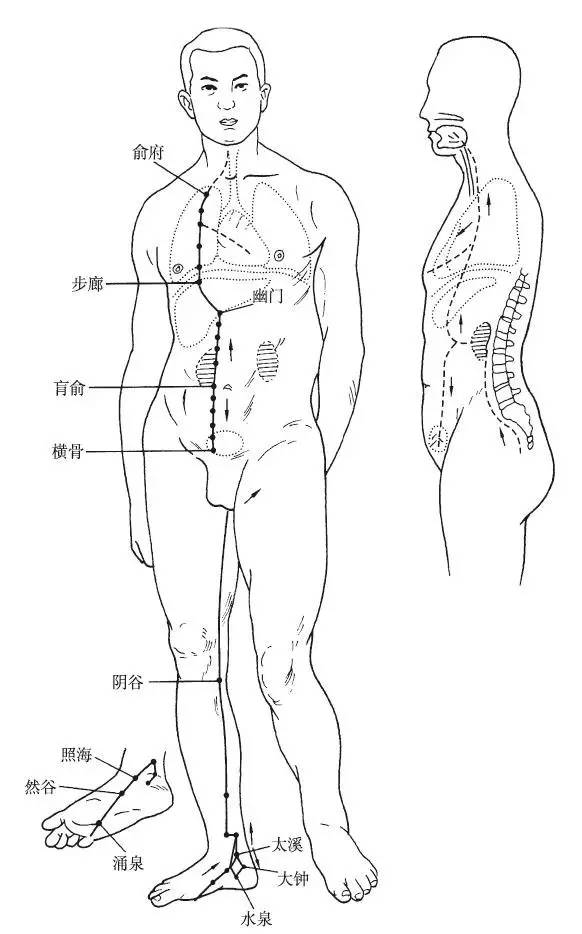
Figure 8 Foot Shaoyin Kidney Meridian (KI)
9. Hand Jueyin Pericardium Meridian (Shou Jueyin Xin Bao Jing)
The Hand Jueyin Pericardium Meridian begins at the center of the chest (Tianchi), belonging to the pericardium, descends through the diaphragm from the chest to the abdomen, connecting with the upper, middle, and lower Jiao. Its branch diverges from the chest, travels outward to the side, reaching 3 cun below the axilla, then ascends to the axilla, descends along the inner side of the upper arm between the Hand Taiyin and Hand Shaoyin meridians, enters the elbow, continues down to the forearm, travels between the two tendons, enters the palm, and extends to the tip of the middle finger (Zhongchong). A branch diverges from the palm, traveling along the ring finger to its tip.
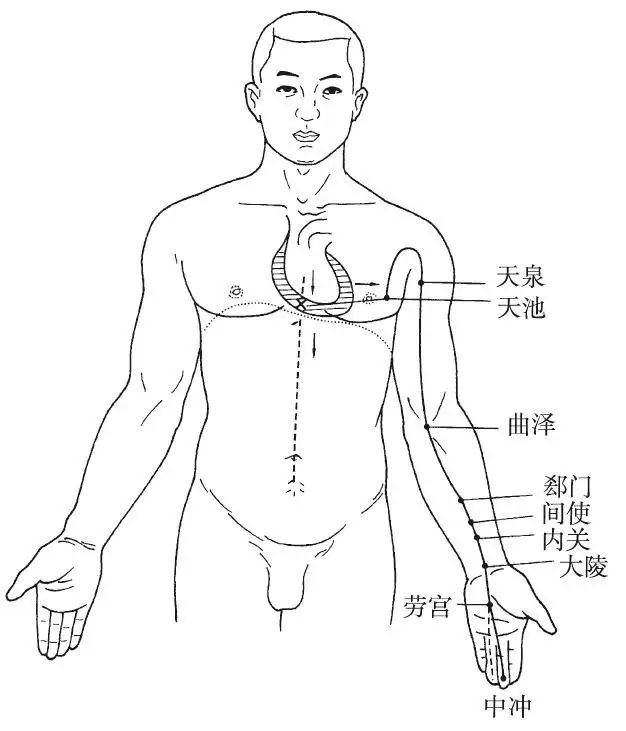
Figure 9 Hand Jueyin Pericardium Meridian (PC)
10. Hand Shaoyang Sanjiao Meridian (Shou Shaoyang San Jiao Jing)
The Hand Shaoyang Sanjiao Meridian begins at the ulnar side of the ring finger (Guanchong), ascends between the little and ring fingers, travels along the back of the wrist, ascends to the outer side of the forearm, passing between the radius and ulna, crossing the elbow, and ascending along the outer side of the upper arm to the shoulder, diverging from the Foot Shaoyang Meridian, entering the chest, distributing in the chest, dispersing in the pericardium, and descending through the diaphragm from the chest to the abdomen, belonging to the upper, middle, and lower Jiao. Its branch diverges from the chest, entering the chest, ascending along the neck, traveling behind the ear, reaching the forehead, descending to the cheek, and reaching the lower part of the eye socket (Sizhu Kong). Another branch diverges from behind the ear, entering the ear, emerging in front of the ear, traveling along the Shangguan, cheek, and reaching the outer canthus of the eye.
