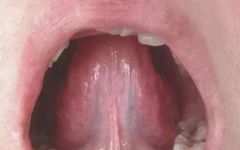
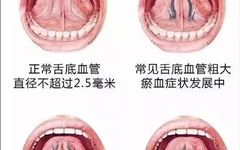
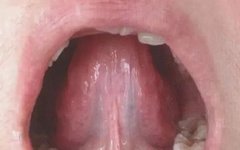
Tongue Diagnosis │ Sublingual Veins
Sublingual veins are the longitudinal veins located on both sides of the lingual frenulum, primarily reflecting the state of Qi and blood circulation. Common abnormal manifestations of the sublingual veins include: coarse and long veins resembling a net, varicose veins, and blood stasis in the veins. Normal sublingual veins: Characteristics of the tongue: The sublingual … Read more