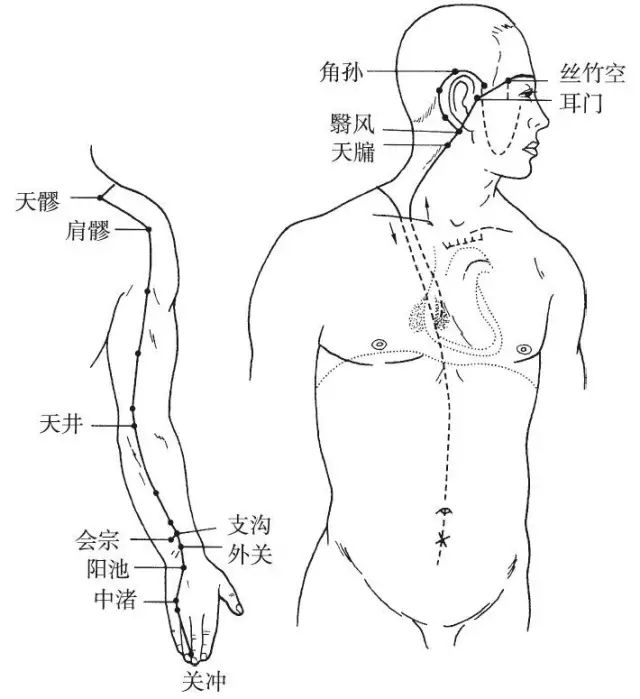
Figure 10 Hand Shaoyang Sanjiao Meridian (TE)
11. Foot Shaoyang Gallbladder Meridian (Zu Shaoyang Dan Jing)
The Foot Shaoyang Gallbladder Meridian begins at the outer canthus of the eye (Tongziliang), ascends to the forehead, descends behind the ear, travels along the neck to the shoulder, and descends into the chest. The branch from the ear enters the ear, emerging in front of the ear to the outer canthus. The branch from the outer canthus descends to the Daying point, converging with the Hand Shaoyang Meridian to reach the lower part of the eye socket, traveling through the cheek, descending along the neck, and converging with the front meridian at the chest, passing through the diaphragm, connecting with the Liver, belonging to the Gallbladder, and descending along the ribs to the groin area, traversing the external genitalia, and horizontally entering the hip joint. The straight pathway of the meridian descends from the chest, traveling through the axilla, lateral chest, and ribs, then descending to converge with the front meridian at the hip joint, continuing down along the outer thigh, along the outer edge of the knee, passing in front of the fibula, reaching the front of the outer ankle, and terminating at the outer tip of the 4th toe (Zuqiaoyin). The branch from the dorsum of the foot diverges, traveling along the 1st and 2nd metatarsals, emerging at the tip of the big toe, passing through the toenail, and exiting at the dorsum of the toe.
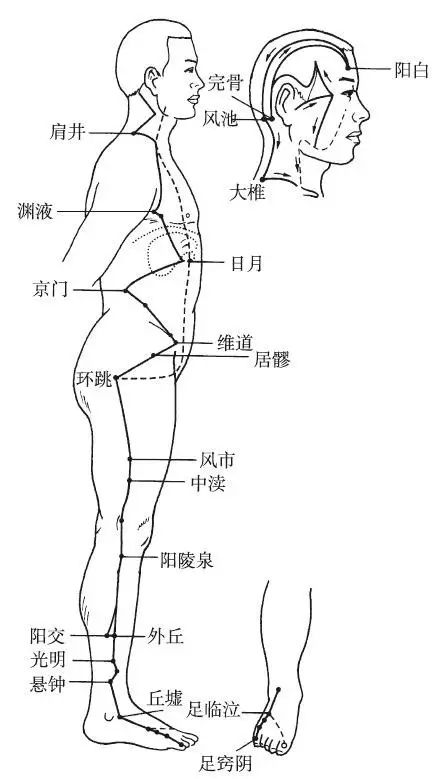
Figure 11 Foot Shaoyang Gallbladder Meridian (GB)
12. Foot Jueyin Liver Meridian (Zu Jueyin Gan Jing)
The Foot Jueyin Liver Meridian begins at the dorsum of the big toe (Dadu), travels along the dorsum of the foot, ascends in front of the inner ankle, intersects with the Foot Taiyin Meridian at 8 cun above the inner ankle, ascends along the inner side of the popliteal fossa, travels along the inner side of the thigh, entering the pubic area, encircling the genitals; it then ascends to the lower abdomen, flanking the Stomach, belonging to the Liver, and connecting with the Gallbladder; it continues upward through the diaphragm, distributing in the rib area (Qimen); it ascends through the back of the throat, entering the nasopharynx, connecting with the eye system, and emerging at the forehead, where it intersects with the Du Meridian at the top of the head. Its branch descends from the eye system, traveling along the cheek, encircling the lips. Another branch diverges from the Liver, passing through the diaphragm, connecting with the Lung.
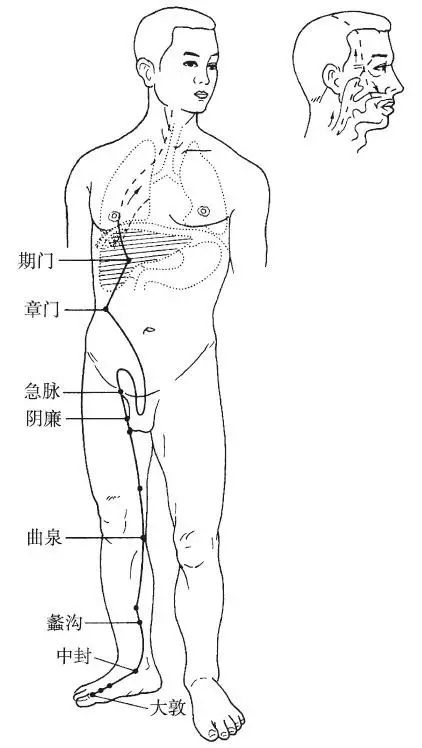
Figure 12 Foot Jueyin Liver Meridian (LR)


